Globalized culture shapes how societies exchange ideas, traditions, and values across borders, fostering a shared human experience. This interconnectedness influences local customs and creates diverse social environments that reflect a blend of global influences. Explore the rest of the article to understand how globalized culture impacts your daily life and identity.
Table of Comparison
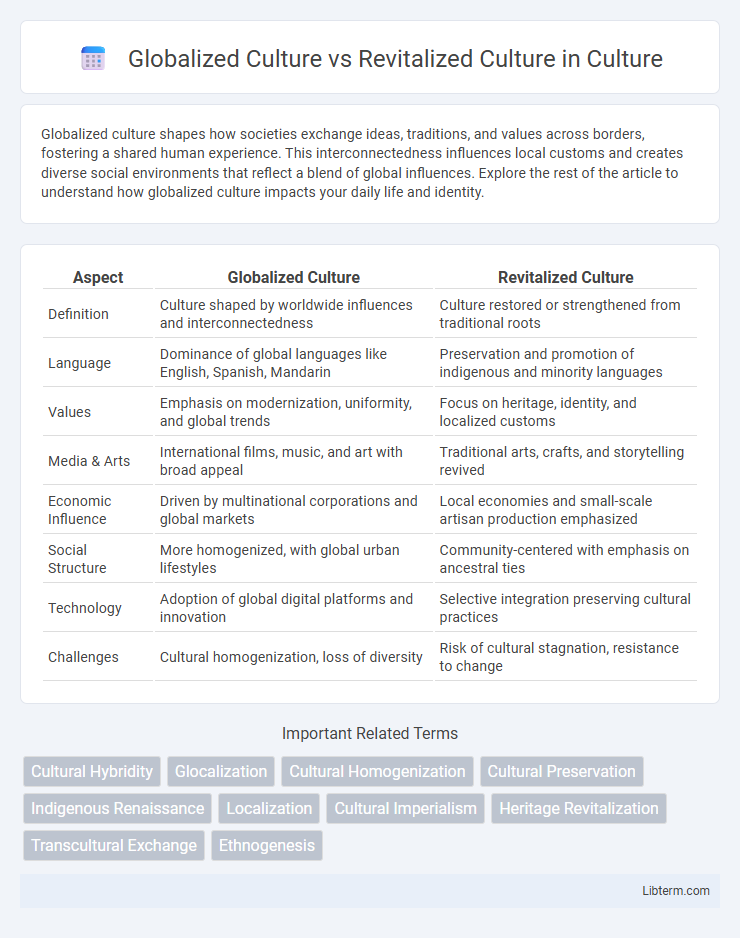
| Aspect | Globalized Culture | Revitalized Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Culture shaped by worldwide influences and interconnectedness | Culture restored or strengthened from traditional roots |
| Language | Dominance of global languages like English, Spanish, Mandarin | Preservation and promotion of indigenous and minority languages |
| Values | Emphasis on modernization, uniformity, and global trends | Focus on heritage, identity, and localized customs |
| Media & Arts | International films, music, and art with broad appeal | Traditional arts, crafts, and storytelling revived |
| Economic Influence | Driven by multinational corporations and global markets | Local economies and small-scale artisan production emphasized |
| Social Structure | More homogenized, with global urban lifestyles | Community-centered with emphasis on ancestral ties |
| Technology | Adoption of global digital platforms and innovation | Selective integration preserving cultural practices |
| Challenges | Cultural homogenization, loss of diversity | Risk of cultural stagnation, resistance to change |
Introduction to Globalized and Revitalized Cultures
Globalized culture refers to the widespread diffusion of cultural elements, such as language, media, and consumer goods, promoting homogeneity across diverse regions. Revitalized culture emphasizes the revival and strengthening of indigenous traditions, languages, and customs to preserve unique cultural identities. The dynamic tension between globalized and revitalized cultures shapes contemporary social landscapes, influencing identity, heritage, and cultural sustainability worldwide.
Defining Globalized Culture
Globalized culture refers to the widespread diffusion of ideas, values, customs, and products across international boundaries, leading to increased interconnectedness and cultural homogenization. It is characterized by the adoption of similar lifestyles, language use, media consumption, and consumer habits influenced largely by dominant economies and multinational corporations. This cultural phenomenon often results in shared global experiences while raising concerns about the erosion of indigenous traditions and local identities.
Understanding Revitalized Culture
Revitalized culture emphasizes the preservation and rejuvenation of unique linguistic, artistic, and social traditions amid the pressures of globalized culture. It plays a critical role in maintaining cultural identity, fostering community cohesion, and promoting indigenous knowledge systems that often face erosion in a homogenized global environment. Supporting revitalized culture involves active efforts such as language revitalization programs, traditional arts education, and policies that protect cultural heritage sites.
Historical Roots of Cultural Globalization
Historical roots of cultural globalization trace back to ancient trade routes like the Silk Road, where exchange of goods also facilitated cross-cultural interactions and spread of ideas. Colonialism further accelerated cultural globalization by imposing European languages, religions, and practices on diverse societies worldwide. In contrast, revitalized culture movements actively reclaim indigenous traditions and heritage, resisting homogenization and emphasizing local identity within a global context.
Key Drivers of Cultural Revitalization
Key drivers of cultural revitalization include community engagement, preservation of indigenous languages, and promotion of traditional customs through education and media. Globalized culture often accelerates homogenization, but targeted efforts in digital archiving and local governance empower marginalized groups to reclaim and sustain their heritage. Investments in cultural institutions and policy frameworks further reinforce the resurgence of unique cultural identities amid global pressures.
Impacts of Globalization on Local Traditions
Globalization introduces widespread cultural influences that often challenge and transform local traditions, leading to increased cultural homogenization and loss of unique heritage practices. Local communities may experience dilution of traditional customs as global media, consumer products, and lifestyles become dominant, sometimes undermining indigenous languages and rituals. However, globalization also enables the revitalization of culture by providing platforms for cultural exchange, preservation, and global awareness of local identities.
The Role of Technology in Cultural Exchange
Technology accelerates cultural exchange by facilitating real-time communication and access to diverse cultural content, promoting a globalized culture where ideas and traditions blend seamlessly. Digital platforms and social media enable the revitalization of endangered languages and customs by connecting dispersed communities and preserving cultural heritage through multimedia archives. Innovations such as virtual reality and augmented reality further immerse users in authentic cultural experiences, bridging gaps between globalized influence and localized cultural identity.
Case Studies: Successes in Cultural Revitalization
Case studies of cultural revitalization demonstrate successful preservation and adaptation of indigenous languages, traditional arts, and customs in the face of globalized culture's homogenizing effects. For example, the Maori language revival in New Zealand showcases how educational programs and government support can restore linguistic heritage and strengthen community identity. Another success is the revitalization of Native American crafts, where collaborations between artisans and global markets have enabled cultural preservation while fostering economic sustainability.
Challenges and Tensions Between Globalization and Revitalization
Globalized culture often imposes homogenized values and consumer behaviors, challenging the preservation of localized identities and traditional practices inherent to revitalized cultures. The tension arises as global media and economic integration can marginalize indigenous languages and customs, leading to cultural erosion and loss of diversity. Efforts to revitalize culture confront obstacles such as limited resources, political resistance, and the pervasive influence of dominant global narratives shaping collective memory and social norms.
Future Prospects for Cultural Diversity
Globalized culture promotes widespread cultural exchange and homogenization, facilitating global connectivity but often risking the erosion of unique cultural identities. Revitalized culture emphasizes preserving and restoring traditional customs, languages, and practices to maintain cultural diversity and foster community resilience. Future prospects for cultural diversity depend on balancing global integration with targeted efforts in cultural preservation, leveraging technology for documentation and education to sustain minority cultures amid globalization pressures.
Globalized Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com