Oral culture preserves history, traditions, and knowledge through spoken word rather than written texts, creating a dynamic way for communities to share their identity and values. This mode of communication strengthens social bonds and keeps stories alive across generations, emphasizing memory and performance. Discover more about how oral culture shapes societies and its enduring relevance in today's world by reading the full article.
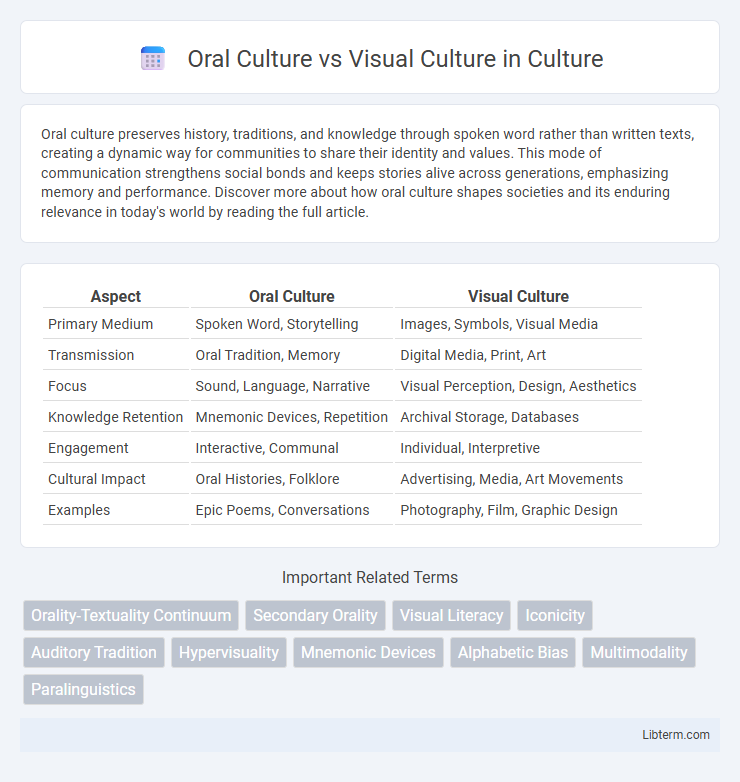
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Oral Culture | Visual Culture |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Medium | Spoken Word, Storytelling | Images, Symbols, Visual Media |
| Transmission | Oral Tradition, Memory | Digital Media, Print, Art |
| Focus | Sound, Language, Narrative | Visual Perception, Design, Aesthetics |
| Knowledge Retention | Mnemonic Devices, Repetition | Archival Storage, Databases |
| Engagement | Interactive, Communal | Individual, Interpretive |
| Cultural Impact | Oral Histories, Folklore | Advertising, Media, Art Movements |
| Examples | Epic Poems, Conversations | Photography, Film, Graphic Design |
Introduction to Oral and Visual Cultures
Oral culture prioritizes spoken language, storytelling, and memory, relying on auditory transmission and communal participation for preserving and sharing knowledge. Visual culture emphasizes images, symbols, and visual media, shaping understanding through sight and representation in art, media, and digital platforms. These cultural forms influence communication methods, cognitive processes, and the preservation of traditions across societies.
Defining Oral Culture: Key Characteristics
Oral culture is defined by its reliance on spoken word for communication, transmission of knowledge, and preservation of tradition, emphasizing memory, storytelling, and face-to-face interaction. Key characteristics include the dynamic nature of narratives, communal participation, and the use of mnemonic devices to retain and convey information across generations. This culture prioritizes auditory channels and human voice as primary mediums, contrasting with visual culture's dependence on written and graphic symbols.
Visual Culture Explained: Concepts and Components
Visual culture encompasses the study of images, symbols, and visual media as key components that shape human communication and cultural expression. It involves analyzing art, photography, film, digital media, and advertising to understand how visual elements influence perception, identity, and social interaction. Key concepts include visual literacy, iconography, and semiotics, which help decode the meanings embedded in visual artifacts across different societies.
Historical Evolution of Communication: From Oral to Visual
Oral culture dominated early human communication, relying on storytelling, spoken language, and mnemonic devices to transmit knowledge across generations. The invention of writing systems around 3200 BCE marked a pivotal shift towards visual culture, enabling the preservation and dissemination of information through visual symbols and texts. This evolution accelerated with the printing press in the 15th century, mass media, and digital technologies, reshaping how societies store and share knowledge.
Memory, Tradition, and Storytelling in Oral Societies
Oral culture relies heavily on memory as the primary vehicle for preserving tradition and storytelling, with narratives passed down through generations via spoken word, song, and ritual. Techniques such as repetition, mnemonic devices, and communal participation enhance recall and ensure cultural values remain intact despite the absence of written records. This dynamic transmission fosters flexibility and adaptability in oral traditions, embedding collective identity and historical knowledge within living memory.
The Power of Images: Visual Culture’s Influence on Perception
Visual culture shapes perception by harnessing the immediacy and emotional impact of images, making complex ideas accessible and memorable. Unlike oral culture, which relies on spoken language and narrative memory, visual culture communicates through symbols, colors, and spatial arrangements that transcend linguistic barriers. The power of images lies in their ability to evoke strong responses and influence social attitudes, making visual media a dominant force in modern communication and cultural transmission.
Cognitive Differences: Processing Oral vs. Visual Information
Oral culture relies on auditory processing, engaging memory and language centers to interpret and retain information through sound and spoken word, fostering narrative-based cognitive patterns. Visual culture emphasizes spatial processing and pattern recognition, activating visual centers responsible for interpreting images, symbols, and written text, which supports immediate perception and conceptual understanding. Cognitive differences between oral and visual cultures influence how information is encoded, stored, and recalled, shaping communication, learning styles, and societal knowledge transmission.
Impact of Technology: Shifting from Oral to Visual Dominance
Technological advancements have dramatically shifted cultural communication from oral traditions to visual media, with the proliferation of digital devices promoting image-based platforms like social media, video streaming, and virtual reality. This transition enhances information accessibility and engagement through visual storytelling and multimodal content, reshaping learning processes and social interactions. The dominance of visual culture influences cognitive patterns by prioritizing visual literacy and changing how societies preserve and transmit knowledge compared to traditional oral methods.
Cultural Identity and Expression in Oral and Visual Contexts
Oral culture shapes cultural identity through storytelling, rituals, and spoken language, preserving heritage by transmitting values and histories across generations. Visual culture expresses identity via symbols, art, and media, reflecting societal beliefs and evolving narratives in tangible forms. Both oral and visual contexts serve as vital mediums for cultural expression, influencing collective memory and social cohesion.
Future Trends: Harmonizing Oral and Visual Communication
The future of communication lies in harmonizing oral culture's storytelling power with visual culture's immersive imagery to create richer, multi-sensory experiences. Emerging technologies like augmented reality and voice-activated interfaces are blending spoken narratives with dynamic visuals, enhancing engagement and comprehension across digital platforms. This integration supports personalized learning, cultural preservation, and more inclusive communication by catering to diverse cognitive and sensory preferences.
Oral Culture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com