Online learning offers flexible access to education anytime and anywhere, making it easier for you to balance studies with personal and professional commitments. It leverages digital tools and interactive platforms to enhance engagement and provide personalized learning experiences. Discover how online learning can transform your educational journey by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
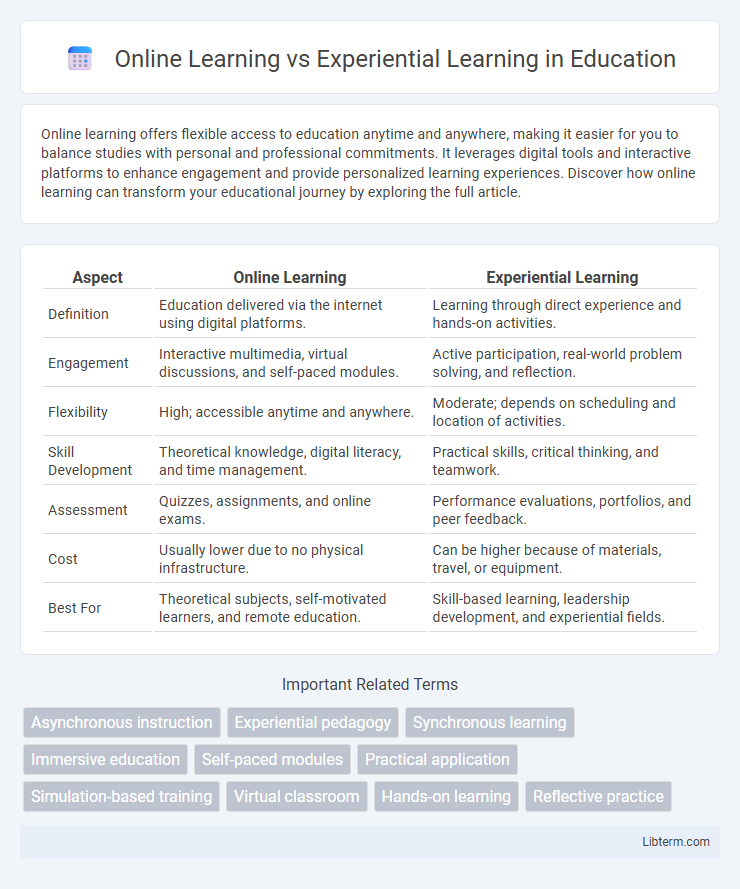
| Aspect | Online Learning | Experiential Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Education delivered via the internet using digital platforms. | Learning through direct experience and hands-on activities. |
| Engagement | Interactive multimedia, virtual discussions, and self-paced modules. | Active participation, real-world problem solving, and reflection. |
| Flexibility | High; accessible anytime and anywhere. | Moderate; depends on scheduling and location of activities. |
| Skill Development | Theoretical knowledge, digital literacy, and time management. | Practical skills, critical thinking, and teamwork. |
| Assessment | Quizzes, assignments, and online exams. | Performance evaluations, portfolios, and peer feedback. |
| Cost | Usually lower due to no physical infrastructure. | Can be higher because of materials, travel, or equipment. |
| Best For | Theoretical subjects, self-motivated learners, and remote education. | Skill-based learning, leadership development, and experiential fields. |
Introduction to Online and Experiential Learning
Online learning leverages digital platforms to deliver educational content, enabling flexible access to courses anytime and anywhere, often through video lectures, quizzes, and interactive modules. Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on, real-world experiences that foster deeper understanding through active participation, reflection, and practical application of knowledge. Both methods target skill development but differ in approach, with online learning focusing on theoretical knowledge dissemination and experiential learning prioritizing immersive, practice-based education.
Defining Online Learning: Features and Formats
Online learning encompasses digital platforms that deliver educational content through various formats such as live webinars, video lectures, and interactive modules, enabling flexible access anytime and anywhere. Key features include self-paced study, multimedia resources, and real-time communication tools that facilitate engagement and personalized feedback. This mode of learning supports diverse learning styles by integrating quizzes, discussion forums, and virtual classrooms, ensuring comprehensive knowledge acquisition without physical presence.
Understanding Experiential Learning: Key Elements
Experiential learning emphasizes active engagement through hands-on experiences, reflection, and application of knowledge in real-world contexts, contrasting with the passive reception common in online learning. Key elements include concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation, enabling deeper comprehension and skill development. This cyclical process promotes critical thinking, adaptability, and retention, which are often limited in online learning environments that rely heavily on digital content delivery.
Flexibility and Accessibility Compared
Online learning offers unparalleled flexibility by allowing learners to access educational content anytime and anywhere, accommodating diverse schedules and learning paces. Experiential learning typically requires physical presence and hands-on participation, which can limit accessibility for remote or time-constrained individuals. The asynchronous nature of most online courses enhances accessibility for global audiences, whereas experiential learning often depends on specific locations and real-time interaction.
Engagement and Interaction in Both Models
Online learning leverages multimedia tools and interactive platforms to enhance student engagement through quizzes, forums, and virtual simulations, fostering active participation despite physical distance. Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on activities and real-world experiences, promoting deeper understanding and skill acquisition through direct interaction and reflection. Both models prioritize interaction but differ in approach; online learning relies on digital engagement methods while experiential learning centers on tangible, contextual experiences.
Skills Development: Theory vs. Practice
Online learning enhances theoretical knowledge through structured modules and interactive content, fostering foundational understanding of key concepts. Experiential learning accelerates skills development by immersing learners in real-world scenarios, enabling practical application and problem-solving abilities. Combining both approaches optimizes skill acquisition by integrating theory with hands-on experience essential for professional growth.
Measuring Learning Outcomes
Measuring learning outcomes in online learning predominantly relies on digital assessments, quizzes, and analytics tracking engagement and test scores to quantify knowledge retention. Experiential learning outcomes are evaluated through practical demonstrations, real-world problem-solving, and reflective assessments that capture skills application and critical thinking. Combining quantitative data from online metrics with qualitative insights from experiential evaluations offers a comprehensive understanding of learner proficiency and development.
Technological Requirements and Challenges
Online learning demands reliable internet connectivity, advanced learning management systems, and digital devices capable of supporting interactive platforms, which can be a barrier in regions with limited technological infrastructure. Experiential learning often requires specialized equipment, physical resources, and real-world environments that may be costly and challenging to simulate digitally. Both modalities face challenges in ensuring technology accessibility, system compatibility, and user proficiency, impacting the effectiveness and scalability of educational delivery.
Suitability for Different Learners and Subjects
Online learning offers flexibility and accessibility, making it suitable for self-motivated learners and theoretical subjects such as mathematics and humanities. Experiential learning engages kinesthetic and social learners by providing hands-on activities ideal for technical skills and fields like engineering, healthcare, and arts. Combining both methods can enhance comprehension by catering to diverse learning styles and subject complexities.
Future Trends in Online and Experiential Learning
Future trends in online learning emphasize artificial intelligence integration, personalized adaptive learning platforms, and immersive technologies like virtual and augmented reality to enhance engagement and retention. Experiential learning is evolving with increased use of simulations, gamification, and real-world problem-solving projects facilitated by digital collaboration tools, promoting deeper skill acquisition and critical thinking. Hybrid models combining online content with hands-on experiences are predicted to dominate, offering flexible, effective education tailored to diverse learner needs and industries.
Online Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com