A norm defines expected behaviors and standards within a society or group, shaping how individuals interact and make decisions. It influences social cohesion and helps maintain order by aligning actions with commonly accepted rules. Explore the article to understand how norms impact your daily life and social environments.
Table of Comparison
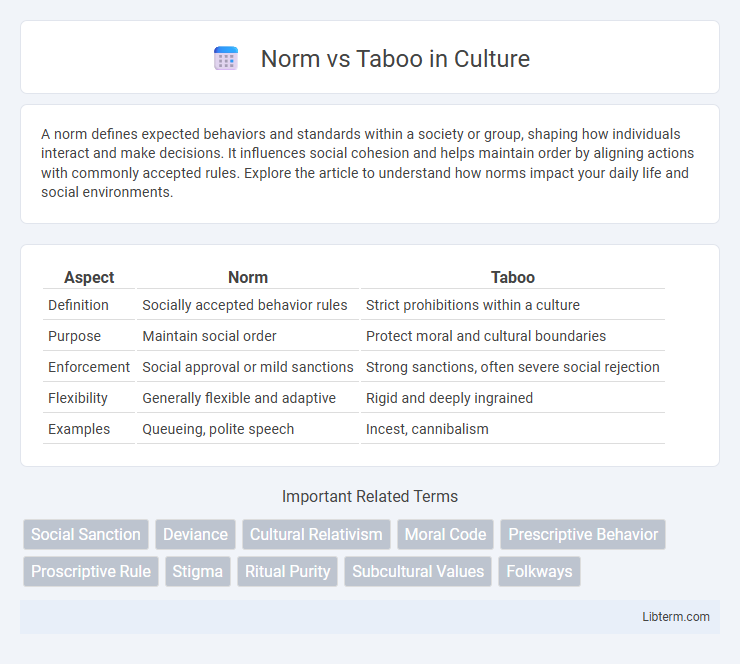
| Aspect | Norm | Taboo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Socially accepted behavior rules | Strict prohibitions within a culture |
| Purpose | Maintain social order | Protect moral and cultural boundaries |
| Enforcement | Social approval or mild sanctions | Strong sanctions, often severe social rejection |
| Flexibility | Generally flexible and adaptive | Rigid and deeply ingrained |
| Examples | Queueing, polite speech | Incest, cannibalism |
Understanding Norms and Taboos
Norms are socially accepted behaviors that guide day-to-day interactions, while taboos represent strong prohibitions that evoke social sanctions if violated. Understanding norms involves recognizing the implicit rules shaping acceptable conduct within a culture, whereas grasping taboos requires acknowledging deeply ingrained cultural or moral boundaries that protect societal values. Both norms and taboos play crucial roles in maintaining social order and cultural identity.
Historical Evolution of Social Norms
Social norms have evolved over centuries, reflecting the changing values and power structures within societies, distinguishing acceptable behaviors (norms) from prohibited actions (taboos). Historically, social norms emerged to regulate group cohesion and cooperation, while taboos functioned as strong prohibitions often linked to morality, religion, or survival. The shift from rigid taboos to more flexible norms demonstrates cultural adaptation to environmental changes and complex social interactions.
The Role of Taboos in Shaping Culture
Taboos function as powerful social prohibitions that enforce cultural values by delineating unacceptable behaviors, thereby maintaining social cohesion and order. These culturally ingrained restrictions often reflect deep moral, religious, or societal codes, shaping collective identity and influencing norms across generations. By reinforcing boundaries, taboos contribute to the preservation of traditions and the regulation of interpersonal conduct within diverse societies.
Psychological Foundations of Norms
Norms originate from psychological mechanisms such as social learning, conformity, and cognitive consistency, which drive individuals to align their behavior with group expectations. These unwritten rules regulate social interactions by fostering predictability and cooperation, rooted in the human need for belonging and social approval. Taboo, contrastingly, operates on stronger psychological foundations involving deep emotional responses like disgust and fear, often linked to survival instincts and moral cognition.
How Taboos Influence Behavior
Taboos shape behavior by establishing strict prohibitions that evoke strong social disapproval or punishment when violated, guiding individuals away from culturally sensitive actions. These social prohibitions influence psychological conditioning, fostering internalized fears and guilt that deter taboo behaviors. As a result, taboos function as powerful mechanisms for maintaining social order and cultural identity by regulating conduct beyond formal laws or norms.
Breaking Norms: Consequences and Reactions
Breaking social norms results in various consequences such as social disapproval, ostracism, or informal sanctions depending on the norm's cultural significance and context. In contrast, violating taboos often triggers stronger reactions including severe stigmatization, moral outrage, or legal penalties due to their embedded sacred or forbidden status. The intensity of reactions to breaking norms versus taboos highlights the role of societal values in regulating behavior and maintaining social order.
The Fluidity of Norms Over Time
Norms evolve continuously due to cultural shifts, technological advancements, and social interactions, reflecting changing values and collective behaviors. Unlike taboos, which often remain rigid to maintain social order or moral boundaries, norms adapt to new contexts, enabling societies to modify acceptable conduct. Understanding the fluidity of norms highlights how communities renegotiate standards, influencing legislation, social policies, and everyday practices.
Taboos in Different Societies
Taboos, deeply rooted in cultural beliefs and values, vary significantly across societies, often governing behaviors considered unacceptable or forbidden. For example, dietary restrictions such as the prohibition of pork in Islamic and Jewish cultures or the avoidance of beef in Hindu communities highlight how taboos shape daily practices. These culturally specific prohibitions help maintain social order and reinforce group identity by delineating clear boundaries between acceptable and forbidden actions.
Social Media and the Shifting Boundaries of Taboo
Social media platforms continuously reshape societal norms by challenging traditional taboos and enabling open discussions around previously forbidden topics such as mental health, sexuality, and politics. The rapid exchange of information and diverse user interactions accelerate the erosion of once rigid boundaries, fostering new cultural standards and acceptance levels. This shift creates dynamic social repertoires where behaviors once deemed unacceptable become normalized or redefined within digital communities.
Challenging Norms: From Stigma to Acceptance
Challenging norms involves confronting deeply ingrained stigmas that often uphold social taboos, leading to gradual shifts in cultural acceptance. Movements advocating for mental health awareness, LGBTQ+ rights, and gender equality exemplify how redefining societal standards transforms taboos into normalized, accepted behaviors. This process relies on sustained education, open dialogue, and visibility to dismantle stereotypes and foster inclusive communities.
Norm Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com