Belief shapes your understanding of the world and influences how you interpret experiences, guiding decisions and behavior through internalized convictions. The power of belief lies in its ability to create meaning and foster resilience, often transcending empirical evidence to inspire hope or motivation. Discover how your beliefs impact your life and how you can harness their power by reading the rest of the article.
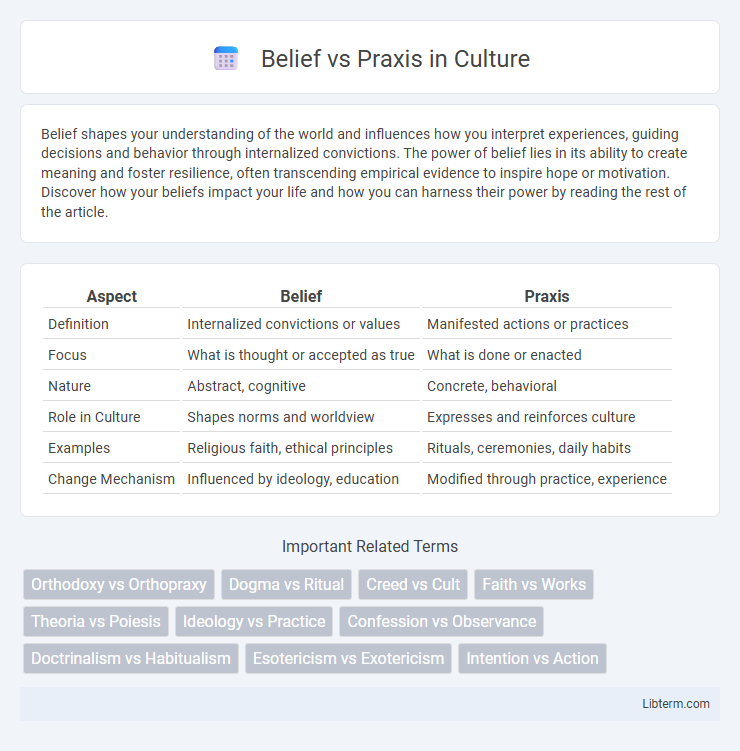
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Belief | Praxis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Internalized convictions or values | Manifested actions or practices |
| Focus | What is thought or accepted as true | What is done or enacted |
| Nature | Abstract, cognitive | Concrete, behavioral |
| Role in Culture | Shapes norms and worldview | Expresses and reinforces culture |
| Examples | Religious faith, ethical principles | Rituals, ceremonies, daily habits |
| Change Mechanism | Influenced by ideology, education | Modified through practice, experience |
Understanding Belief: Core Definitions
Belief refers to the acceptance or conviction in the truth or existence of something without immediate proof, forming the cognitive foundation of an individual's worldview. It encompasses personal, cultural, and religious convictions that guide behavior and decision-making. Understanding belief involves analyzing its psychological, philosophical, and sociological dimensions to grasp how core definitions shape human perception and action.
Praxis Explained: From Theory to Practice
Praxis refers to the process of translating belief or theory into concrete action and practical application. It involves reflective practice where individuals critically engage with ideas to inform their behaviors and decisions in real-world contexts. This dynamic interplay between theory and practice ensures that abstract concepts are tested, refined, and made meaningful through lived experience.
Historical Perspectives on Belief and Praxis
Historical perspectives on belief and praxis reveal a dynamic interplay where religious or ideological convictions often shaped social and political actions. In ancient civilizations, rituals and daily practices were deeply intertwined with prevailing belief systems, reflecting a unified worldview exemplified by Egyptian and Mesopotamian cultures. During the Enlightenment, thinkers like Rousseau and Kant emphasized praxis as a means to enact moral philosophy, highlighting the evolution of belief from mere ideology to actionable frameworks.
The Interplay Between Faith and Action
The interplay between belief and praxis highlights how faith shapes ethical behavior and decision-making in daily life. Praxis serves as the tangible expression of belief, reinforcing spiritual values through actions that reflect doctrinal principles. This dynamic relationship ensures that faith is not only a private conviction but also a transformative force influencing social and personal conduct.
Belief Systems: Foundations and Implications
Belief systems serve as the cognitive frameworks through which individuals and societies interpret reality, shaping values, norms, and decision-making processes. These foundational mental models influence behaviors and social practices by embedding assumptions about existence, ethics, and knowledge within cultural contexts. Understanding the implications of belief systems reveals how deeply held convictions guide human actions, affect social cohesion, and drive ideological conflicts throughout history.
Praxis in Religious and Secular Contexts
Praxis in religious contexts involves the active embodiment of faith through rituals, ethical conduct, and communal worship, serving as a tangible expression of belief systems. In secular contexts, praxis refers to the practical application of theories and ideas in social, political, or professional settings, emphasizing action that transforms society or personal development. Both domains value praxis as a crucial mechanism linking abstract concepts to lived experience, driving meaningful change and authenticity.
Theoretical Frameworks: Bridging Belief and Praxis
Theoretical frameworks explore the dynamic interplay between belief systems and praxis, emphasizing how abstract convictions inform concrete actions within social and cultural contexts. These frameworks highlight the bidirectional influence where praxis not only enacts belief but also reshapes and validates theoretical understandings. Key models, such as Paulo Freire's pedagogy and Pierre Bourdieu's habitus, illustrate the integration of ideology and practice through reflective and embodied processes.
Challenges of Aligning Belief with Praxis
Aligning belief with praxis presents challenges such as cognitive dissonance when actions contradict core values, creating internal conflict and resistance to change. Practical constraints like social pressures, institutional norms, and resource limitations often hinder the consistent application of beliefs in real-world scenarios. Overcoming these challenges requires reflective practice, adaptive strategies, and ongoing commitment to align intentions with behaviors effectively.
Case Studies: Belief vs Praxis in Real Life
Case studies of belief versus praxis reveal consistent gaps between ideological commitments and practical actions, especially in social justice movements and corporate ethics. For example, the Black Lives Matter movement demonstrates strong collective beliefs in racial equality but faces challenges in translating consensus into sustainable policy reforms and community programs. Similarly, corporate social responsibility often highlights disparities where stated environmental values fail to materialize fully in business operations or supply chain practices.
The Future of Belief and Praxis Integration
The future of belief and praxis integration involves a dynamic interplay where core values increasingly guide actionable strategies within organizations and communities. Emerging technologies and data analytics enable real-time feedback loops that align belief systems with practical implementation, fostering adaptive and resilient frameworks. This integration promises a more cohesive approach to addressing complex social, economic, and environmental challenges by embedding ethical considerations into measurable outcomes.
Belief Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com