Curriculum differentiation tailors educational content to meet the diverse learning needs, interests, and abilities of students, ensuring that each learner can engage meaningfully with the material. By incorporating varied instructional strategies, assessments, and learning environments, it enhances student motivation and achievement. Discover how effective differentiation can transform Your teaching approach by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
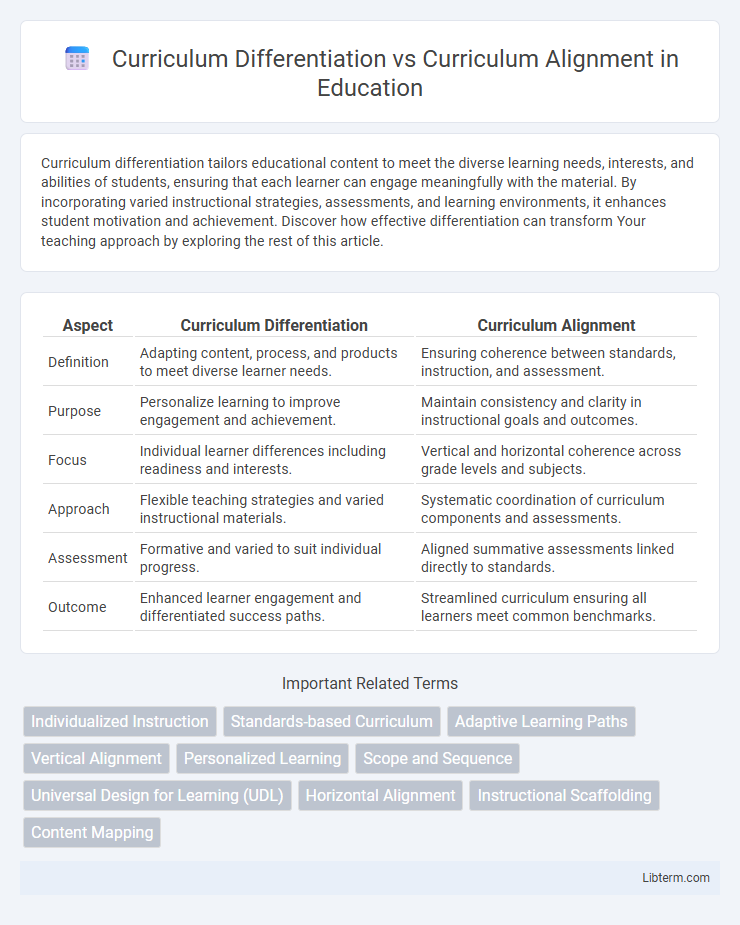
| Aspect | Curriculum Differentiation | Curriculum Alignment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adapting content, process, and products to meet diverse learner needs. | Ensuring coherence between standards, instruction, and assessment. |
| Purpose | Personalize learning to improve engagement and achievement. | Maintain consistency and clarity in instructional goals and outcomes. |
| Focus | Individual learner differences including readiness and interests. | Vertical and horizontal coherence across grade levels and subjects. |
| Approach | Flexible teaching strategies and varied instructional materials. | Systematic coordination of curriculum components and assessments. |
| Assessment | Formative and varied to suit individual progress. | Aligned summative assessments linked directly to standards. |
| Outcome | Enhanced learner engagement and differentiated success paths. | Streamlined curriculum ensuring all learners meet common benchmarks. |
Understanding Curriculum Differentiation
Curriculum differentiation involves tailoring educational content, processes, and products to meet diverse learners' needs, abilities, and interests, which enhances student engagement and achievement. It requires teachers to modify instructional strategies and materials to accommodate varying learning styles and readiness levels, ensuring equitable access to the curriculum. Unlike curriculum alignment, which focuses on standardizing learning objectives with assessments and standards, differentiation emphasizes personalized learning pathways within the curriculum framework.
Defining Curriculum Alignment
Curriculum alignment ensures that learning objectives, instructional methods, and assessments are cohesively interconnected to support student achievement and curriculum standards. It involves mapping content across grade levels and subjects to create a seamless educational experience that addresses academic goals. Effective curriculum alignment improves instructional consistency and helps identify gaps or overlaps in learning outcomes.
Key Differences Between Differentiation and Alignment
Curriculum differentiation involves tailoring instructional methods and content to meet diverse student needs, ensuring personalized learning experiences, while curriculum alignment focuses on ensuring consistency between learning objectives, teaching practices, and assessment standards across grade levels. Differentiation prioritizes adaptability and student-centered approaches, catering to varying abilities and interests, whereas alignment emphasizes structured coherence and systematic progression within the curriculum framework. Key differences lie in their goals: differentiation promotes individualized learning paths, and alignment secures uniformity and instructional integrity.
Goals and Objectives of Each Approach
Curriculum Differentiation emphasizes tailoring educational goals and objectives to meet diverse student needs, promoting personalized learning outcomes and individual skill development. Curriculum Alignment focuses on synchronizing goals and objectives across standards, instruction, and assessments to ensure consistency and coherence in student learning experiences. Both approaches aim to enhance academic achievement, but differentiation prioritizes adaptability, while alignment stresses uniformity and systematic coordination.
Instructional Strategies in Differentiation
Curriculum differentiation emphasizes tailored instructional strategies such as flexible grouping, tiered assignments, and scaffolded support to address diverse learner needs and maximize student engagement. In contrast, curriculum alignment ensures consistency and coherence between learning objectives, assessments, and instructional activities without necessarily adapting instruction to individual differences. Effective differentiation requires dynamic adjustments in teaching methods to foster equity and accommodate varied readiness levels, interests, and learning profiles.
Alignment with Standards and Assessments
Curriculum alignment ensures instructional content, teaching methods, and assessments correspond precisely with established educational standards, fostering consistency and clarity in learning objectives. Differentiation addresses individual student needs by modifying content delivery or assessment methods without altering the core standards, ensuring equitable access to curriculum goals. Aligning curriculum with standards and assessments allows educators to measure student progress accurately and maintain accountability across diverse learning environments.
Benefits of Curriculum Differentiation
Curriculum differentiation enhances student engagement by tailoring instructional methods and content to diverse learning styles, abilities, and interests, resulting in improved academic outcomes. It fosters inclusivity by addressing individual strengths and challenges, promoting equity within heterogeneous classrooms. This personalized approach supports higher motivation and confidence, enabling learners to achieve their full potential beyond standardized curriculum constraints.
Advantages of Curriculum Alignment
Curriculum alignment enhances instructional coherence by ensuring that learning objectives, teaching methods, and assessments are consistently connected, leading to improved student understanding and performance. This approach facilitates standardized evaluation across diverse classrooms, promoting equity and accountability in education systems. By aligning curricula with state standards and benchmarks, educators can more effectively track progress and address gaps in student learning.
Challenges in Implementation
Curriculum differentiation faces challenges in implementation due to varied student learning needs and the need for extensive teacher training to create personalized learning experiences. Curriculum alignment struggles with balancing state standards and diverse classroom realities, often causing rigidity that hinders adaptability to individual learner requirements. Both approaches demand significant resource allocation and professional development, highlighting systemic constraints in educational infrastructure.
Best Practices for Integrating Both Approaches
Effective integration of curriculum differentiation and curriculum alignment involves tailoring instruction to meet diverse learner needs while ensuring content consistency with established standards. Utilizing data-driven assessments to identify student readiness, interests, and learning profiles supports personalized learning paths within a coherent curricular framework. Collaborative planning among educators enhances alignment and differentiation, promoting equity and maximizing student achievement through targeted strategies embedded in standardized learning goals.
Curriculum Differentiation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com