Traditional economies rely on customs, beliefs, and habits to determine production and distribution of goods. This system emphasizes sustainability, community cooperation, and inherited skills passed through generations. Explore the rest of the article to understand how traditional economies function in today's global landscape.
Table of Comparison
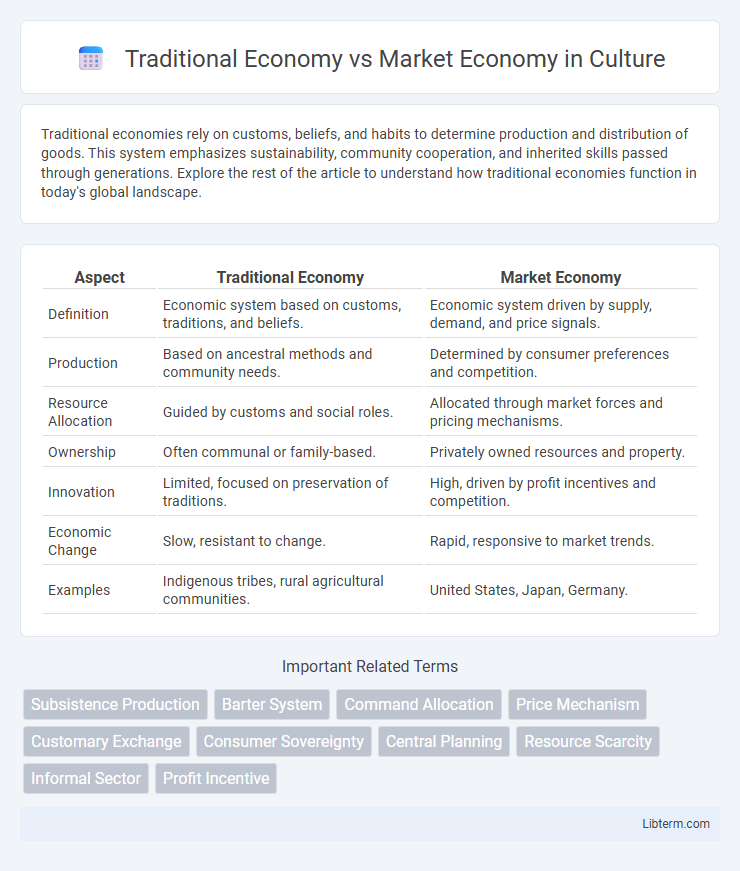
| Aspect | Traditional Economy | Market Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic system based on customs, traditions, and beliefs. | Economic system driven by supply, demand, and price signals. |
| Production | Based on ancestral methods and community needs. | Determined by consumer preferences and competition. |
| Resource Allocation | Guided by customs and social roles. | Allocated through market forces and pricing mechanisms. |
| Ownership | Often communal or family-based. | Privately owned resources and property. |
| Innovation | Limited, focused on preservation of traditions. | High, driven by profit incentives and competition. |
| Economic Change | Slow, resistant to change. | Rapid, responsive to market trends. |
| Examples | Indigenous tribes, rural agricultural communities. | United States, Japan, Germany. |
Introduction to Economic Systems
Traditional economy relies on customs, rituals, and social roles to allocate resources, emphasizing stability and community needs. Market economy operates through supply and demand with minimal government intervention, promoting efficiency and innovation. Economic systems shape how societies distribute goods, manage resources, and respond to economic challenges.
Defining Traditional Economy
A traditional economy relies on customs, traditions, and beliefs to shape its economic activities, often centered around subsistence agriculture, hunting, fishing, and barter trade. This economic system is prevalent in rural and indigenous communities where economic roles are inherited and production methods remain unchanged over generations. Market economies, by contrast, depend on supply and demand dynamics with private ownership driving production, innovation, and resource allocation.
Characteristics of Traditional Economies
Traditional economies rely heavily on customs, rituals, and established practices to guide production and distribution methods, often centered on agriculture, hunting, and fishing. Economic roles and activities are typically inherited and based on community or family ties, resulting in limited technological advancement and low economic growth. Resource allocation depends on subsistence needs rather than market demand, prioritizing stability and sustainability over profit.
Advantages of Traditional Economy
Traditional economy offers sustainability through reliance on age-old customs and practices that promote environmental balance and resource conservation. It fosters strong community bonds and social cohesion by emphasizing collective decision-making and shared responsibilities. This economic system ensures cultural preservation and stability by maintaining time-tested production methods and local knowledge passed down through generations.
Defining Market Economy
A market economy is an economic system where supply and demand determine the production, distribution, and pricing of goods and services, with minimal government intervention. Businesses and consumers freely interact in competitive markets, driving innovation and efficient resource allocation. This contrasts with a traditional economy, which relies on customs and historical precedent to guide economic decisions.
Key Features of Market Economies
Market economies operate on the principles of supply and demand, where prices are determined by consumers and producers without central planning. Private ownership of resources and businesses drives competition, innovation, and efficient allocation of goods and services. Consumer choice and profit motives are key forces that encourage productivity and economic growth in market economies.
Benefits of Market Economy
Market economies promote efficient resource allocation through supply and demand, enabling competitive markets that drive innovation and economic growth. They empower consumers with diverse choices and encourage entrepreneurship by rewarding risk-taking and investment. Increased productivity and higher living standards often result from the decentralized decision-making inherent in market economies.
Key Differences: Traditional vs Market Economy
Traditional economies rely on customs, traditions, and cultural beliefs to make economic decisions, often emphasizing subsistence farming and barter systems. Market economies allocate resources through supply and demand dynamics, driven by private ownership and competitive markets that determine prices and production. Key differences include the role of innovation, with market economies fostering technological advancement, while traditional economies prioritize stability and community continuity.
Challenges and Limitations
Traditional economies face challenges such as limited technological advancement and vulnerability to environmental changes due to reliance on subsistence farming and bartering systems. Market economies encounter limitations including income inequality, market failures, and susceptibility to economic cycles that can lead to recessions or inflation. Both systems struggle with resource allocation efficiency, but market economies typically provide greater innovation incentives while traditional economies emphasize social cohesion.
Conclusion: Which System Is More Sustainable?
Market economies often demonstrate higher sustainability due to their ability to efficiently allocate resources through supply and demand mechanisms, fostering innovation and adaptability. Traditional economies prioritize environmental harmony and long-term resource conservation by relying on time-tested customs and sustainable practices within communities. Balancing market-driven growth with the ecological mindfulness of traditional methods can enhance overall sustainability in diverse economic systems.
Traditional Economy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com