Lecture-based learning remains a foundational educational method where instructors deliver structured content directly to students. This approach efficiently conveys complex information to large groups, fostering a shared understanding and promoting note-taking skills. Explore the article to discover how lecture-based learning can enhance your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
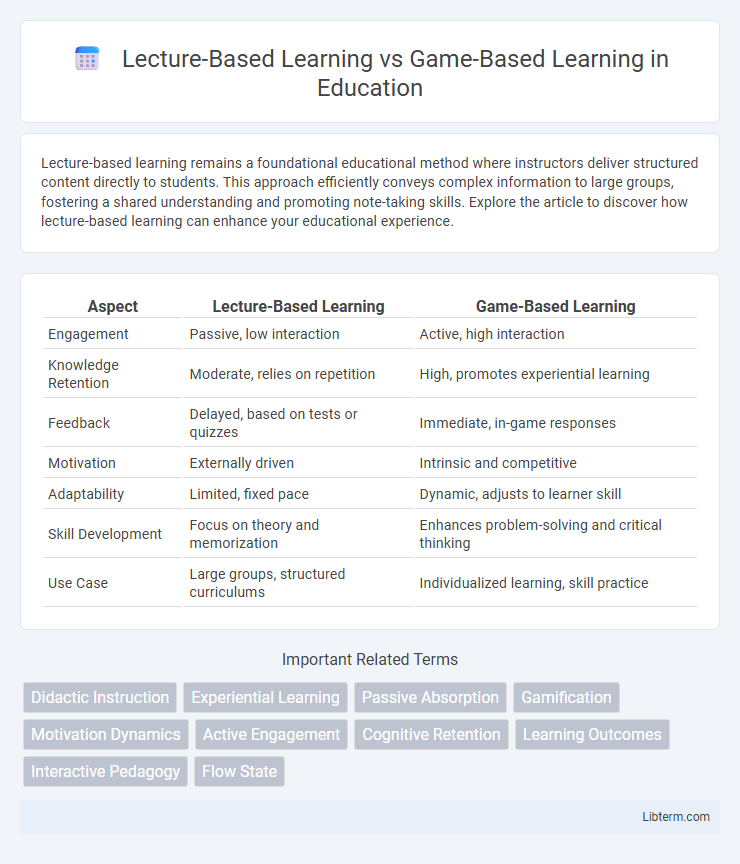
| Aspect | Lecture-Based Learning | Game-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Engagement | Passive, low interaction | Active, high interaction |
| Knowledge Retention | Moderate, relies on repetition | High, promotes experiential learning |
| Feedback | Delayed, based on tests or quizzes | Immediate, in-game responses |
| Motivation | Externally driven | Intrinsic and competitive |
| Adaptability | Limited, fixed pace | Dynamic, adjusts to learner skill |
| Skill Development | Focus on theory and memorization | Enhances problem-solving and critical thinking |
| Use Case | Large groups, structured curriculums | Individualized learning, skill practice |
Introduction to Learning Methodologies
Lecture-Based Learning primarily involves structured presentations where instructors deliver content directly to students, emphasizing passive information absorption and note-taking. Game-Based Learning integrates interactive games and simulations to foster active participation, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills through experiential engagement. Research indicates that combining these methodologies enhances knowledge retention, motivation, and application of concepts across diverse educational settings.
Defining Lecture-Based Learning
Lecture-based learning refers to a traditional educational approach where an instructor delivers content directly to students, primarily through verbal explanation and note-taking. This method emphasizes structured presentation of information, often relying on passive student engagement and a fixed curriculum. Lecture-based learning is effective for efficiently transmitting large amounts of knowledge but may lack the interactive elements found in more dynamic teaching strategies.
Exploring Game-Based Learning
Game-Based Learning enhances engagement and retention by integrating interactive elements and real-time feedback, making complex concepts more accessible compared to traditional Lecture-Based Learning. It promotes active participation, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills through immersive scenarios and challenges that simulate real-world applications. Research shows that students exposed to Game-Based Learning exhibit higher motivation and improved learning outcomes, particularly in STEM education and language acquisition.
Historical Evolution of Educational Approaches
Lecture-based learning originated in ancient Greece, where Socratic methods emphasized direct instruction and oral transmission of knowledge. Game-based learning gained traction in the late 20th century with advances in digital technology, promoting interactive and experiential education through simulations and serious games. The historical shift reflects a move from passive reception in traditional classrooms to active engagement, enhancing motivation and retention in contemporary pedagogical models.
Comparing Engagement Levels
Lecture-based learning often results in lower student engagement due to passive information reception, while game-based learning significantly increases interaction by incorporating challenges and rewards. Studies show game-based methods enhance motivation and active participation, leading to better knowledge retention. Engagement metrics, including time-on-task and emotional involvement, consistently favor game-based environments over traditional lectures.
Impact on Knowledge Retention
Lecture-Based Learning often results in passive information absorption, which can lead to lower long-term knowledge retention. Game-Based Learning engages multiple cognitive processes through interactivity and immediate feedback, enhancing memory encoding and retrieval. Studies show students in game-based environments retain information 30% longer compared to traditional lecture formats.
Adaptability to Different Learning Styles
Lecture-Based Learning primarily caters to auditory and visual learners by delivering structured content through speaking and presentations, but it often lacks flexibility for kinesthetic or interactive learning preferences. Game-Based Learning offers high adaptability by incorporating multisensory engagement and active participation, appealing to diverse learning styles such as visual, kinesthetic, and social learners. Research indicates that game mechanics and immediate feedback in Game-Based Learning enhance motivation and retention across varied learner profiles compared to traditional lectures.
Assessment and Evaluation Techniques
Lecture-based learning primarily utilizes traditional assessment techniques such as quizzes, written exams, and oral presentations to measure knowledge retention and comprehension. In contrast, game-based learning leverages real-time data analytics, performance metrics, and adaptive feedback systems to evaluate student engagement, problem-solving skills, and application of concepts within interactive environments. Effective evaluation in game-based learning integrates formative assessment with immediate feedback, promoting continuous improvement and deeper cognitive development.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Lecture-Based Learning often faces challenges such as limited student engagement, passive information absorption, and difficulty in catering to diverse learning paces. Game-Based Learning can encounter limitations including high development costs, potential distraction from educational goals, and the need for substantial technological resources. Both methods require careful implementation to overcome these obstacles and maximize educational effectiveness.
Future Trends in Educational Practices
Future trends in educational practices highlight the increasing integration of game-based learning (GBL) alongside traditional lecture-based learning to enhance student engagement and retention. Emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and artificial intelligence (AI) are driving the evolution of immersive, interactive game-based environments that promote personalized learning experiences. Educational institutions are investing in hybrid models that combine the structured knowledge delivery of lectures with the motivational and experiential benefits of game-based learning to prepare students for a digitally-driven future.
Lecture-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com