Legal-rational authority derives its power from a system of established laws and procedures that ensure legitimacy and predictability in governance. This form of authority emphasizes rules, formal structures, and the rational-legal order rather than individual charisma or tradition. Explore the article to understand how legal-rational authority shapes modern institutions and affects your everyday interactions with governance.
Table of Comparison
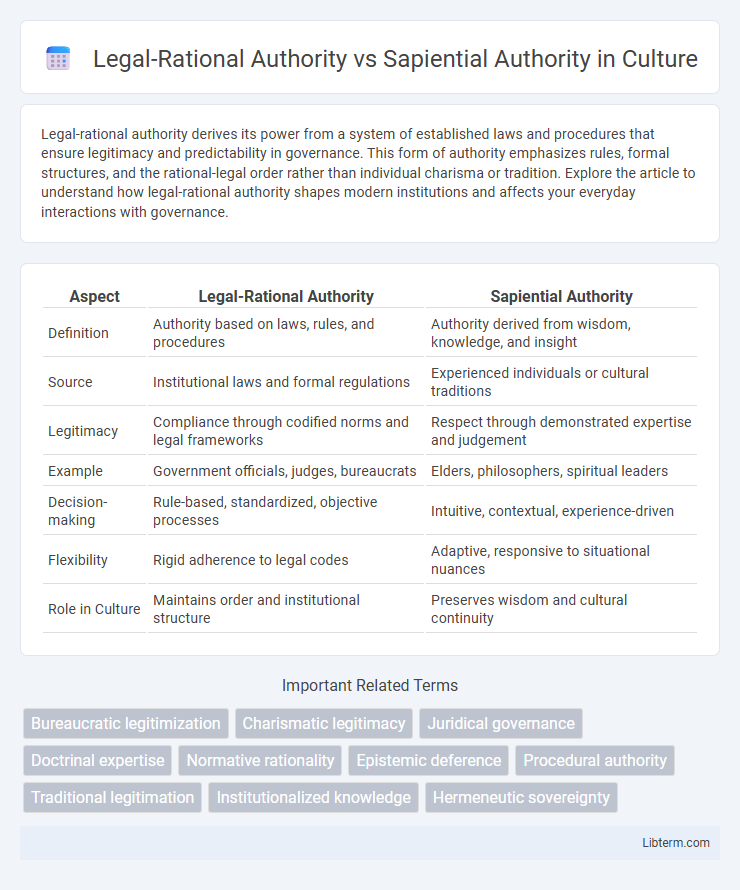
| Aspect | Legal-Rational Authority | Sapiential Authority |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authority based on laws, rules, and procedures | Authority derived from wisdom, knowledge, and insight |
| Source | Institutional laws and formal regulations | Experienced individuals or cultural traditions |
| Legitimacy | Compliance through codified norms and legal frameworks | Respect through demonstrated expertise and judgement |
| Example | Government officials, judges, bureaucrats | Elders, philosophers, spiritual leaders |
| Decision-making | Rule-based, standardized, objective processes | Intuitive, contextual, experience-driven |
| Flexibility | Rigid adherence to legal codes | Adaptive, responsive to situational nuances |
| Role in Culture | Maintains order and institutional structure | Preserves wisdom and cultural continuity |
Defining Legal-Rational Authority
Legal-rational authority is a form of governance grounded in established laws, rules, and procedures that are formally enacted and systematically applied, emphasizing the impersonal nature of power. This type of authority is characterized by legitimacy derived from a legal framework, where officials hold office based on codified norms and operate within clearly defined roles. It contrasts with sapiential authority, which is based on wisdom or expertise rather than formal legal structures.
Understanding Sapiential Authority
Sapiential authority derives from recognized wisdom, expertise, or deep knowledge within a specific domain, granting individuals a unique influence based on their intellectual or experiential insight. Unlike legal-rational authority, which is grounded in formal rules, laws, or institutional frameworks, sapiential authority relies on the credibility and respect earned through demonstrated understanding and judgment. This form of authority often plays a critical role in fields such as academia, science, and traditional societies where knowledge and expertise guide decision-making processes.
Historical Development of Both Authority Types
Legal-rational authority emerged during the rise of modern bureaucratic states in the 19th century, emphasizing rule-based governance and codified laws to legitimize power. Sapiential authority traces back to ancient societies where wisdom, sacred knowledge, and expertise established leaders' legitimacy, often rooted in religious or philosophical traditions. The historical development of these authority types reflects a shift from personal, knowledge-based legitimacy toward impersonal, institutionalized legal frameworks.
Key Features of Legal-Rational Authority
Legal-rational authority is characterized by a formalized system of rules and procedures where legitimacy is derived from legally established laws and offices rather than individual traits. It emphasizes impersonal governance, bureaucratic organization, and adherence to codified regulations, ensuring consistency and predictability in decision-making. This form of authority contrasts with sapiential authority, which relies on perceived wisdom, expertise, or traditional knowledge held by individuals.
Fundamental Characteristics of Sapiential Authority
Sapiential authority is fundamentally characterized by its reliance on deep knowledge, wisdom, and expertise, contrasting with legal-rational authority, which is based on established rules and formal procedures. It derives its legitimacy from the perceived intellectual competence and moral insight of the authority figure, often grounded in tradition, experience, or scholarly understanding. This form of authority emphasizes interpretative skills and the ability to provide meaningful guidance beyond codified laws or regulations.
Comparative Analysis: Structure and Function
Legal-rational authority is structured around codified laws and formal rules, emphasizing bureaucratic hierarchy and predictable procedures for decision-making. Sapiential authority derives from recognized wisdom or expertise, relying on the knowledge and judgement of an individual or a body, often informal and personalized in function. Legal-rational authority functions to maintain order and legitimacy through institutional frameworks, whereas sapiential authority guides through intellectual influence and moral persuasion.
Impact on Governance and Decision-Making
Legal-rational authority shapes governance by establishing rules, procedures, and bureaucracy that ensure consistency, predictability, and accountability in decision-making processes. Sapiential authority relies on expertise, wisdom, and knowledge, influencing decisions through the legitimacy of specialized insight and moral guidance. Governance under legal-rational authority emphasizes institutional frameworks, whereas sapiential authority centers on individual or collective intellectual and ethical competence.
Advantages and Limitations of Legal-Rational Authority
Legal-rational authority thrives on codified rules and institutional frameworks, ensuring predictability, consistency, and impartiality in decision-making. Its advantages include clear guidelines for governance and accountability, facilitating efficient administration within bureaucratic organizations. Limitations arise from rigidity, potential bureaucratic delays, and the risk of depersonalized leadership that may overlook contextual nuances or moral considerations.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Sapiential Authority
Sapiential authority is rooted in expertise and deep knowledge, offering the benefit of well-informed decision-making based on experience and wisdom, which can enhance organizational credibility and trust. However, its drawbacks include potential resistance to change due to overreliance on tradition and expertise, and challenges in verifying the legitimacy of claimed knowledge. Unlike legal-rational authority, which relies on formal rules and procedures, sapiential authority may lack structured accountability, risking subjective or biased judgments.
Contemporary Relevance and Future Implications
Legal-rational authority, grounded in formal rules and procedures, remains foundational for modern governance and institutional legitimacy, ensuring accountability and predictability. Sapiential authority, based on expertise and wisdom, gains increasing importance in a knowledge-driven society, influencing decision-making in technology, science, and ethics. Future implications suggest a hybrid governance model where legal frameworks integrate sapiential insights to address complex global challenges like AI regulation and climate change policy.
Legal-Rational Authority Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com