Inquiry-based learning promotes critical thinking by encouraging students to explore questions and problems actively. This approach fosters deeper understanding through hands-on investigation and continuous reflection. Discover how inquiry-based learning can transform your educational experience in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
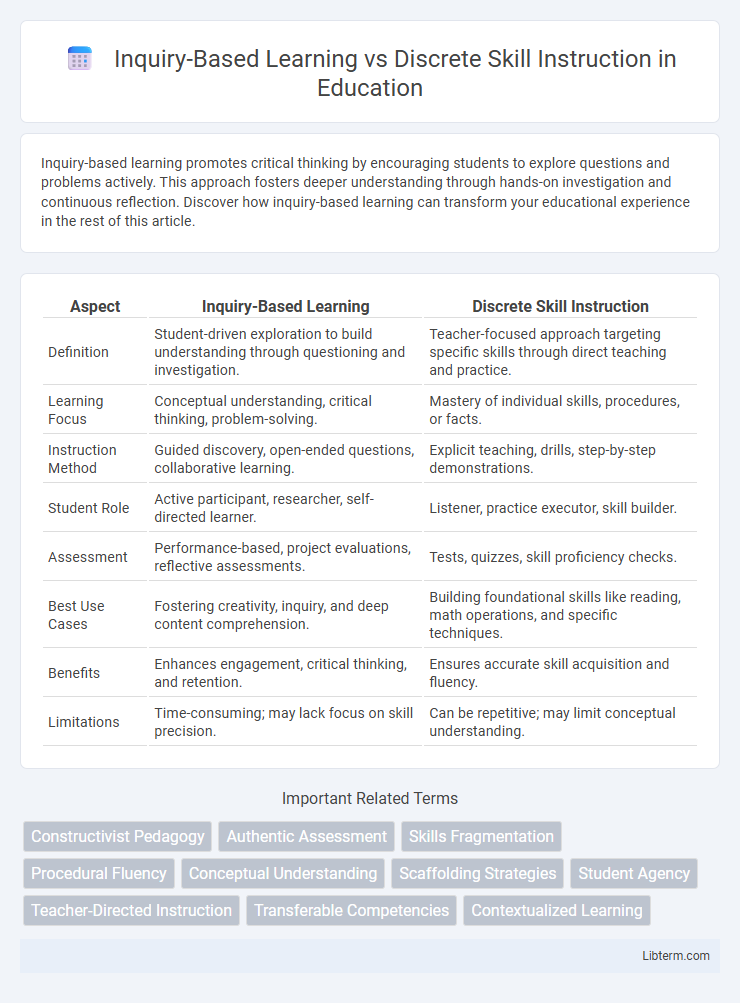
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning | Discrete Skill Instruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-driven exploration to build understanding through questioning and investigation. | Teacher-focused approach targeting specific skills through direct teaching and practice. |
| Learning Focus | Conceptual understanding, critical thinking, problem-solving. | Mastery of individual skills, procedures, or facts. |
| Instruction Method | Guided discovery, open-ended questions, collaborative learning. | Explicit teaching, drills, step-by-step demonstrations. |
| Student Role | Active participant, researcher, self-directed learner. | Listener, practice executor, skill builder. |
| Assessment | Performance-based, project evaluations, reflective assessments. | Tests, quizzes, skill proficiency checks. |
| Best Use Cases | Fostering creativity, inquiry, and deep content comprehension. | Building foundational skills like reading, math operations, and specific techniques. |
| Benefits | Enhances engagement, critical thinking, and retention. | Ensures accurate skill acquisition and fluency. |
| Limitations | Time-consuming; may lack focus on skill precision. | Can be repetitive; may limit conceptual understanding. |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based Learning and Discrete Skill Instruction
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and problem-solving by engaging students in exploration and questioning, promoting deeper understanding through active discovery. Discrete Skill Instruction emphasizes the step-by-step teaching of specific skills or knowledge, focusing on mastery and repetition to build competence. Both methods serve distinct educational purposes, with inquiry-based approaches encouraging conceptual connections and discrete instruction ensuring foundational skill acquisition.
Defining Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters active student engagement through exploration and question-driven investigation, promoting critical thinking and deep understanding. This approach contrasts with Discrete Skill Instruction, which emphasizes the direct teaching of specific skills or facts in isolation. Inquiry-Based Learning encourages learners to construct knowledge by formulating hypotheses, conducting experiments, and reflecting on outcomes, creating a more dynamic and personalized educational experience.
Defining Discrete Skill Instruction
Discrete Skill Instruction emphasizes teaching individual skills in isolation, allowing students to master specific tasks before integrating them into broader contexts. This method relies heavily on repetition and direct feedback to ensure skill acquisition. It contrasts with Inquiry-Based Learning by prioritizing structured practice over exploratory problem-solving.
Historical Context and Educational Theories
Inquiry-Based Learning emerged from constructivist theories of education, emphasizing learner-centered exploration rooted in the work of John Dewey and Jean Piaget during the early 20th century. Discrete Skill Instruction, grounded in behaviorist principles advocated by B.F. Skinner, gained prominence in the mid-20th century focused on rote memorization and repetitive practice to master specific skills. The historical shift reflects evolving educational paradigms from passive knowledge reception toward active cognitive engagement and critical thinking development.
Key Differences Between the Two Approaches
Inquiry-based learning emphasizes student-driven exploration and critical thinking by encouraging learners to ask questions and investigate problems, fostering deeper understanding and cognitive engagement. Discrete skill instruction focuses on targeted teaching of specific skills or facts through structured lessons and repetition, aiming to build proficiency and mastery in well-defined areas. The inquiry approach promotes adaptability and creativity, while discrete instruction prioritizes precision and incremental skill development.
Benefits of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning enhances critical thinking and deep understanding by engaging students in active problem-solving and exploration, fostering long-term retention of knowledge. This approach promotes intrinsic motivation and curiosity, enabling learners to connect concepts across disciplines and apply skills in real-world contexts. Research shows that inquiry-based methods improve higher-order cognitive skills more effectively than discrete skill instruction alone.
Advantages of Discrete Skill Instruction
Discrete Skill Instruction offers clear advantages by providing focused, explicit teaching of specific skills, which accelerates mastery and builds a strong foundation for more complex tasks. This approach allows for precise assessment and immediate feedback, ensuring learners correct errors early and reinforce correct techniques. Its structured nature benefits students requiring step-by-step guidance, particularly in subjects like math, reading, and language acquisition where sequential skills are essential.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Methods
Inquiry-based learning faces challenges such as increased cognitive load on students and difficulty in guiding novice learners without clear scaffolding, leading to potential misconceptions. Discrete skill instruction may limit critical thinking and creativity by focusing on rote memorization and isolated skills, which can hinder application in complex, real-world contexts. Both methods require careful balance to address diverse learner needs and ensure effective knowledge retention and transfer.
Practical Applications in the Classroom
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills by engaging students in exploring real-world questions and developing hypotheses, making it ideal for science and social studies classrooms where investigation is key. Discrete Skill Instruction emphasizes targeted practice of specific abilities, such as phonics in reading or algorithmic procedures in math, ensuring mastery of foundational skills through repetition and direct feedback. Combining both approaches allows educators to build essential competencies while encouraging deeper understanding and application of knowledge across subjects.
Integrating Inquiry-Based and Discrete Skill Strategies
Integrating inquiry-based learning with discrete skill instruction enhances student comprehension by combining exploratory, question-driven approaches with targeted skill development, promoting deeper understanding and practical application. Utilizing inquiry-based strategies encourages critical thinking and problem-solving, while discrete skill instruction ensures mastery of foundational concepts through structured practice. This blended method supports diverse learning styles and fosters a balanced educational environment that prepares students for complex real-world challenges.
Inquiry-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com