A Content Management System (CMS) facilitates the creation, management, and modification of digital content without requiring specialized technical knowledge. This tool streamlines website development and content organization, improving efficiency and user experience for businesses and individuals. Explore the full article to understand how a CMS can transform your digital presence and simplify content handling.
Table of Comparison
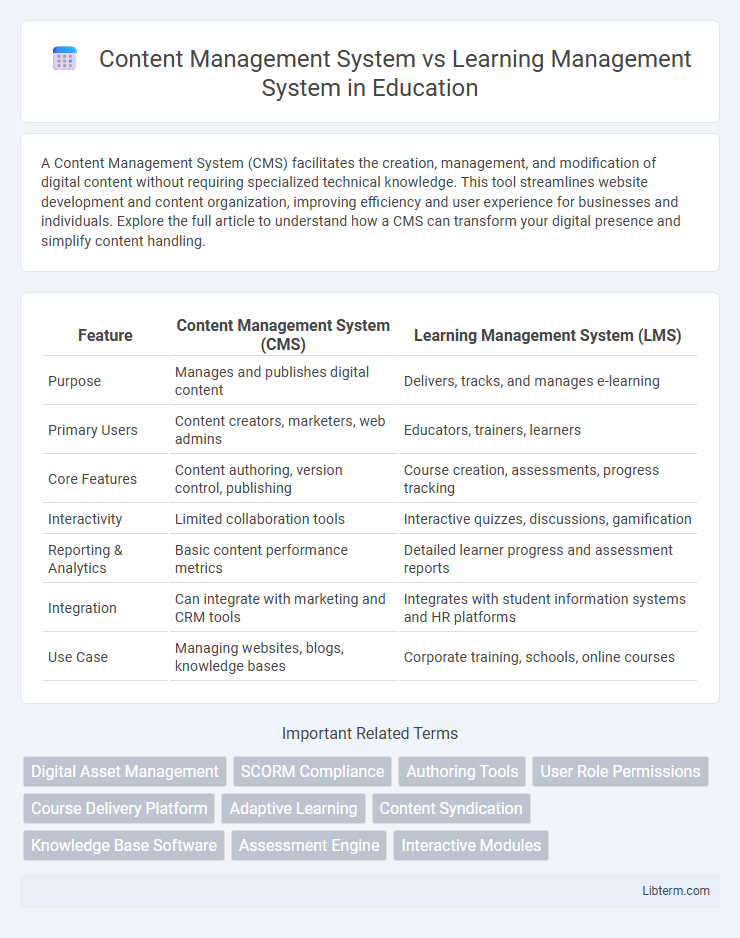
| Feature | Content Management System (CMS) | Learning Management System (LMS) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Manages and publishes digital content | Delivers, tracks, and manages e-learning |
| Primary Users | Content creators, marketers, web admins | Educators, trainers, learners |
| Core Features | Content authoring, version control, publishing | Course creation, assessments, progress tracking |
| Interactivity | Limited collaboration tools | Interactive quizzes, discussions, gamification |
| Reporting & Analytics | Basic content performance metrics | Detailed learner progress and assessment reports |
| Integration | Can integrate with marketing and CRM tools | Integrates with student information systems and HR platforms |
| Use Case | Managing websites, blogs, knowledge bases | Corporate training, schools, online courses |
Introduction to Content Management Systems (CMS)
Content Management Systems (CMS) are software platforms designed to create, manage, and modify digital content without requiring specialized technical knowledge, enabling users to efficiently publish and organize web content. Popular CMS examples include WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal, which offer customizable templates, plugin integrations, and user-friendly interfaces for managing blogs, websites, and e-commerce stores. Unlike Learning Management Systems (LMS) that focus on delivering educational content and tracking learner progress, CMS platforms primarily facilitate website content creation and workflow management across various industries.
Overview of Learning Management Systems (LMS)
Learning Management Systems (LMS) are software platforms designed specifically to deliver, track, and manage educational courses or training programs. Unlike Content Management Systems (CMS), which primarily handle website content creation and organization, LMSs focus on facilitating online learning experiences, assessments, and learner progress monitoring. Key features of LMS include course enrollment, interactive modules, certification management, and detailed analytics to optimize educational outcomes.
Key Features of CMS
Content Management Systems (CMS) primarily offer key features such as intuitive content creation and editing tools, customizable templates, and robust media management to streamline website content organization. They support workflow management, user roles, and version control, enabling efficient collaboration and content updates. Integration capabilities with SEO tools and analytics further optimize content visibility and performance across digital platforms.
Core Functions of LMS
Learning Management Systems (LMS) primarily focus on delivering, tracking, and managing educational courses and training programs, enabling features such as course enrollment, progress monitoring, assessments, and certifications. Unlike Content Management Systems (CMS) that handle general content creation and publishing, LMS platforms emphasize learner engagement, interactive content delivery, and compliance reporting. Key functions of LMS include user management, training administration, event scheduling, and detailed analytics for learning outcomes.
CMS vs LMS: Main Differences
A Content Management System (CMS) primarily facilitates the creation, management, and distribution of digital content across websites, focusing on flexible content organization and publication workflows. In contrast, a Learning Management System (LMS) is designed to deliver, track, and assess educational courses or training programs, emphasizing learner progress, quizzes, and certification management. While CMS platforms like WordPress or Drupal excel in content customization, LMS solutions such as Moodle or Blackboard prioritize user enrollment, course completion metrics, and interactive learning tools.
Use Cases: When to Choose a CMS
A Content Management System (CMS) is ideal for websites focused on dynamic content creation, such as blogs, news portals, and e-commerce platforms, where frequent updates and content organization are crucial. It excels in managing multimedia assets, SEO optimization, and user-friendly web publishing without requiring advanced technical skills. Choose a CMS when the primary goal is to deliver versatile content to a broad audience rather than structured learning experiences or educational tracking found in Learning Management Systems (LMS).
Use Cases: When to Opt for an LMS
A Learning Management System (LMS) is ideal for organizations needing to deliver, track, and assess training programs, employee development, or educational courses with structured pathways and progress monitoring. Use cases include corporate compliance training, onboarding processes, and academic institutions requiring interactive content and certification management. In contrast, Content Management Systems (CMS) primarily serve website content creation and digital publishing without integrated learner analytics or assessment features.
Integration and Scalability
A Content Management System (CMS) primarily manages digital content and supports seamless integration with various plugins, APIs, and external tools to enhance website functionality, offering high scalability for growing content needs. In contrast, a Learning Management System (LMS) is designed to deliver, track, and assess educational courses, featuring specialized integration with e-learning standards like SCORM and xAPI, while scalability focuses on accommodating increasing numbers of learners and training modules. Both systems benefit from cloud-based architectures that enable flexible scaling and robust integration capabilities tailored to their specific operational domains.
Cost and Implementation Considerations
Content Management Systems (CMS) typically have lower upfront costs and simpler implementation processes compared to Learning Management Systems (LMS), which often require specialized setup for user tracking, assessments, and compliance features. CMS platforms are designed primarily for managing digital content, making them more cost-effective for general purposes, whereas LMS solutions involve higher expenses due to integration of educational tools and support for large-scale learner management. Organizations must evaluate budget constraints and technical resources when choosing between CMS and LMS, ensuring alignment with intended training or content delivery goals.
CMS vs LMS: Which Is Right for Your Organization?
A Content Management System (CMS) is designed to create, manage, and publish digital content, making it ideal for organizations focused on website management and content delivery. In contrast, a Learning Management System (LMS) specializes in delivering, tracking, and assessing educational courses or training programs, supporting employee development and compliance training. Choosing between CMS and LMS depends on whether your organization prioritizes content dissemination or structured learning experiences for users.
Content Management System Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com