Syntax governs the structure of sentences, determining how words combine to convey clear and meaningful ideas. Mastering syntax improves your communication skills by enhancing clarity and coherence in both writing and speech. Explore this article to deepen your understanding of syntax and elevate your language proficiency.
Table of Comparison
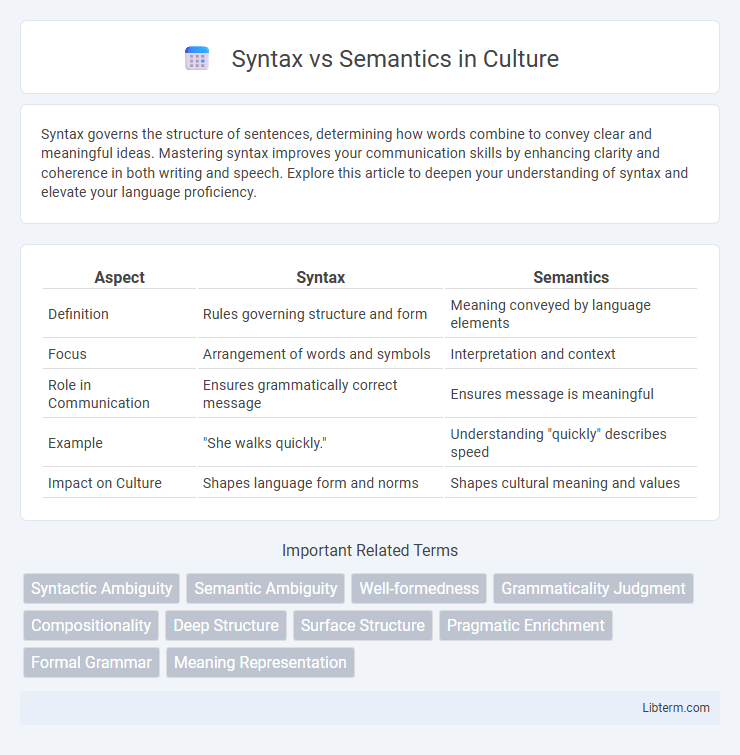
| Aspect | Syntax | Semantics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Rules governing structure and form | Meaning conveyed by language elements |
| Focus | Arrangement of words and symbols | Interpretation and context |
| Role in Communication | Ensures grammatically correct message | Ensures message is meaningful |
| Example | "She walks quickly." | Understanding "quickly" describes speed |
| Impact on Culture | Shapes language form and norms | Shapes cultural meaning and values |
Introduction to Syntax and Semantics
Syntax explores the rules and structure governing how words combine to form valid sentences, emphasizing grammatical arrangement without considering meaning. Semantics studies the meaning conveyed by words, phrases, and sentences, focusing on how language represents ideas and concepts. Understanding both syntax and semantics is essential for effective communication and natural language processing applications.
Defining Syntax: Rules and Structures
Syntax refers to the set of rules and structures that govern the arrangement of words and symbols in a language or programming code, ensuring proper formation of sentences or statements. It defines how components like phrases, clauses, or code instructions combine to create well-formed expressions, independent of their meaning. Mastery of syntax is crucial for parsing, compiling, and interpreting language constructs accurately in both natural and formal languages.
Understanding Semantics: Meaning and Interpretation
Understanding semantics involves exploring how meaning is constructed and interpreted in language, emphasizing the relationship between signs, symbols, and their referents. Semantics delves into how words, phrases, and sentences convey meaning beyond their syntactic arrangement, focusing on context, intent, and cultural factors. This field enables effective communication by clarifying ambiguity and ensuring accurate interpretation in both natural and formal languages.
Syntax vs Semantics: Key Differences
Syntax governs the structure and rules for forming valid sentences or expressions in a language, ensuring correct arrangement of words or symbols. Semantics deals with the meaning and interpretation of those syntactically correct sentences or expressions, focusing on their significance in context. Key differences include syntax being about form and pattern, while semantics emphasizes meaning and understanding within language or programming.
The Role of Syntax in Language Processing
Syntax governs the arrangement of words and phrases to create well-formed sentences, serving as the structural backbone in language processing. It enables the parser to identify grammatical relationships and hierarchical structures, facilitating accurate interpretation and generation of meaning. Efficient syntactic analysis is crucial for natural language understanding, speech recognition, and machine translation systems.
The Importance of Semantics in Communication
Semantics plays a crucial role in communication by ensuring that the intended meaning of words and sentences is accurately understood, beyond mere syntactic structure. While syntax governs the arrangement of words, semantics provides the context and interpretation, enabling effective information exchange and reducing misunderstandings. In linguistic processing and natural language understanding, semantic analysis is essential for capturing nuances and conveying precise messages.
Syntax and Semantics in Programming Languages
Syntax in programming languages defines the set of rules and structure for writing valid code, including grammar, symbols, and language-specific keywords. Semantics concerns the meaning and behavior of syntactically correct code, determining how instructions execute and affect program state. Understanding both syntax and semantics is crucial for developers to write functional, error-free programs and to facilitate code interpretation by compilers or interpreters.
Common Misconceptions about Syntax and Semantics
Syntax refers to the rules that govern the structure of sentences, ensuring that words are arranged in a grammatically correct order, while semantics deals with the meaning conveyed by those sentences. A common misconception is that a syntactically correct sentence is always meaningful, but sentences can be grammatically correct yet semantically nonsensical, as demonstrated by Chomsky's example, "Colorless green ideas sleep furiously." Another frequent misunderstanding is that semantics only involves dictionary definitions, whereas it also encompasses context, connotation, and pragmatic factors that influence meaning beyond mere word definitions.
Real-World Examples: Syntax and Semantics in Action
Syntax governs the structure of sentences, dictating the order of words such as "The cat sat on the mat," while semantics deals with the meaning, ensuring that the sentence conveys the idea of a cat positioned on a mat. In programming languages like Python, correct syntax requires proper use of colons and indentation, but semantics ensures that code performs the intended operation, such as calculating the sum of numbers rather than concatenating strings. Real-world applications like natural language processing rely on syntax to parse sentences and semantics to understand context, enabling technologies like chatbots and virtual assistants to respond accurately.
Conclusion: Bridging Syntax and Semantics
Bridging syntax and semantics is essential to achieve a comprehensive understanding of language structure and meaning in computational linguistics. While syntax governs sentence formation rules, semantics ensures those sentences convey accurate and relevant information. Integrating both fields enhances natural language processing systems and improves machine interpretation of human language.
Syntax Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com