Formative assessment is a vital educational strategy used to monitor student learning and provide ongoing feedback that helps improve teaching and student performance. It includes various techniques such as quizzes, observations, and discussions designed to identify learning gaps and tailor instruction accordingly. Explore the rest of this article to discover effective formative assessment methods and how they can enhance Your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
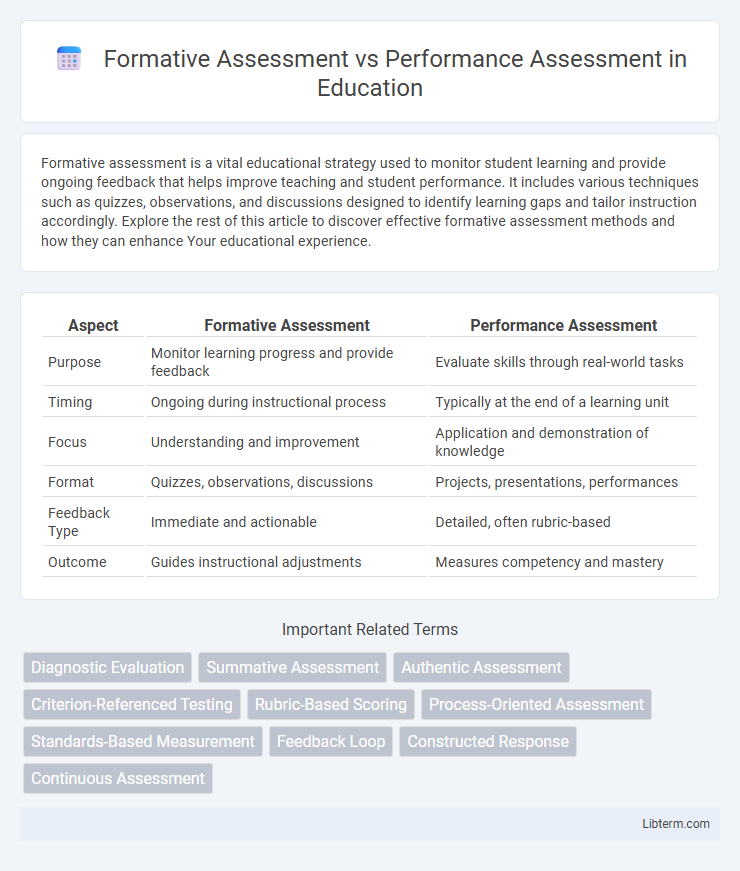
| Aspect | Formative Assessment | Performance Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Monitor learning progress and provide feedback | Evaluate skills through real-world tasks |
| Timing | Ongoing during instructional process | Typically at the end of a learning unit |
| Focus | Understanding and improvement | Application and demonstration of knowledge |
| Format | Quizzes, observations, discussions | Projects, presentations, performances |
| Feedback Type | Immediate and actionable | Detailed, often rubric-based |
| Outcome | Guides instructional adjustments | Measures competency and mastery |
Introduction to Formative and Performance Assessment
Formative assessment involves continuous evaluation during the learning process to provide feedback that guides student improvement and instructional adjustments. Performance assessment requires students to demonstrate their knowledge and skills through real-world tasks or projects, emphasizing application over rote memorization. Both types support diverse learning objectives, with formative assessments fostering ongoing development and performance assessments measuring practical competence.
Defining Formative Assessment
Formative assessment is an ongoing process used by educators to monitor student learning and provide continuous feedback for improvement. It involves low-stakes activities such as quizzes, discussions, and observations designed to identify learning gaps and guide instructional adjustments. Unlike performance assessments, which evaluate mastery through complex tasks, formative assessment emphasizes real-time data to enhance teaching and learning outcomes.
Understanding Performance Assessment
Performance assessment evaluates students' ability to apply skills and knowledge in real-world or practical tasks, emphasizing critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity. Unlike formative assessment, which provides ongoing feedback to support learning, performance assessment measures competence through projects, presentations, or demonstrations. This type of assessment offers deep insights into students' mastery and readiness for real-life challenges.
Key Differences Between Formative and Performance Assessments
Formative assessment focuses on ongoing student feedback during the learning process, enabling educators to identify areas for improvement and adjust instruction accordingly. Performance assessment evaluates students' ability to apply knowledge and skills through real-world tasks or projects, emphasizing demonstration over traditional testing. Key differences include the timing of assessment, purpose--formative for learning enhancement and performance for skill demonstration--and the methods used, with formative assessments being informal and performance assessments typically more structured and summative.
Goals and Purposes of Each Assessment Type
Formative assessment aims to monitor student learning progress and provide ongoing feedback to improve instructional methods and learner understanding, emphasizing skill development and knowledge acquisition during the learning process. Performance assessment evaluates students' ability to apply skills and knowledge in real-world or simulated tasks, focusing on authentic demonstration of competencies and higher-order thinking. Both assessment types serve distinct goals: formative assessment targets continuous improvement and learning enhancement, while performance assessment measures practical application and mastery of complex skills.
Methods and Examples of Formative Assessment
Formative assessment methods include quizzes, observations, discussions, and feedback sessions designed to monitor student learning and inform instruction in real time. Examples of formative assessments are exit tickets, think-pair-share activities, and peer reviews, which help identify areas for improvement before final evaluations. These techniques promote continuous learning by providing immediate insights into student understanding and guiding targeted teaching strategies.
Methods and Examples of Performance Assessment
Performance assessment methods include project presentations, portfolios, experiments, and simulations that require students to apply knowledge in real-world or practical contexts. Examples of performance assessment are science lab experiments where students demonstrate procedures and results, oral presentations evaluating communication skills, and art portfolios showcasing creative process and final work. These assessments emphasize active learning, critical thinking, and the demonstration of skills beyond traditional tests.
Advantages and Limitations of Formative Assessment
Formative assessment offers advantages such as real-time feedback, enabling educators to identify student learning gaps and adjust instruction for improved outcomes. It promotes continuous learning and motivation by encouraging student reflection and self-assessment, fostering deeper understanding. However, limitations include potential time constraints for thorough implementation and the challenge of maintaining consistency and objectivity in informal evaluations.
Benefits and Challenges of Performance Assessment
Performance assessment offers the benefit of evaluating students' practical skills and real-world application of knowledge, providing a more comprehensive understanding of their competencies. Challenges include the time-consuming nature of designing and grading authentic tasks, along with potential subjectivity in scoring. Despite these obstacles, performance assessments enhance critical thinking and problem-solving abilities by requiring active demonstration rather than passive recall.
Choosing the Right Assessment for Effective Learning
Formative assessment provides ongoing feedback during the learning process, enabling educators to identify student strengths and areas for improvement in real time, which supports adaptive teaching strategies. Performance assessment evaluates students' ability to apply skills and knowledge through real-world tasks, offering a practical measure of competency and deeper understanding. Choosing the right assessment depends on learning objectives: formative assessment is ideal for guiding instruction and fostering growth, while performance assessment excels at measuring applied skills and authentic learning outcomes.
Formative Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com