Experiential learning engages you in hands-on activities that enhance understanding through real-world experience, making concepts more memorable and applicable. This approach fosters critical thinking, problem-solving, and personal growth by encouraging active participation rather than passive observation. Discover how experiential learning can transform your educational journey in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
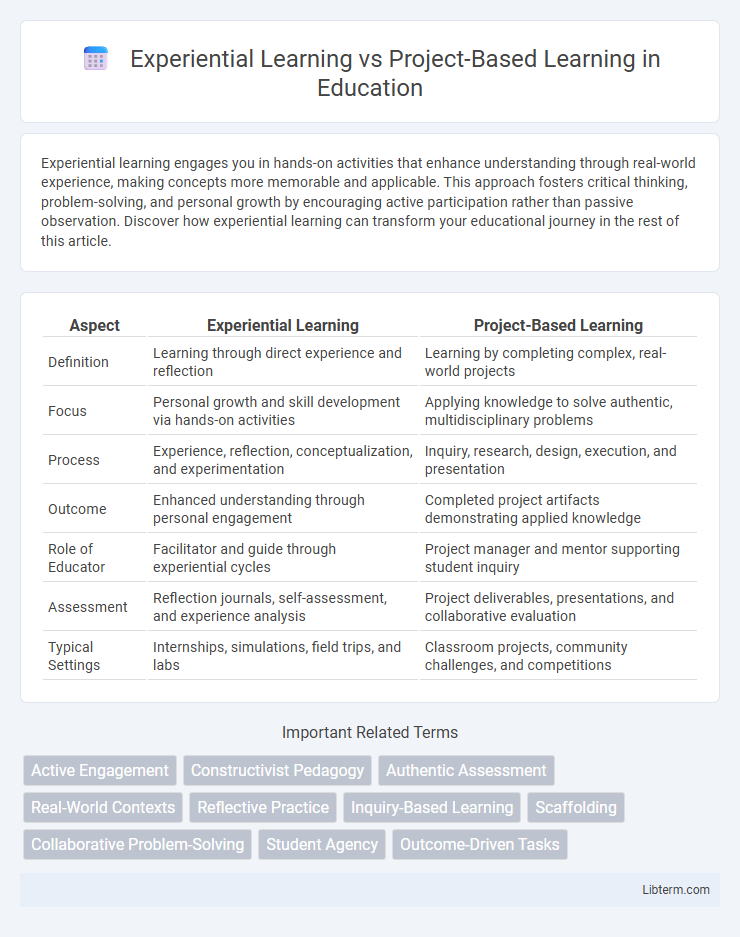
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Project-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection | Learning by completing complex, real-world projects |
| Focus | Personal growth and skill development via hands-on activities | Applying knowledge to solve authentic, multidisciplinary problems |
| Process | Experience, reflection, conceptualization, and experimentation | Inquiry, research, design, execution, and presentation |
| Outcome | Enhanced understanding through personal engagement | Completed project artifacts demonstrating applied knowledge |
| Role of Educator | Facilitator and guide through experiential cycles | Project manager and mentor supporting student inquiry |
| Assessment | Reflection journals, self-assessment, and experience analysis | Project deliverables, presentations, and collaborative evaluation |
| Typical Settings | Internships, simulations, field trips, and labs | Classroom projects, community challenges, and competitions |
Introduction to Experiential Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes acquiring knowledge through direct experience and reflection, fostering deeper understanding and skill application. This approach engages learners in hands-on activities that simulate real-world scenarios, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Contrasting with project-based learning, experiential learning prioritizes immersive experiences as the primary method for knowledge construction.
Understanding Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) emphasizes hands-on, real-world projects that develop critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills through sustained inquiry. It requires students to engage deeply with content by creating tangible outcomes, such as presentations, models, or reports, reflecting authentic challenges. Unlike experiential learning, which may include varied activities, PBL is structured around a central project that integrates multiple disciplines and standards to promote applied knowledge.
Key Principles of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning centers on the principle of learning through direct experience, emphasizing active participation and reflection to deepen understanding. It involves a continuous cycle of doing, observing, and thinking, which enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Key elements include concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation, distinguishing it from project-based learning's focus on completing specific projects.
Core Components of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) centers on real-world challenges, collaboration, and critical thinking, leveraging student-driven inquiry to produce tangible outcomes. Core components include a driving question or problem, sustained inquiry, authentic public presentations, and reflection, ensuring deeper engagement and knowledge retention. This method differs from Experiential Learning by emphasizing a structured, outcome-oriented approach that integrates rigorous academic standards into extended projects.
Differences Between Experiential and Project-Based Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes acquiring knowledge through direct experience and reflection, often involving real-world tasks that engage learners actively in the learning process. Project-based learning centers on completing a specific project over a period, integrating multiple skills and knowledge areas to solve complex problems or create tangible outcomes. The primary difference lies in experiential learning's broader focus on personal growth and skill development through experience, while project-based learning is structured around delivering a final product or solution linked to curriculum objectives.
Benefits of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning enhances knowledge retention by engaging learners in hands-on activities that stimulate critical thinking and problem-solving skills, fostering deeper understanding compared to traditional methods. It promotes adaptability and real-world application by immersing individuals in authentic scenarios, preparing them for complex challenges in professional environments. This approach also boosts learner motivation and confidence through active participation, making education more personalized and impactful.
Advantages of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) promotes deeper understanding by engaging students in real-world projects that develop critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. It fosters intrinsic motivation through hands-on experiences and meaningful outcomes directly linked to curriculum standards. PBL also enhances retention by allowing learners to apply knowledge in practical contexts, bridging theory and practice effectively.
Challenges in Implementing Both Approaches
Implementing experiential learning faces challenges such as ensuring authentic, real-world experiences that align with learning objectives and providing sufficient guidance while promoting student autonomy. Project-based learning struggles with maintaining student motivation throughout extended timelines, balancing scope and resources, and assessing individual contributions within group projects. Both approaches require significant instructor training and institutional support to effectively integrate hands-on, student-centered methodologies into existing curricula.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Experiential Learning emphasizes direct engagement with real-world scenarios to foster deep understanding, demonstrated through immersive case studies such as medical simulations and business role-plays. Project-Based Learning centers on solving complex, authentic problems like designing sustainable urban plans, promoting collaboration and critical thinking. Both approaches leverage practical, contextual experiences to enhance knowledge retention and skill application across disciplines.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Educational Goals
Experiential Learning emphasizes direct experience and reflection, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills through hands-on activities. Project-Based Learning centers on completing complex projects over time, promoting collaboration, creativity, and application of knowledge to real-world problems. Choosing the right approach depends on educational goals such as developing practical skills versus driving innovation and teamwork in subject-specific contexts.
Experiential Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com