Multidisciplinary approaches integrate knowledge and methods from various disciplines to address complex challenges effectively. This collaboration fosters innovation and enhances problem-solving by combining diverse perspectives and expertise. Discover how embracing multidisciplinary strategies can transform your projects by reading the full article.
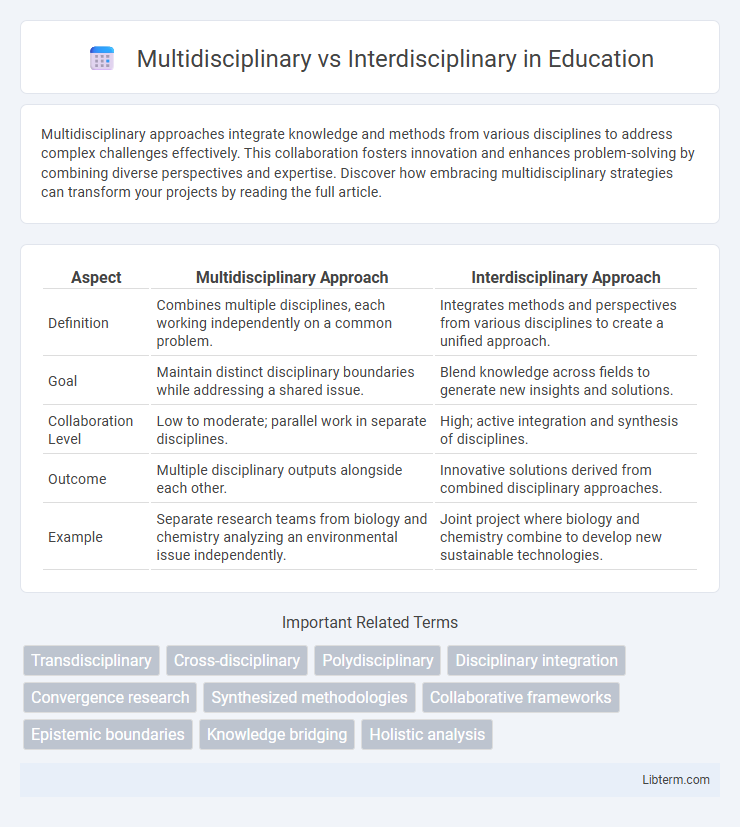
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Multidisciplinary Approach | Interdisciplinary Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines multiple disciplines, each working independently on a common problem. | Integrates methods and perspectives from various disciplines to create a unified approach. |
| Goal | Maintain distinct disciplinary boundaries while addressing a shared issue. | Blend knowledge across fields to generate new insights and solutions. |
| Collaboration Level | Low to moderate; parallel work in separate disciplines. | High; active integration and synthesis of disciplines. |
| Outcome | Multiple disciplinary outputs alongside each other. | Innovative solutions derived from combined disciplinary approaches. |
| Example | Separate research teams from biology and chemistry analyzing an environmental issue independently. | Joint project where biology and chemistry combine to develop new sustainable technologies. |
Understanding Multidisciplinary and Interdisciplinary Approaches
Multidisciplinary approaches involve integrating knowledge from multiple disciplines where each maintains its methods and perspectives, addressing a problem in parallel. Interdisciplinary approaches blend theories, methods, and frameworks from different fields to create cohesive solutions and generate new insights. Understanding these approaches highlights how interdisciplinary work promotes innovation through synthesis, while multidisciplinary collaboration leverages diverse expertise without merging disciplinary boundaries.
Key Differences Between Multidisciplinary and Interdisciplinary Collaboration
Multidisciplinary collaboration involves experts from distinct fields working side by side on a common problem, each contributing their specialized knowledge independently, while interdisciplinary collaboration integrates methodologies and concepts from multiple disciplines to create a unified approach. In multidisciplinary teams, the emphasis is on parallel contributions without necessarily blending perspectives, whereas interdisciplinary work fosters synthesis and cognitive integration to develop innovative solutions. Key differences include the level of interaction, with interdisciplinary collaboration requiring deeper communication and shared frameworks, contrasted with the more segmented roles in multidisciplinary projects.
Core Principles of Multidisciplinary Teams
Multidisciplinary teams integrate experts from various fields who work parallelly, contributing distinct insights without merging methodologies, emphasizing respect for diverse expertise and clear role definitions. Core principles include collaboration through shared goals, communication transparency, and maintaining individual disciplinary boundaries while coordinating efforts. This structure ensures comprehensive problem-solving by harnessing specialized knowledge in a coordinated yet independent manner.
Core Principles of Interdisciplinary Teams
Interdisciplinary teams integrate knowledge, methods, and perspectives from multiple disciplines to develop innovative solutions beyond the scope of any single field, emphasizing collaboration, communication, and mutual learning among team members. Core principles include shared goals, joint problem-solving, and the synthesis of diverse expertise into cohesive outcomes that address complex problems holistically. Unlike multidisciplinary approaches, which involve parallel contributions, interdisciplinary teams foster deep integration and co-creation of new frameworks and insights.
Advantages of Multidisciplinary Methods
Multidisciplinary methods gather expertise from various specialized fields, offering comprehensive perspectives and enabling tailored solutions for complex problems. These approaches facilitate parallel workflows, which can speed up project completion and enhance efficiency by leveraging distinct disciplinary strengths independently. Multidisciplinarity also fosters innovation by combining diverse methodologies without necessarily blending disciplines, maintaining clarity in roles and responsibilities among team members.
Benefits of Interdisciplinary Integration
Interdisciplinary integration fosters innovation by combining diverse disciplinary perspectives to solve complex problems more effectively than multidisciplinary approaches, which often keep disciplines separate. This approach enhances collaboration, leading to deeper insights and comprehensive solutions through the synthesis of methodologies and knowledge. It also improves adaptability and creativity in research and practice by transcending traditional boundaries and promoting holistic understanding.
Common Challenges in Each Approach
Multidisciplinary approaches often face challenges related to siloed knowledge, where experts work independently within their disciplines, leading to limited integration and communication barriers. Interdisciplinary approaches encounter difficulties in blending diverse methodologies and terminologies, causing conflicts in problem-solving strategies and inconsistent results. Both approaches require effective collaboration frameworks and shared goals to overcome misunderstandings and leverage diverse expertise efficiently.
Real-World Examples: Multidisciplinary vs Interdisciplinary Work
Multidisciplinary work involves experts from various fields working side-by-side on a problem, such as architects, engineers, and environmental scientists collaborating on urban development projects. Interdisciplinary work integrates knowledge and methods from different disciplines, exemplified by bioinformatics where biology, computer science, and statistics merge to analyze genetic data. The distinction lies in multidisciplinary approaches maintaining disciplinary boundaries while interdisciplinary approaches create new frameworks blending those disciplines for innovative solutions.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
When choosing between multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary approaches, consider the project's complexity and integration needs. Multidisciplinary methods allow specialists to work independently within their fields, ideal for tasks requiring discrete expertise without extensive collaboration. Interdisciplinary approaches suit challenges demanding deep synthesis of knowledge across fields, fostering innovation through seamless integration of diverse perspectives.
Future Trends in Collaborative Research and Practice
Future trends in collaborative research emphasize increasing integration of multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary approaches, leveraging diverse expertise to solve complex global challenges such as climate change and public health. Multidisciplinary research maintains distinct disciplinary boundaries while contributing varied perspectives, whereas interdisciplinary research fosters deeper synthesis and innovation by combining theoretical frameworks and methodologies. Advances in digital communication and data sharing platforms will accelerate interdisciplinary collaborations, enhancing knowledge integration and driving transformative solutions across sectors.
Multidisciplinary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com