Conformity shapes how individuals align their behaviors and beliefs to match group norms, influencing social dynamics and personal identity. Understanding the psychological mechanisms behind conformity can empower Your decision-making and awareness in social situations. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how conformity impacts your daily life and relationships.
Table of Comparison
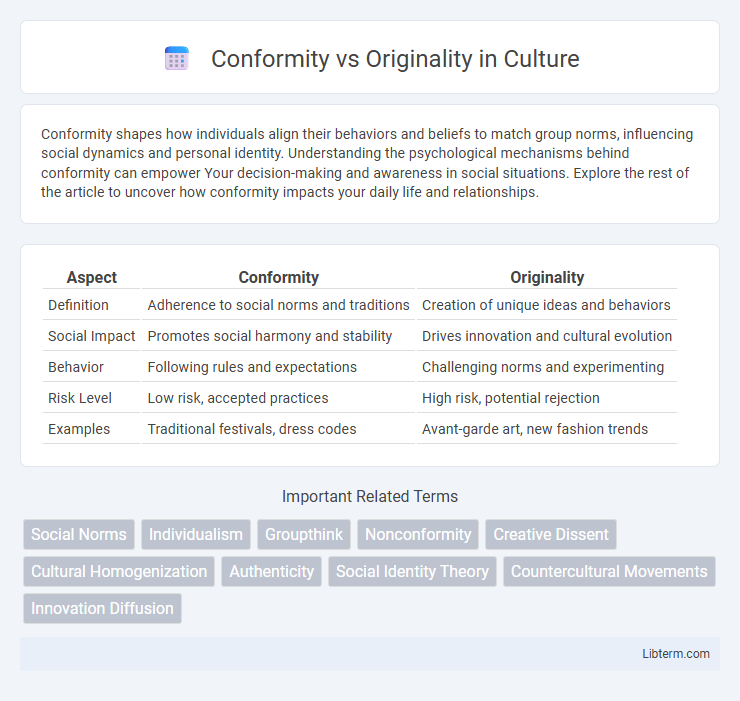
| Aspect | Conformity | Originality |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adherence to social norms and traditions | Creation of unique ideas and behaviors |
| Social Impact | Promotes social harmony and stability | Drives innovation and cultural evolution |
| Behavior | Following rules and expectations | Challenging norms and experimenting |
| Risk Level | Low risk, accepted practices | High risk, potential rejection |
| Examples | Traditional festivals, dress codes | Avant-garde art, new fashion trends |
Understanding Conformity: Definition and Dynamics
Conformity refers to the act of aligning attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors with group norms to gain acceptance or avoid conflict, playing a crucial role in social cohesion and influence. It involves dynamic processes like normative conformity, driven by the desire for social approval, and informational conformity, based on the need for accurate information in ambiguous situations. Understanding these dynamics helps differentiate between adaptive social behavior and the suppression of individual originality.
What Drives Originality? Key Psychological Factors
Originality is driven primarily by intrinsic motivation, where individuals pursue creative tasks out of genuine interest and personal satisfaction rather than external rewards. Cognitive flexibility allows people to approach problems from diverse perspectives, fostering innovative ideas. Furthermore, a supportive environment that encourages risk-taking and tolerates failure enhances originality by reducing fear of judgment and promoting exploration.
Historical Perspectives: Conformity and Original Thinkers
Historical perspectives reveal that conformity often ensured social cohesion and stability within societies, promoting shared values and collective norms. Original thinkers like Galileo Galilei and Leonardo da Vinci challenged prevailing beliefs, driving scientific and artistic revolutions that reshaped cultural paradigms. Their contributions highlight the tension between maintaining tradition and advancing innovation in human history.
Social Influence: The Power of Group Norms
Group norms exert a powerful influence on individual behavior by establishing standards for acceptable actions within social settings, often leading people to conform to these unwritten rules to gain acceptance and avoid social rejection. The pressure to align with collective expectations can suppress originality, as deviating from group norms might result in social sanctions or isolation. However, understanding the dynamics of social influence reveals opportunities to balance conformity with creativity, fostering environments where original ideas can emerge without undermining group cohesion.
Creativity vs. Assimilation in the Workplace
Creativity in the workplace drives innovation by encouraging unique ideas and diverse perspectives, while assimilation promotes uniformity and adherence to established norms, potentially limiting creative expression. Balancing conformity and originality is crucial for organizations aiming to foster a dynamic environment where employees feel empowered to contribute novel solutions without compromising team cohesion. Research shows that workplaces valuing originality alongside clear guidelines enhance problem-solving capabilities and employee engagement.
The Impact of Conformity on Personal Identity
Conformity often shapes personal identity by encouraging individuals to align their beliefs, values, and behaviors with societal norms, potentially limiting self-expression and uniqueness. The pressure to conform can lead to internal conflicts, where personal desires and authentic traits are suppressed to gain acceptance or avoid rejection. This dynamic challenges the development of a distinct personal identity and may result in reduced creativity and diminished self-awareness.
Benefits and Risks of Being Original
Being original fosters innovation, creativity, and unique problem-solving skills that can differentiate individuals or brands in competitive markets. However, originality involves risks such as social rejection, misunderstanding, and potential failure due to untested ideas. Balancing originality with strategic conformity can maximize benefits while minimizing risks in personal and professional growth.
Education Systems: Fostering Conformity or Originality?
Education systems often emphasize conformity through standardized testing and rigid curricula, which can limit creativity and original thought. However, progressive educational models integrate project-based learning and critical thinking exercises to nurture originality and innovation. Balancing structured knowledge acquisition with opportunities for creative expression fosters well-rounded individuals capable of both adherence to societal norms and inventive problem-solving.
Cultural Differences in Conformity and Individualism
Cultures with high collectivism, such as many East Asian societies, emphasize conformity to group norms and social harmony, often prioritizing collective goals over individual desires. In contrast, Western cultures, particularly those valuing individualism like the United States, encourage originality and self-expression, promoting personal achievement and independence. The degree of conformity varies significantly across cultures due to differing socialization processes, moral values, and historical context influencing attitudes toward community and individuality.
Striking a Balance: Navigating Conformity and Originality
Striking a balance between conformity and originality involves integrating societal norms with unique personal expression to foster innovation without alienation. Embracing conformity provides a stable framework for communication and collaboration, while originality drives creativity and problem-solving essential for progress. Effective navigation requires recognizing when to adhere to established conventions and when to challenge them, ensuring harmonious adaptability in diverse social and professional environments.
Conformity Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com