Didactic teaching focuses on clear, structured instruction where the teacher imparts knowledge directly to students, using lectures, demonstrations, and guided practice. This method emphasizes mastery of specific content and skills through repetition and reinforcement, making it effective for foundational learning. Discover how this approach can enhance Your educational techniques by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
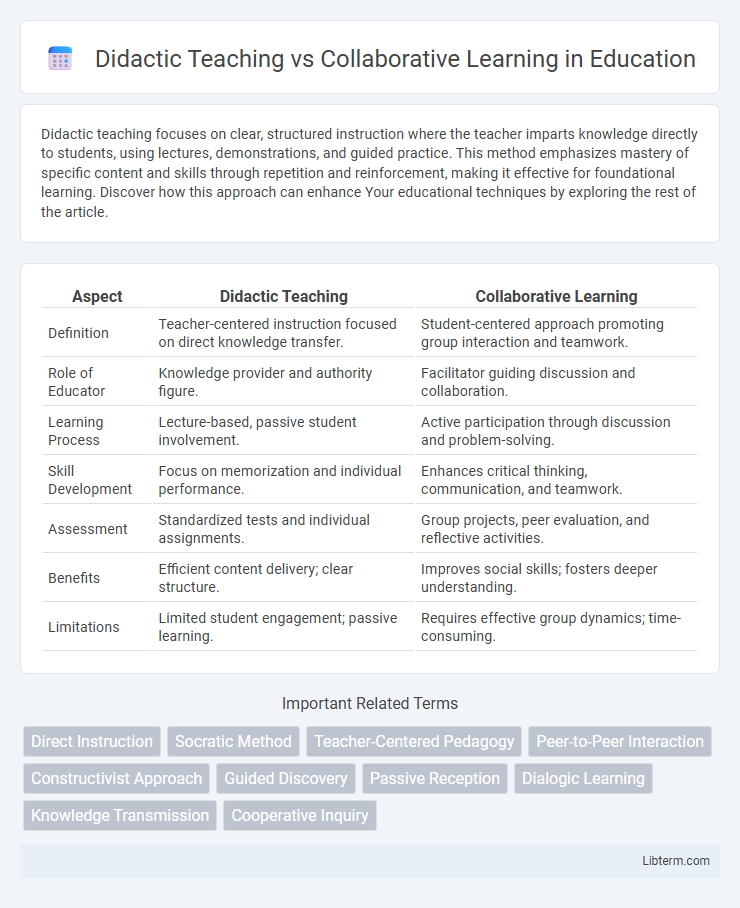
| Aspect | Didactic Teaching | Collaborative Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teacher-centered instruction focused on direct knowledge transfer. | Student-centered approach promoting group interaction and teamwork. |
| Role of Educator | Knowledge provider and authority figure. | Facilitator guiding discussion and collaboration. |
| Learning Process | Lecture-based, passive student involvement. | Active participation through discussion and problem-solving. |
| Skill Development | Focus on memorization and individual performance. | Enhances critical thinking, communication, and teamwork. |
| Assessment | Standardized tests and individual assignments. | Group projects, peer evaluation, and reflective activities. |
| Benefits | Efficient content delivery; clear structure. | Improves social skills; fosters deeper understanding. |
| Limitations | Limited student engagement; passive learning. | Requires effective group dynamics; time-consuming. |
Introduction to Didactic Teaching and Collaborative Learning
Didactic teaching centers on structured, instructor-led delivery of content, emphasizing clear objectives and step-by-step knowledge transmission. Collaborative learning fosters interactive engagement among students, promoting critical thinking and problem-solving through group activities and shared responsibilities. Both approaches influence educational outcomes by shaping student participation and comprehension strategies.
Defining Didactic Teaching: Key Characteristics
Didactic teaching is characterized by a structured, teacher-centered approach where the instructor delivers knowledge through lectures and direct instruction. It emphasizes clear objectives, content mastery, and often relies on repetition and memorization to reinforce learning. This method focuses on unidirectional information flow, prioritizing control over the learning environment and assessment of student comprehension through standardized tests.
Understanding Collaborative Learning: Core Principles
Collaborative learning centers on active student engagement through group interactions, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills in real-world contexts. Emphasizing shared responsibility and diverse perspectives, it enhances comprehension by encouraging dialogue, negotiation, and reflection among peers. This learner-centered approach contrasts with didactic teaching by promoting autonomy and deeper understanding through collective knowledge construction.
Historical Evolution of Teaching Methods
Didactic teaching, rooted in traditional education systems dating back to ancient Greece, emphasizes teacher-centered instruction where knowledge flows directly from educator to student. Collaborative learning emerged prominently in the 20th century, influenced by constructivist theories from scholars like Vygotsky, promoting shared knowledge construction through peer interaction. The shift from didactic to collaborative methods reflects an evolving understanding of cognitive development and the social nature of learning.
Benefits of Didactic Teaching in Modern Education
Didactic teaching ensures structured knowledge delivery, enabling efficient coverage of curriculum content and standardized assessment preparation. This approach supports learners who benefit from clear, expert-guided instruction and immediate feedback, enhancing comprehension and retention. It also facilitates classroom management and ensures consistency in education quality across diverse learning environments.
Advantages of Collaborative Learning Strategies
Collaborative learning strategies enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills by promoting active engagement and diverse perspectives among students. These methods foster communication, teamwork, and social interaction, leading to deeper understanding and retention of knowledge. Research indicates that collaborative learning increases motivation and academic achievement compared to traditional didactic teaching approaches.
Comparing Outcomes: Student Engagement and Achievement
Didactic teaching often results in lower student engagement due to passive learning, while collaborative learning fosters active participation and deeper comprehension. Studies show collaborative learning improves critical thinking skills and academic achievement by encouraging peer interaction and diverse perspectives. Student outcomes are generally more positive in collaborative settings, where motivation and retention rates increase compared to traditional didactic methods.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Didactic teaching often faces challenges such as limited student engagement and passive knowledge absorption, which can hinder critical thinking and creativity. Collaborative learning encounters limitations including group dynamics issues, unequal participation, and difficulties in assessing individual contributions. Both approaches require strategic implementation to overcome these barriers and optimize educational outcomes.
Integrating Didactic and Collaborative Methods
Integrating didactic teaching with collaborative learning enhances student engagement by combining structured content delivery with interactive, student-centered activities. This blended approach leverages the clarity and efficiency of didactic methods while fostering critical thinking, communication, and teamwork skills through collaboration. Educational research indicates that such integration improves knowledge retention and application across diverse learning environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach for Effective Learning
Didactic teaching emphasizes structured content delivery ideal for foundational knowledge acquisition, while collaborative learning fosters critical thinking and interpersonal skills through peer interaction. Effective learning outcomes often arise from a blended approach, tailoring methods to subject complexity and learner needs. Educators should assess curricular goals and student profiles to select the optimal balance that maximizes engagement and comprehension.
Didactic Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com