Summative assessment evaluates your overall learning by measuring knowledge and skills acquired at the end of an instructional period. It provides critical feedback on academic achievement and helps educators determine if educational goals have been met. Explore the rest of the article to understand how summative assessments can effectively shape your learning journey.
Table of Comparison
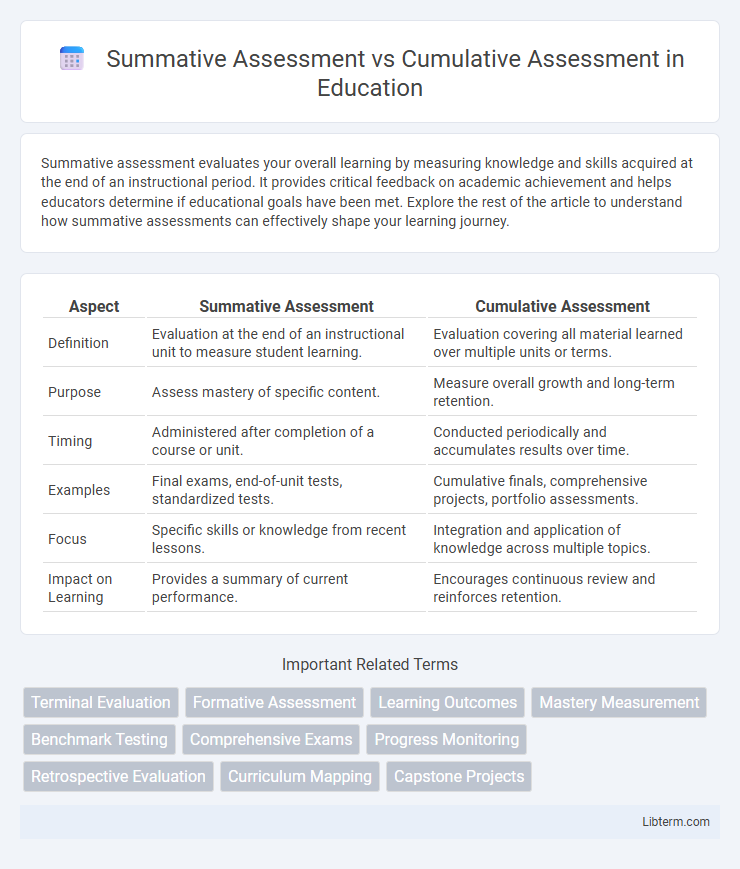
| Aspect | Summative Assessment | Cumulative Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Evaluation at the end of an instructional unit to measure student learning. | Evaluation covering all material learned over multiple units or terms. |
| Purpose | Assess mastery of specific content. | Measure overall growth and long-term retention. |
| Timing | Administered after completion of a course or unit. | Conducted periodically and accumulates results over time. |
| Examples | Final exams, end-of-unit tests, standardized tests. | Cumulative finals, comprehensive projects, portfolio assessments. |
| Focus | Specific skills or knowledge from recent lessons. | Integration and application of knowledge across multiple topics. |
| Impact on Learning | Provides a summary of current performance. | Encourages continuous review and reinforces retention. |
Introduction to Summative and Cumulative Assessment
Summative assessment evaluates student learning by measuring mastery of specific units or courses at the end of an instructional period, providing a clear benchmark of achievement through exams, projects, or standardized tests. Cumulative assessment integrates knowledge and skills acquired over multiple periods, emphasizing retention and application across broader content scopes, often through comprehensive final exams or portfolios. Both approaches serve distinct purposes in education by offering insights into immediate learning outcomes and long-term knowledge consolidation.
Defining Summative Assessment
Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of an instructional period, providing a summary judgment on mastery of course objectives. Typical formats include final exams, standardized tests, and end-of-unit projects designed to measure overall achievement. This form of assessment contrasts with cumulative assessment, which aggregates knowledge and skills over time to track ongoing progression.
Defining Cumulative Assessment
Cumulative assessment evaluates student learning by covering material from the entire duration of a course or program, integrating knowledge from multiple units or semesters to measure overall mastery. Unlike summative assessment, which typically targets specific learning outcomes at the end of an instructional period, cumulative assessments provide a comprehensive analysis of long-term retention and skill development. This approach is essential for identifying deep understanding and the ability to apply concepts cohesively across a broader curriculum.
Key Differences Between Summative and Cumulative Assessments
Summative assessment measures student learning at the end of an instructional unit by evaluating mastery of specific objectives, while cumulative assessment reviews knowledge acquired over a longer period, encompassing multiple units or topics. Key differences include purpose, scope, and timing: summative assessments are typically administered once per unit to provide a final grade, whereas cumulative assessments aggregate information from several units to track overall progress. Summative assessments often involve tests or projects, while cumulative assessments may incorporate portfolios or comprehensive exams.
Purpose and Goals of Each Assessment Type
Summative assessment aims to evaluate student learning by measuring mastery of specific content or skills at the end of an instructional period, providing a final judgment of student performance. Cumulative assessment, on the other hand, focuses on reviewing and integrating knowledge and skills acquired over multiple instructional units, promoting long-term retention and deeper understanding. Both assessments serve distinct purposes: summative for accountability and grading, and cumulative for reinforcing and connecting prior learning.
Advantages of Summative Assessments
Summative assessments provide a clear and objective measure of student learning by evaluating knowledge at the end of an instructional period, ensuring alignment with learning objectives. They offer actionable feedback to educators for curriculum adjustments and help in making informed decisions about student progress and academic achievement. These assessments also motivate students to consolidate their learning and prepare thoroughly for final evaluations, enhancing overall educational outcomes.
Benefits of Cumulative Assessments
Cumulative assessments provide a comprehensive evaluation of student learning by covering material from the entire course, promoting long-term retention and deep understanding. They help identify knowledge gaps across various topics, allowing educators to address weaknesses more effectively. Cumulative assessments also encourage consistent study habits and reinforce connections between concepts, leading to improved academic performance.
Common Examples in Educational Settings
Summative assessments typically include final exams, standardized tests, and end-of-unit projects that evaluate student learning at the conclusion of an instructional period. Cumulative assessments often appear as comprehensive exams or portfolios that integrate knowledge and skills acquired throughout multiple units or semesters. Both assessment types are crucial in educational settings for measuring mastery and long-term retention of course content.
Choosing the Right Assessment Method
Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of an instructional period, providing a snapshot of mastery through exams, final projects, or standardized tests. Cumulative assessment tracks progress over time by integrating previous content, often using portfolios or multiple quizzes to measure growth comprehensively. Choosing the right assessment method depends on instructional goals, with summative assessments suited for final evaluation and cumulative assessments ideal for ongoing feedback and skill development.
Conclusion: Selecting Effective Assessment Strategies
Summative assessment provides targeted evaluation of learning outcomes at specific points, while cumulative assessment measures knowledge retention over an extended period. Choosing effective assessment strategies depends on aligning the method with instructional goals, whether emphasizing mastery of discrete units or overall content integration. Educators optimize learner evaluation by balancing both approaches to enhance academic achievement and inform instructional adjustments.
Summative Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com