Mobile payment solutions empower you to complete transactions quickly and securely using your smartphone or wearable device. These systems utilize technologies like NFC, QR codes, and mobile wallets to streamline purchases both online and in physical stores, enhancing convenience and reducing reliance on cash or cards. Explore the rest of the article to discover how mobile payment can transform your shopping experience and improve financial management.
Table of Comparison
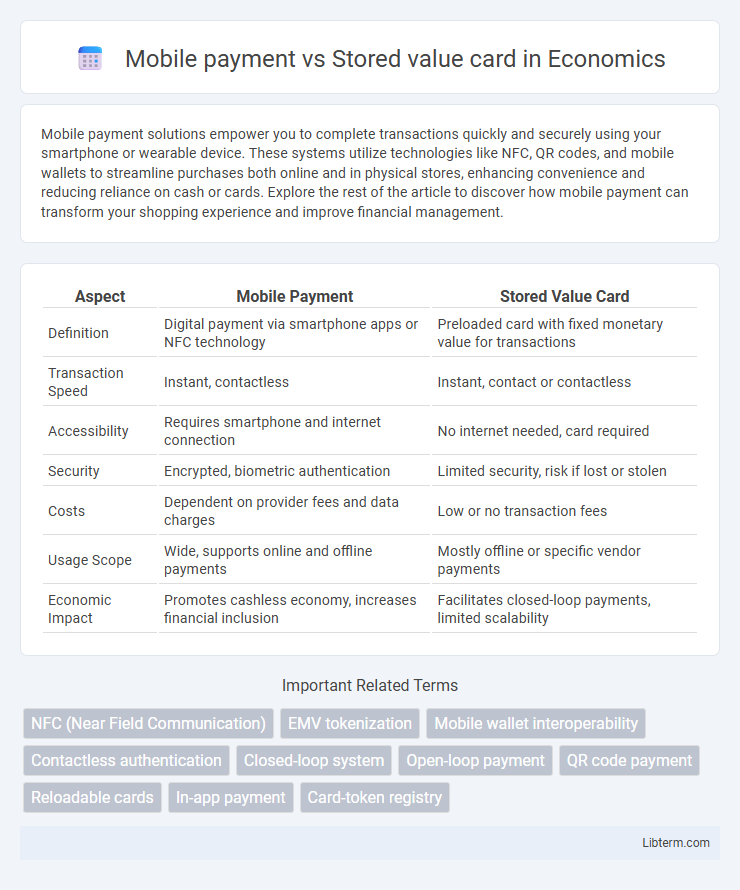
| Aspect | Mobile Payment | Stored Value Card |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digital payment via smartphone apps or NFC technology | Preloaded card with fixed monetary value for transactions |
| Transaction Speed | Instant, contactless | Instant, contact or contactless |
| Accessibility | Requires smartphone and internet connection | No internet needed, card required |
| Security | Encrypted, biometric authentication | Limited security, risk if lost or stolen |
| Costs | Dependent on provider fees and data charges | Low or no transaction fees |
| Usage Scope | Wide, supports online and offline payments | Mostly offline or specific vendor payments |
| Economic Impact | Promotes cashless economy, increases financial inclusion | Facilitates closed-loop payments, limited scalability |
Introduction to Mobile Payment and Stored Value Card
Mobile payment systems enable users to complete transactions using smartphones or other mobile devices by linking to bank accounts, credit cards, or digital wallets, offering convenience and quick access to funds. Stored value cards, such as prepaid cards or gift cards, contain a fixed monetary value loaded onto the card and can be used for purchases without direct connection to a bank account. Both technologies provide secure, cashless payment options but differ in their funding mechanisms and usage flexibility.
Key Differences Between Mobile Payment and Stored Value Card
Mobile payment relies on digital wallets and smartphones to process transactions through NFC or QR codes, while stored value cards store a preloaded monetary balance on a physical card. Mobile payments often integrate with bank accounts, offering real-time reconciliation, whereas stored value cards operate offline and require manual top-ups. Security protocols differ significantly, with mobile payments utilizing encryption and biometrics, contrasting the simpler PIN or signature validation on stored value cards.
How Mobile Payments Work
Mobile payments function through wireless communication technologies like NFC (Near Field Communication) or QR codes, enabling users to transfer funds directly from a linked bank account or digital wallet to a merchant's point-of-sale system. These transactions are secured via tokenization and encryption to protect sensitive information, ensuring buyer and seller data privacy. Unlike stored value cards, mobile payments do not require preloading cash onto a physical card, allowing real-time access to bank funds or credit lines for seamless, contactless purchases.
How Stored Value Cards Operate
Stored value cards function by preloading a specific monetary amount onto the card, allowing users to make transactions without the need for direct bank or credit card connectivity. These cards store balance information securely in the card's chip or magnetic stripe, enabling offline use and quick payment processing at compatible terminals. Unlike mobile payments that require internet access and device authentication, stored value cards provide a reliable and straightforward payment method by deducting funds instantly from the stored balance for each purchase.
Security Features: Mobile Payment vs Stored Value Card
Mobile payment systems utilize advanced encryption, biometric authentication, and tokenization to protect transaction data, significantly reducing the risk of fraud and unauthorized access. Stored value cards rely on physical card security measures, such as PIN protection and chip technology, but are more vulnerable to loss or theft without immediate remote deactivation options. Mobile payments benefit from real-time monitoring and remote disabling capabilities, offering enhanced security compared to the more static protection of stored value cards.
User Experience and Convenience Comparison
Mobile payments offer seamless, contactless transactions through smartphones, enhancing user convenience by eliminating the need to carry physical cards. Stored value cards require pre-loading funds but provide quick access to a fixed balance without relying on internet connectivity. Users benefit from real-time transaction tracking and instant payments with mobile payments, whereas stored value cards offer simplicity and offline usability in environments with limited digital infrastructure.
Popular Mobile Payment Platforms and Stored Value Card Providers
Popular mobile payment platforms include Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay, offering seamless transactions via smartphones and wearable devices with high security features like tokenization and biometric authentication. Leading stored value card providers such as Visa Prepaid, Mastercard Prepaid, and American Express Serve offer prepaid cards that can be loaded with funds for controlled spending without requiring a bank account. Both payment methods enhance consumer convenience, with mobile payments excelling in contactless, app-based transactions while stored value cards provide offline usability and budget management tools.
Cost Considerations and Hidden Fees
Mobile payment systems often have lower upfront costs but may include transaction fees, monthly service charges, or surcharge fees depending on the provider. Stored value cards typically involve initial purchase fees, reload fees, and inactivity charges that can accumulate over time, impacting the overall value. Detailed cost comparison is necessary to evaluate which option offers greater transparency and long-term savings.
Suitability for Different Types of Users
Mobile payment solutions suit tech-savvy users who prioritize convenience and quick transactions through smartphones or wearable devices. Stored value cards are ideal for users who prefer prepaid budgeting and limited digital exposure, especially suitable for younger consumers or those without smartphones. Businesses targeting frequent, small-value purchases benefit from stored value cards, while mobile payments cater to users seeking seamless integration with other digital services.
Future Trends in Digital Payments
Mobile payments are rapidly evolving with advancements in biometric authentication and AI-driven transaction security, offering seamless and personalized user experiences. Stored value cards maintain relevance in closed-loop ecosystems but face limitations in scalability compared to mobile wallets integrated with NFC and blockchain technologies. Future trends indicate a shift towards unified digital ecosystems where mobile payments dominate through enhanced interoperability, real-time processing, and increased adoption of decentralized finance platforms.
Mobile payment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com