Project-Based Learning engages students by immersing them in real-world challenges that develop critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. This hands-on approach promotes deep understanding by integrating knowledge across subjects and encouraging creativity. Explore the rest of the article to discover how Project-Based Learning can transform Your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
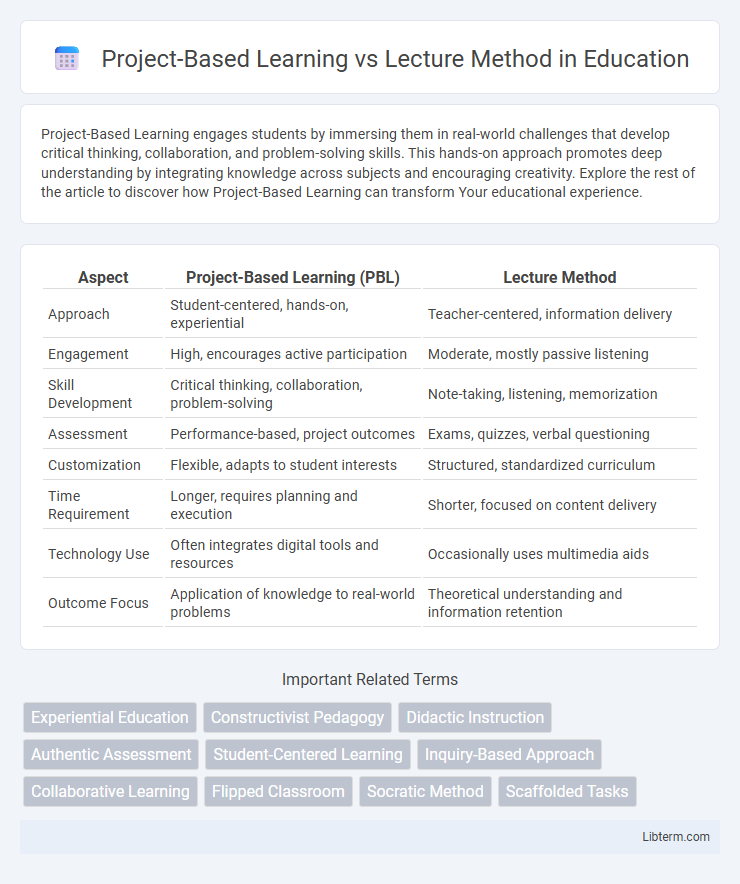
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Lecture Method |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Student-centered, hands-on, experiential | Teacher-centered, information delivery |
| Engagement | High, encourages active participation | Moderate, mostly passive listening |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, collaboration, problem-solving | Note-taking, listening, memorization |
| Assessment | Performance-based, project outcomes | Exams, quizzes, verbal questioning |
| Customization | Flexible, adapts to student interests | Structured, standardized curriculum |
| Time Requirement | Longer, requires planning and execution | Shorter, focused on content delivery |
| Technology Use | Often integrates digital tools and resources | Occasionally uses multimedia aids |
| Outcome Focus | Application of knowledge to real-world problems | Theoretical understanding and information retention |
Introduction to Project-Based Learning and Lecture Method
Project-Based Learning (PBL) engages students in hands-on projects that promote critical thinking, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving, enabling deeper understanding and retention of subject matter. The Lecture Method delivers structured content through direct instruction, facilitating efficient coverage of extensive material but often limiting interactive student engagement. Integrating PBL fosters active learning environments, whereas the Lecture Method remains effective for foundational knowledge dissemination.
Core Principles of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) centers on student-driven inquiry, real-world problem-solving, and collaboration, fostering deeper engagement and critical thinking. Unlike the traditional Lecture Method, which relies on passive information delivery, PBL emphasizes active learning through projects that integrate cross-disciplinary knowledge and authentic assessment. Core principles include sustained inquiry, student autonomy, reflection, and producing a meaningful artifact or presentation that demonstrates mastery of the subject matter.
Key Features of the Traditional Lecture Method
The traditional lecture method emphasizes a teacher-centered approach where information is delivered verbally to a large group of students, focusing on passive reception of knowledge. Key features include structured content presentation, limited student interaction, and assessment primarily through exams and quizzes to measure retention. This method supports efficient coverage of extensive curricular material but may restrict active engagement and critical thinking development.
Student Engagement: PBL vs Lecture
Project-Based Learning (PBL) significantly increases student engagement by promoting active participation, critical thinking, and collaboration through hands-on projects. In contrast, the Lecture Method often results in passive learning, where students receive information but have limited interaction or opportunities for applying knowledge. Research shows that PBL improves motivation and retention, fostering deeper understanding compared to traditional lecture-based instruction.
Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Project-Based Learning enhances critical thinking by engaging students in real-world problem solving and collaborative inquiry, promoting analysis, evaluation, and synthesis of information. The Lecture Method primarily delivers information passively, limiting opportunities for active reasoning and problem-solving practice. Research shows that students in Project-Based Learning environments demonstrate higher levels of critical thinking skills compared to those in traditional lecture settings.
Assessment Methods in Both Approaches
Project-Based Learning employs formative and performance-based assessments, emphasizing real-world application, collaboration, and critical thinking skills through continuous feedback and self-assessment. Lecture Method primarily uses summative assessments such as quizzes, exams, and standardized tests to evaluate knowledge retention and comprehension of presented material. Both approaches benefit from rubric-based evaluations, but Project-Based Learning assessments prioritize creativity and problem-solving, whereas Lecture Method assessments focus on recall and understanding of facts.
Teacher’s Role in Each Learning Model
In project-based learning, the teacher acts as a facilitator and guide, supporting student inquiry and collaboration while fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. In contrast, the lecture method positions the teacher as the primary knowledge transmitter, delivering structured content and controlling the classroom environment. This shift in the teacher's role influences student engagement, with project-based learning promoting active participation and the lecture method emphasizing passive absorption of information.
Real-World Application and Knowledge Retention
Project-Based Learning enhances real-world application by engaging students in hands-on tasks that mimic professional challenges, thereby fostering deeper understanding and practical skills. This method improves knowledge retention through active participation and continuous problem-solving, which reinforce memory consolidation. In contrast, the Lecture Method often limits students to passive information reception, resulting in lower engagement and reduced long-term retention of concepts.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Methods
Project-Based Learning faces challenges including time-intensive planning, uneven student participation, and difficulties in assessing individual contributions accurately. The Lecture Method often results in passive learning, limited student engagement, and insufficient accommodation of diverse learning styles, which can hinder knowledge retention. Both methods require careful adaptation to address these limitations and optimize educational outcomes.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right teaching approach depends on factors such as learning objectives, student engagement levels, and subject matter complexity. Project-Based Learning (PBL) excels in cultivating critical thinking, problem-solving skills, and real-world application, making it ideal for disciplines requiring practical experience. Conversely, the Lecture Method efficiently delivers foundational knowledge and accommodates large groups, best suited for theoretical subjects and content-heavy curricula.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com