Differentiation is a fundamental concept in calculus focusing on how functions change and the rate at which these changes occur. Mastering differentiation enables you to solve problems related to slopes of curves, optimization, and motion analysis with precision. Explore the rest of this article to deepen your understanding and apply differentiation effectively.
Table of Comparison
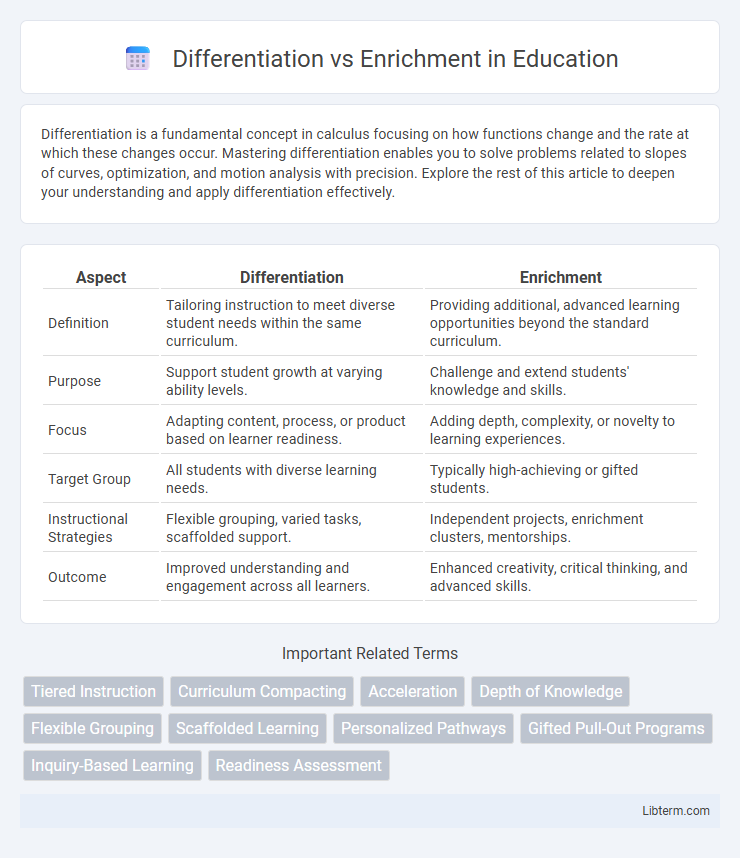
| Aspect | Differentiation | Enrichment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tailoring instruction to meet diverse student needs within the same curriculum. | Providing additional, advanced learning opportunities beyond the standard curriculum. |
| Purpose | Support student growth at varying ability levels. | Challenge and extend students' knowledge and skills. |
| Focus | Adapting content, process, or product based on learner readiness. | Adding depth, complexity, or novelty to learning experiences. |
| Target Group | All students with diverse learning needs. | Typically high-achieving or gifted students. |
| Instructional Strategies | Flexible grouping, varied tasks, scaffolded support. | Independent projects, enrichment clusters, mentorships. |
| Outcome | Improved understanding and engagement across all learners. | Enhanced creativity, critical thinking, and advanced skills. |
Understanding Differentiation: Key Concepts
Differentiation involves tailoring instruction to meet diverse student needs by modifying content, process, or product based on learners' readiness, interests, and learning profiles. It emphasizes formative assessment and flexible grouping to provide personalized support that maximizes individual growth. Understanding key concepts of differentiation enables educators to create inclusive classrooms where all students can access rigorous and meaningful learning experiences.
What is Enrichment in Education?
Enrichment in education refers to instructional strategies designed to deepen students' understanding and extend their knowledge beyond the standard curriculum. It involves providing opportunities for advanced learning, creative projects, and critical thinking activities that challenge students at their individual levels. Unlike differentiation, which adapts instruction to meet diverse learner needs within the same content area, enrichment offers additional, often exploratory, experiences to enhance student engagement and mastery.
Core Differences Between Differentiation and Enrichment
Differentiation customizes instruction based on students' learning levels, styles, and interests to meet diverse needs within the same classroom content framework. Enrichment expands learning beyond the standard curriculum by offering deeper, more complex, or broader content to enhance students' knowledge and skills. The core difference lies in differentiation adapting the approach to help all students grasp essential concepts, while enrichment provides advanced opportunities for extension and exploration.
Goals and Objectives: Differentiation vs. Enrichment
Differentiation aims to address diverse student readiness levels by modifying content, process, or product to meet varying academic needs, ensuring all learners achieve mastery of essential standards. Enrichment focuses on expanding depth and complexity beyond the standard curriculum, encouraging critical thinking and creativity without altering core objectives. Both strategies target student growth but differ in approach: differentiation prioritizes accessibility and mastery, while enrichment emphasizes intellectual challenge and extension.
Strategies for Effective Differentiation
Effective differentiation strategies include tailoring instruction to meet diverse learner needs through flexible grouping, targeted scaffolding, and tiered assignments that challenge students at varying levels of readiness. Integrating formative assessments allows teachers to adjust content, process, and product based on student progress and interests. Using learning profiles and ongoing data analysis enhances personalized learning, ensuring each student receives appropriate support and enrichment opportunities within the differentiated classroom framework.
Approaches to Implementing Enrichment Programs
Enrichment programs are implemented through strategies such as interest centers, compacted curriculum, and independent projects that extend learning beyond the standard curriculum. These approaches prioritize depth and complexity, allowing students to explore topics more thoroughly and develop critical thinking skills. Enrichment differs from differentiation by emphasizing optional, advanced learning experiences rather than modifying the core curriculum for all students.
Classroom Examples: Differentiation in Practice
Differentiation in practice involves tailoring instruction to meet diverse student needs, such as using tiered assignments where students work on tasks at varying difficulty levels based on their readiness. For example, a math teacher might provide advanced problem-solving challenges for gifted students while offering foundational exercises for those requiring reinforcement. Enrichment, contrastingly, extends learning beyond the standard curriculum, like organizing clubs or special projects that deepen subject engagement without modifying core lessons.
Real-World Applications of Enrichment
Enrichment in education enhances learning by tailoring content to students' interests and extending beyond standard curricula, fostering deeper engagement and creativity. Real-world applications of enrichment include project-based learning, mentorship programs, and access to advanced technology, which allow students to explore subjects in greater depth and connect knowledge to practical scenarios. These strategies promote critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and lifelong learning habits essential for success in diverse professional fields.
Impact on Student Learning Outcomes
Differentiation delivers tailored instruction based on individual students' learning styles, readiness levels, and interests, significantly improving engagement and academic achievement by addressing diverse needs within the classroom. Enrichment offers advanced, supplementary activities that deepen knowledge and skills for high-achieving students, fostering critical thinking and creativity without altering core curriculum standards. Both strategies positively impact student learning outcomes by promoting personalized growth, but differentiation emphasizes equity by supporting all learners, whereas enrichment targets enhancement for those ready to move beyond grade-level expectations.
Choosing the Right Approach: Differentiation, Enrichment, or Both?
Choosing the right approach between differentiation and enrichment depends on the specific needs of learners and educational goals. Differentiation tailors instruction to diverse student readiness levels, interests, and learning profiles by modifying content, process, or product. Enrichment enhances the curriculum with deeper, more complex activities that extend learning beyond the standard expectations, making combining both approaches effective for addressing varied learning styles and fostering advanced critical thinking skills.
Differentiation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com