Inclusion fosters diverse perspectives, creating environments where every individual feels valued and respected. Embracing inclusion enhances collaboration, innovation, and overall organizational success. Explore the rest of this article to discover how you can promote inclusion effectively in your community or workplace.
Table of Comparison
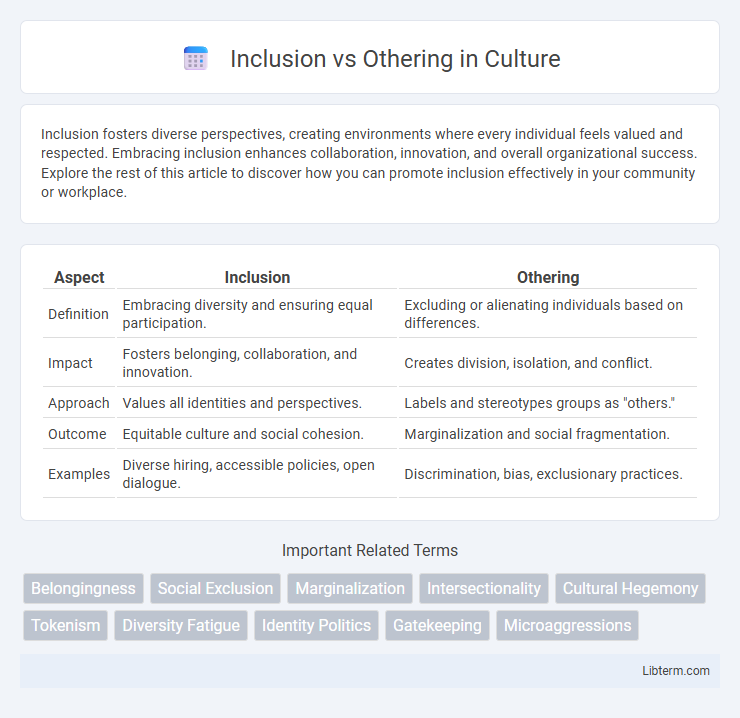
| Aspect | Inclusion | Othering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Embracing diversity and ensuring equal participation. | Excluding or alienating individuals based on differences. |
| Impact | Fosters belonging, collaboration, and innovation. | Creates division, isolation, and conflict. |
| Approach | Values all identities and perspectives. | Labels and stereotypes groups as "others." |
| Outcome | Equitable culture and social cohesion. | Marginalization and social fragmentation. |
| Examples | Diverse hiring, accessible policies, open dialogue. | Discrimination, bias, exclusionary practices. |
Understanding Inclusion: Definitions and Importance
Inclusion promotes an environment where diverse individuals feel valued, respected, and have equal access to opportunities, fostering innovation and collaboration. Understanding inclusion involves recognizing the significance of psychological safety and equitable participation across all social, cultural, and demographic groups. Research highlights that organizations with inclusive practices experience higher employee engagement, retention, and overall performance, underscoring its critical role in sustainable success.
What is Othering? Origins and Impact
Othering refers to the process of perceiving or portraying a person or group as fundamentally different or alien, often leading to marginalization and exclusion. Originating in social and postcolonial theory, the concept highlights power dynamics that create divisions based on race, ethnicity, gender, or cultural identity. The impact of othering includes social inequality, discrimination, and the undermining of social cohesion by reinforcing stereotypes and deepening societal divides.
Key Differences: Inclusion vs. Othering
Inclusion fosters a sense of belonging by actively embracing diversity, ensuring equitable participation and recognition of all individuals. Othering creates social exclusion by highlighting differences, often leading to discrimination and marginalization of certain groups. The key difference lies in inclusion's focus on unity and respect, while othering emphasizes separation and alienation.
Psychological Effects of Othering
Othering triggers psychological effects such as increased anxiety, diminished self-esteem, and chronic stress, which contribute to feelings of isolation and marginalization. This process undermines individuals' sense of belonging and can lead to social exclusion, impairing mental health and cognitive functioning. Research shows that prolonged experiences of othering are linked to depression, identity conflict, and reduced overall well-being.
Benefits of Fostering Inclusion
Fostering inclusion enhances organizational performance by promoting diverse perspectives and driving innovation. Inclusive environments improve employee engagement and retention, reducing turnover costs and fostering a sense of belonging among team members. Embracing inclusion also strengthens brand reputation and attracts top talent, contributing to sustainable business growth.
Cultural and Social Roots of Othering
Othering arises from cultural and social roots embedded in historical power dynamics, prejudices, and identity politics that marginalize groups based on race, ethnicity, religion, or social class. Cultural narratives often reinforce stereotypes and social hierarchies, creating in-group and out-group distinctions that hinder inclusion efforts. Addressing othering requires dismantling systemic biases and fostering intercultural understanding to promote social cohesion and equity.
Barriers to Achieving True Inclusion
Barriers to achieving true inclusion often stem from unconscious biases, systemic inequalities, and lack of representation within organizations and communities. Cognitive dissonance and fear of change hinder efforts to embrace diverse identities, leading to exclusion or "othering" of marginalized groups. Overcoming these challenges requires intentional policies, continuous education, and fostering environments that celebrate authentic belonging.
Strategies to Reduce Othering in Communities
Effective strategies to reduce othering in communities include fostering intercultural dialogue, promoting empathy through shared experiences, and implementing inclusive policies that ensure equal representation and participation. Community-based programs that celebrate diversity and encourage collaboration help dismantle stereotypes and build mutual respect. Educational initiatives emphasizing social cohesion and anti-discrimination create environments where every individual feels valued and connected.
The Role of Leadership in Promoting Inclusion
Effective leadership cultivates an inclusive culture by actively embracing diverse perspectives and fostering psychological safety within teams. Leaders who prioritize equitable practices and model inclusive behaviors reduce instances of othering, thereby enhancing collaboration and innovation. Strategic leadership commitment to diversity initiatives drives organizational success through increased employee engagement and retention.
Building a Culture of Inclusion: Practical Steps
Building a culture of inclusion involves implementing practical steps such as fostering open communication, providing diversity training, and establishing policies that promote equity and respect. Organizations should create safe spaces for dialogue where diverse perspectives are valued and actively encouraged. Regularly assessing workplace practices through inclusion metrics helps identify gaps and ensures continuous improvement toward an inclusive environment.
Inclusion Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com