Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) are essential tools designed to address challenging behaviors by identifying triggers and implementing effective strategies tailored to individual needs. These plans focus on promoting positive behavior changes and improving overall well-being through targeted interventions. Explore the rest of the article to discover how a well-crafted BIP can support your goals for behavior management.
Table of Comparison
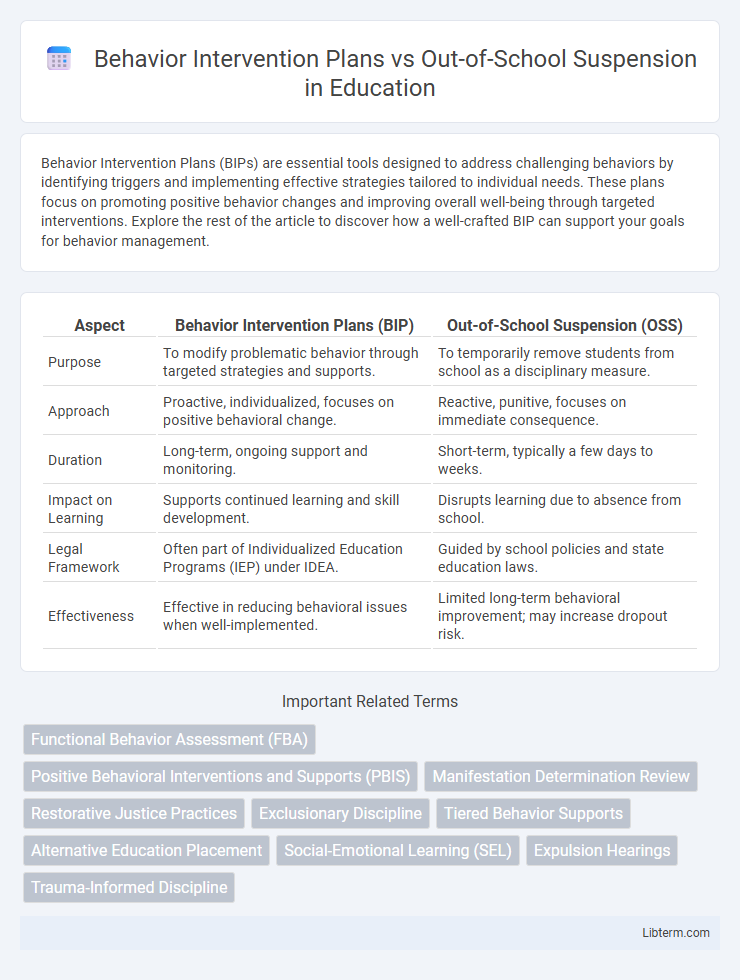
| Aspect | Behavior Intervention Plans (BIP) | Out-of-School Suspension (OSS) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To modify problematic behavior through targeted strategies and supports. | To temporarily remove students from school as a disciplinary measure. |
| Approach | Proactive, individualized, focuses on positive behavioral change. | Reactive, punitive, focuses on immediate consequence. |
| Duration | Long-term, ongoing support and monitoring. | Short-term, typically a few days to weeks. |
| Impact on Learning | Supports continued learning and skill development. | Disrupts learning due to absence from school. |
| Legal Framework | Often part of Individualized Education Programs (IEP) under IDEA. | Guided by school policies and state education laws. |
| Effectiveness | Effective in reducing behavioral issues when well-implemented. | Limited long-term behavioral improvement; may increase dropout risk. |
Understanding Behavior Intervention Plans
Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) are structured strategies designed to address and modify challenging student behaviors through positive reinforcement and targeted support, differing significantly from Out-of-School Suspension (OSS), which temporarily removes a student from the educational environment. BIPs focus on individualized assessment, setting clear behavioral goals, and implementing consistent interventions to promote long-term behavioral change and academic success. Understanding BIPs involves recognizing their role in preventing disruptive behaviors by addressing underlying causes rather than relying on exclusionary discipline like OSS.
Defining Out-of-School Suspension
Out-of-School Suspension (OSS) is a disciplinary action where a student is temporarily removed from regular school activities and classroom instruction due to behavioral violations. OSS aims to address misconduct by separating the student from the school environment, but it often results in missed instructional time and decreased academic engagement. Unlike Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs), which provide structured support and strategies to modify student behavior, OSS is primarily punitive and does not include individualized interventions.
Key Differences: Support vs. Punishment
Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) emphasize support by providing tailored strategies and positive reinforcement to address and improve a student's behavior. Out-of-School Suspension primarily serves as a punitive measure, removing the student from the learning environment without addressing underlying behavioral issues. BIPs promote long-term behavior change through proactive interventions, whereas suspensions focus on immediate consequences and deterrence.
Effects on Student Academic Performance
Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) provide structured, individualized support to address behavioral issues, promoting consistent attendance and engagement that positively impacts student academic performance. Out-of-School Suspension often results in missed instructional time, leading to gaps in learning and a decline in academic achievement. Research indicates that BIPs improve behavioral outcomes while maintaining academic continuity, whereas suspensions correlate with increased dropout rates and lower test scores.
Addressing Root Causes of Misbehavior
Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) target the root causes of student misbehavior by implementing personalized strategies that teach appropriate skills and modify environmental triggers. Out-of-School Suspension (OSS) serves as a punitive measure that removes the student from the learning environment without addressing underlying behavioral issues. Research shows that BIPs promote long-term positive behavior change by focusing on prevention and support, whereas OSS often leads to negative academic and social outcomes.
Impact on School Climate and Culture
Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) foster a positive school climate by addressing individual student needs through tailored support and proactive strategies, reducing disruptions and promoting inclusivity. Out-of-School Suspension (OSS) often leads to increased absenteeism and disengagement, negatively impacting school culture by creating gaps in learning and fostering feelings of exclusion. Implementing BIPs contributes to a supportive environment that encourages behavioral growth, whereas reliance on OSS can undermine community trust and student relationships.
Legal and Policy Considerations
Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) are mandated under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) to provide tailored support for students with disabilities, ensuring compliance with legal requirements for individualized behavioral strategies. Out-of-School Suspension (OSS) must adhere to strict procedural safeguards, including due process rights and limitations on duration, especially for students with disabilities under Section 504 and IDEA protections. School districts face legal and policy considerations to balance disciplinary actions with mandated accommodations, minimizing exclusionary practices while promoting positive behavioral outcomes.
Equity and Disproportionality Concerns
Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) offer individualized strategies that address students' specific behavioral needs, promoting equity by reducing reliance on punitive measures disproportionately affecting marginalized groups. Out-of-school suspension (OSS) disproportionately impacts students of color and those with disabilities, contributing to achievement gaps and increased dropout rates. Implementing BIPs instead of OSS supports fairer disciplinary practices, reduces racial disparities, and fosters inclusive school environments.
Collaboration with Families and Educators
Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) foster collaborative efforts between educators and families by creating tailored strategies that address student behavior within a supportive framework, ensuring consistent communication and shared goals. In contrast, out-of-school suspension often isolates students from the learning environment and reduces opportunities for family engagement and collaborative problem-solving. Effective collaboration through BIPs enhances positive behavioral outcomes by involving families in the intervention process and promoting continuity between home and school settings.
Long-Term Outcomes for Students
Behavior Intervention Plans (BIPs) provide structured strategies tailored to address underlying behavioral issues, promoting skill development and positive reinforcement that contribute to improved long-term academic and social outcomes for students. Out-of-school suspension often results in missed instructional time and increased risk of academic decline, truancy, and dropout, negatively affecting students' future educational and social success. Research indicates that BIPs support sustained behavioral improvements and better school engagement compared to the temporary and punitive nature of suspensions.
Behavior Intervention Plans Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com