Cross-disciplinary approaches integrate knowledge and methods from multiple fields to solve complex problems more effectively. This strategy fosters innovation by breaking down traditional academic barriers and encouraging collaboration among experts with diverse perspectives. Discover how applying cross-disciplinary techniques can transform your projects by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
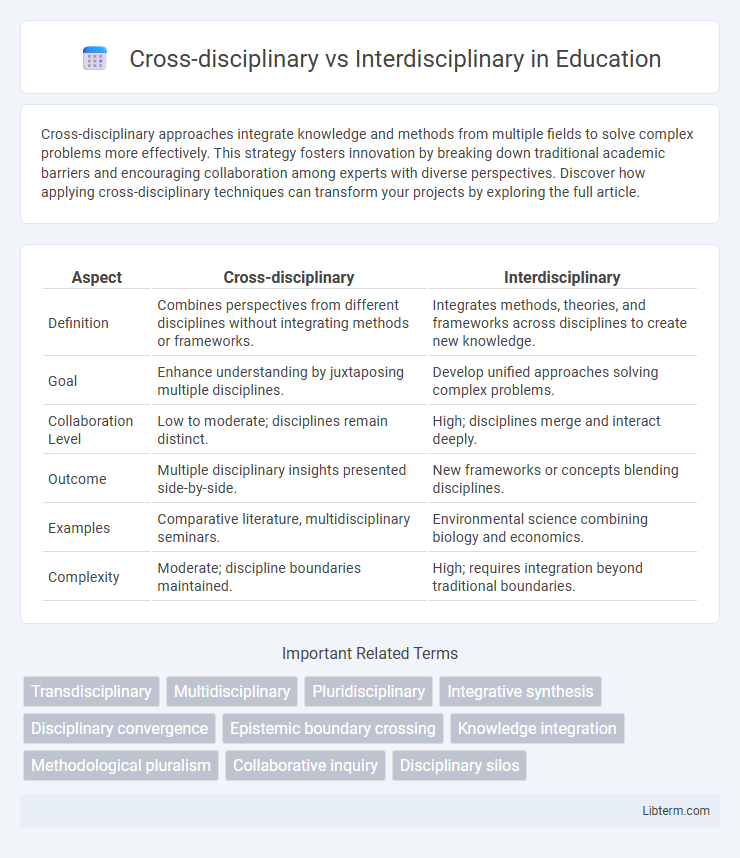
| Aspect | Cross-disciplinary | Interdisciplinary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines perspectives from different disciplines without integrating methods or frameworks. | Integrates methods, theories, and frameworks across disciplines to create new knowledge. |
| Goal | Enhance understanding by juxtaposing multiple disciplines. | Develop unified approaches solving complex problems. |
| Collaboration Level | Low to moderate; disciplines remain distinct. | High; disciplines merge and interact deeply. |
| Outcome | Multiple disciplinary insights presented side-by-side. | New frameworks or concepts blending disciplines. |
| Examples | Comparative literature, multidisciplinary seminars. | Environmental science combining biology and economics. |
| Complexity | Moderate; discipline boundaries maintained. | High; requires integration beyond traditional boundaries. |
Introduction to Cross-disciplinary and Interdisciplinary Approaches
Cross-disciplinary approaches integrate insights from multiple disciplines to address a topic, maintaining each field's distinct methods and perspectives. Interdisciplinary approaches go further by synthesizing theories, concepts, and methodologies to create new frameworks that transcend traditional boundaries. Both methods enhance problem-solving capabilities by leveraging diverse expertise for comprehensive understanding and innovation.
Defining Cross-disciplinary: Scope and Characteristics
Cross-disciplinary approaches integrate methods and perspectives from multiple distinct disciplines while maintaining the boundaries of each field. This scope emphasizes collaboration without fully blending frameworks, allowing for comparative analysis and problem-solving that respects disciplinary identities. Key characteristics include leveraging expertise from various fields to address complex issues through parallel contributions rather than synthesis.
Understanding Interdisciplinary: Key Features and Goals
Interdisciplinary approaches integrate knowledge, methods, and perspectives from multiple disciplines to create novel frameworks addressing complex problems. Key features include collaboration, synthesis of diverse expertise, and innovation beyond traditional boundaries. The primary goal of interdisciplinary work is to generate holistic solutions and new insights unattainable within single disciplines.
Differences Between Cross-disciplinary and Interdisciplinary Methods
Cross-disciplinary methods involve applying concepts or techniques from one discipline to address problems in another, often maintaining clear boundaries between fields, while interdisciplinary methods integrate knowledge and frameworks from multiple disciplines to create new approaches or solutions. Cross-disciplinary approaches typically borrow tools or insights without deeply blending disciplines, whereas interdisciplinary approaches emphasize collaboration and synthesis across disciplines to generate holistic understanding. The core difference lies in the level of integration: cross-disciplinary maintains discrete disciplinary perspectives, whereas interdisciplinary fosters convergence and co-creation of knowledge.
Benefits of Cross-disciplinary Collaboration
Cross-disciplinary collaboration fosters innovation by combining expertise from separate fields, enabling unique problem-solving approaches and expanding knowledge boundaries. This collaboration enhances creativity and productivity through the integration of diverse perspectives and methodologies. Leveraging varied skill sets accelerates research advancements and drives comprehensive outcomes across multiple domains.
Advantages of Interdisciplinary Integration
Interdisciplinary integration fosters innovation by combining methods and perspectives from multiple disciplines to solve complex problems more effectively. This approach enhances creativity, encourages collaboration, and leads to a deeper understanding of intricate issues that single-discipline methods may overlook. Research shows that interdisciplinary teams can produce more impactful and comprehensive solutions in fields like healthcare, environmental science, and technology development.
Common Challenges in Cross-disciplinary Projects
Cross-disciplinary projects often face challenges such as communication barriers due to differing terminologies and methodologies across fields, conflicting priorities among team members, and difficulties in integrating diverse perspectives into a cohesive outcome. These obstacles can lead to misunderstandings and inefficiencies, hindering collaboration and progress. Effective management and the establishment of clear shared goals are crucial for overcoming such challenges and ensuring successful cross-disciplinary outcomes.
Obstacles in Interdisciplinary Research
Interdisciplinary research faces significant obstacles such as communication barriers stemming from diverse terminologies and methodologies across disciplines. Differing epistemological frameworks and evaluation criteria create challenges in integrating knowledge effectively. Resource allocation and institutional support often lag behind, hindering collaboration and innovation in cross-disciplinary projects.
Real-world Examples: Cross-disciplinary vs Interdisciplinary Applications
Cross-disciplinary approaches integrate methods and insights from multiple disciplines to address complex problems, exemplified by urban planning involving architects, sociologists, and environmental scientists collaborating separately but towards a common goal. Interdisciplinary applications involve blending concepts and techniques from different fields to create new frameworks, such as bioinformatics combining biology, computer science, and statistics to develop innovative medical diagnostics. Both methodologies enhance problem-solving by leveraging diverse expertise, but interdisciplinary work fosters deeper integration leading to novel solutions.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
Cross-disciplinary approaches involve combining perspectives from different fields without integrating their methodologies, which suits projects needing broad insights without deep synthesis. Interdisciplinary methods merge theories and techniques from multiple disciplines, ideal for complex problems requiring innovative, holistic solutions. Selecting the right approach depends on project goals, desired depth of integration, and the nature of challenges being addressed.
Cross-disciplinary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com