Linguistic codes shape how individuals communicate within different social contexts, influencing meaning and understanding. Mastering various linguistic codes enhances your ability to navigate complex conversations and cultural nuances effectively. Explore the rest of the article to deepen your insight into the impact of linguistic codes on communication.
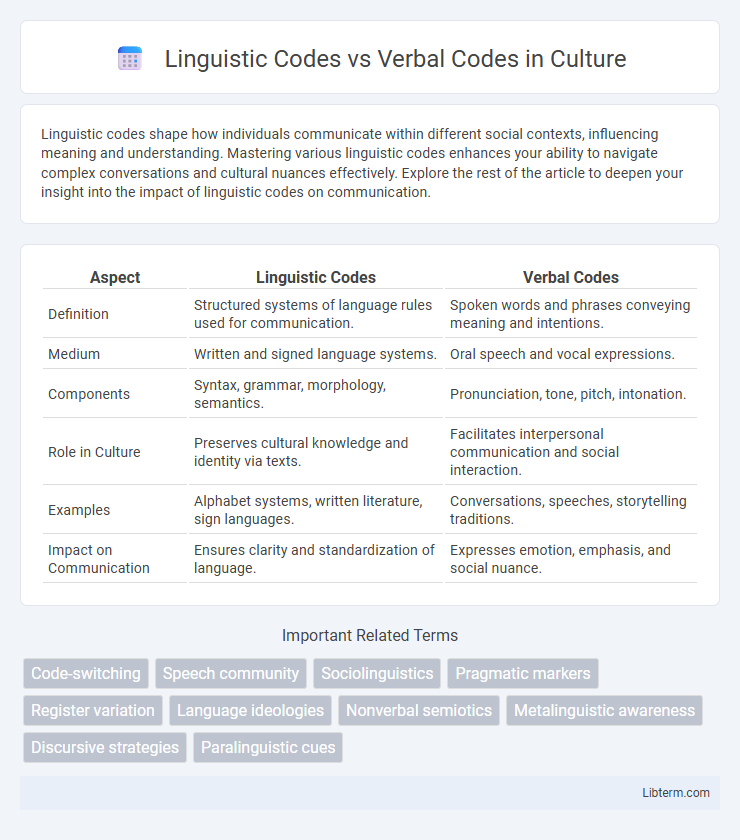
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Linguistic Codes | Verbal Codes |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Structured systems of language rules used for communication. | Spoken words and phrases conveying meaning and intentions. |
| Medium | Written and signed language systems. | Oral speech and vocal expressions. |
| Components | Syntax, grammar, morphology, semantics. | Pronunciation, tone, pitch, intonation. |
| Role in Culture | Preserves cultural knowledge and identity via texts. | Facilitates interpersonal communication and social interaction. |
| Examples | Alphabet systems, written literature, sign languages. | Conversations, speeches, storytelling traditions. |
| Impact on Communication | Ensures clarity and standardization of language. | Expresses emotion, emphasis, and social nuance. |
Introduction to Linguistic and Verbal Codes
Linguistic codes refer to the structured system of language, including grammar and vocabulary, used for communication within a speech community. Verbal codes specifically focus on the spoken aspect of language, encompassing pronunciation, intonation, and articulation patterns. Understanding the distinction between linguistic and verbal codes is essential for fields such as sociolinguistics, language acquisition, and communication studies.
Defining Linguistic Codes
Linguistic codes refer to the systematic use of language rules and structures that individuals employ to communicate effectively within specific social contexts. These codes encompass vocabulary, grammar, syntax, and phonology to convey meaning and establish social relationships. Understanding linguistic codes is crucial for analyzing how language varies across different communities and influences interaction patterns.
Understanding Verbal Codes
Verbal codes encompass spoken or written language systems used to communicate explicit information, emphasizing syntax, vocabulary, and grammar for clear message transmission. Understanding verbal codes requires recognizing the structured rules and symbols that facilitate precise expression and comprehension in diverse linguistic contexts. Mastery of verbal codes enhances effective communication, enabling accurate interpretation and response in both everyday interactions and specialized fields.
Key Differences Between Linguistic and Verbal Codes
Linguistic codes refer to the structured system of language, including syntax, semantics, and phonology, that enables communication, while verbal codes specifically involve the actual words and phrases spoken or written in communication. Key differences include that linguistic codes encompass the underlying rules and grammar guiding language use, whereas verbal codes focus on the explicit verbal expressions used to convey meaning. Understanding these distinctions is essential in fields such as sociolinguistics, where language choices reflect social identity and context.
The Role of Context in Code Usage
Linguistic codes and verbal codes differ significantly in how context shapes their usage; linguistic codes rely heavily on shared social and cultural understanding to convey meaning beyond literal expressions. Verbal codes, comprising specific language structures and vocabulary, depend on situational context to determine the appropriateness and interpretation of utterances. Contextual cues such as setting, relationship between speakers, and cultural norms govern the choice and effectiveness of both code types in communication.
Types of Linguistic Codes
Linguistic codes encompass various systems of language use, including formal, informal, and dialectal language, each serving distinct social functions within communication. Types of linguistic codes commonly studied include formal standard language, colloquial speech, jargon, and slang, which reflect differences in context, audience, and purpose. Understanding these types aids in analyzing how verbal codes, as subsets of linguistic expression, convey meaning through structured language elements in spoken or written forms.
Examples of Verbal Codes in Communication
Verbal codes in communication include spoken language, written text, and sign language, serving as primary tools for conveying messages through words. Examples of verbal codes are everyday conversations, formal speeches, emails, and text messages, which rely on vocabulary, grammar, and syntax to transmit information accurately. These codes enable precise expression of ideas, emotions, and intentions, making them essential in both interpersonal and mass communication contexts.
Impact on Cross-Cultural Communication
Linguistic codes, encompassing grammar, syntax, and vocabulary differences, directly influence message interpretation and clarity in cross-cultural communication, often leading to misunderstandings due to literal translation errors. Verbal codes include tone, intonation, and speech patterns that convey emotional nuance and intent beyond words, impacting rapport and trust between diverse cultural groups. Misalignment in these codes reduces effective communication, highlighting the necessity for cultural competence and adaptive language strategies in global interactions.
Applications in Language Learning and Teaching
Linguistic codes encompass the comprehensive system of grammar, syntax, and vocabulary used in language learning, enabling learners to understand and produce meaningful communication. Verbal codes specifically relate to spoken language features, such as intonation, pronunciation, and speech patterns, which are critical in developing oral proficiency and listening comprehension. Effective language teaching integrates both linguistic and verbal codes to enhance communicative competence, fostering accurate language use and natural speech in learners.
Conclusion: Interplay Between Linguistic and Verbal Codes
Linguistic codes, encompassing the structured grammar and vocabulary of a language, interact dynamically with verbal codes that include phonetics, intonation, and speech patterns to shape effective communication. The interplay between these codes facilitates nuanced expression and comprehension by integrating formal linguistic rules with contextual verbal cues. Understanding this synergy is essential for advancing studies in sociolinguistics, language acquisition, and cognitive communication processes.
Linguistic Codes Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com