Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) is a proactive framework designed to improve school climate by teaching and reinforcing positive behaviors. It emphasizes consistent expectations, data-driven decision making, and collaborative efforts to reduce disciplinary issues and enhance student engagement. Discover how PBIS can transform your educational environment and support student success in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
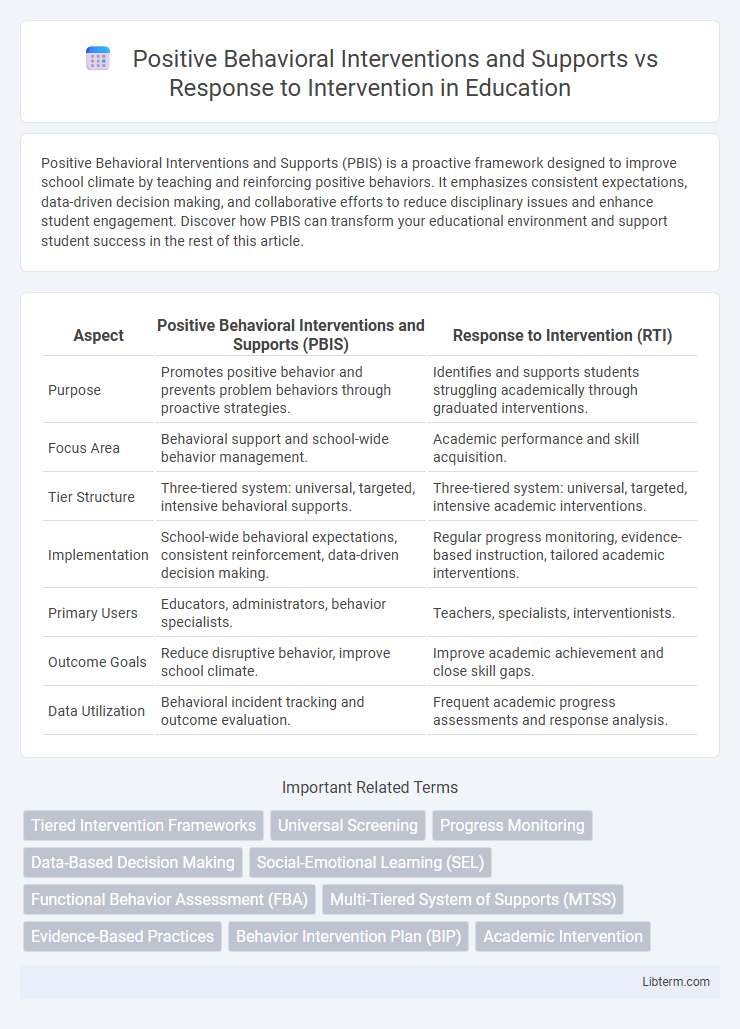
| Aspect | Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) | Response to Intervention (RTI) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Promotes positive behavior and prevents problem behaviors through proactive strategies. | Identifies and supports students struggling academically through graduated interventions. |
| Focus Area | Behavioral support and school-wide behavior management. | Academic performance and skill acquisition. |
| Tier Structure | Three-tiered system: universal, targeted, intensive behavioral supports. | Three-tiered system: universal, targeted, intensive academic interventions. |
| Implementation | School-wide behavioral expectations, consistent reinforcement, data-driven decision making. | Regular progress monitoring, evidence-based instruction, tailored academic interventions. |
| Primary Users | Educators, administrators, behavior specialists. | Teachers, specialists, interventionists. |
| Outcome Goals | Reduce disruptive behavior, improve school climate. | Improve academic achievement and close skill gaps. |
| Data Utilization | Behavioral incident tracking and outcome evaluation. | Frequent academic progress assessments and response analysis. |
Understanding Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS)
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) is a proactive framework that establishes consistent behavioral expectations and rewards across educational settings to promote positive student behavior and enhance learning environments. PBIS relies on data-driven decision making and tiered support systems to prevent and address behavioral issues before they escalate, contrasting with traditional reactive approaches. Its emphasis on teaching social skills and reinforcing positive conduct aligns with broader goals of improving school climate and reducing disciplinary referrals.
Exploring Response to Intervention (RTI) Framework
Response to Intervention (RTI) framework is a multi-tiered approach designed to identify and support students with learning and behavioral challenges through targeted interventions and continuous progress monitoring. It emphasizes early detection and data-driven decision-making to provide increasingly intensive levels of support tailored to individual student needs. RTI integrates assessment and instruction, promoting collaboration among educators to prevent academic failure and improve student outcomes.
Core Principles of PBIS
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) centers on proactive strategies to enhance social, emotional, and academic outcomes by establishing clear expectations, teaching appropriate behaviors, and consistently reinforcing positive conduct. It emphasizes data-driven decision-making, tiered support systems, and school-wide implementation to create a positive and inclusive learning environment. PBIS prioritizes prevention and early intervention, contrasting Response to Intervention (RTI), which primarily targets academic challenges through identifying and supporting struggling students.
Essential Components of RTI
Response to Intervention (RTI) consists of essential components including multiple tiers of support, data-based decision making, and progress monitoring to identify and address students' academic and behavioral needs. RTI emphasizes systematic screening, evidence-based interventions, and continuous evaluation to tailor instruction and prevent learning failure. Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) complements RTI by focusing more specifically on proactive behavioral strategies and creating a positive school climate.
PBIS vs RTI: Key Differences
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) focuses on promoting positive behavior through proactive strategies and system-wide supports, while Response to Intervention (RTI) emphasizes early identification and support for academic difficulties using a tiered approach. PBIS targets behavior management in educational settings by establishing clear expectations and reinforcing positive actions, whereas RTI provides targeted instructional interventions based on student performance data. PBIS is primarily behavior-centered, and RTI integrates academic and behavioral assessments to guide intervention decisions.
PBIS vs RTI: Areas of Overlap
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) and Response to Intervention (RTI) share a tiered framework aimed at providing early and systematic support to students, emphasizing data-driven decision-making to monitor progress and adjust interventions. Both models prioritize proactive strategies to improve student outcomes, collaborating across educators, families, and specialists to address academic and behavioral challenges. Integration of PBIS and RTI often enhances school-wide systems by combining behavioral supports with targeted academic interventions, promoting a comprehensive approach to student success.
Data-Driven Decision Making in PBIS and RTI
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) and Response to Intervention (RTI) both utilize data-driven decision making to enhance student outcomes through systematic monitoring of behavioral and academic performance. In PBIS, teams analyze behavioral data such as office discipline referrals and functional behavior assessments to implement tiered interventions tailored to student needs. RTI relies on academic progress monitoring data, including curriculum-based measurements and benchmark assessments, to guide instructional adjustments and provide targeted support within a multi-tiered framework.
School-Wide Implementation Strategies
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) utilize a tiered framework emphasizing proactive behavior management through school-wide expectations, explicit teaching, and data-driven decision making to foster positive student behavior. Response to Intervention (RTI) implements a multi-tiered system targeting academic support with frequent progress monitoring and individualized interventions to address learning difficulties. Successful school-wide implementation of PBIS focuses on consistent reinforcement and staff training, whereas RTI requires structured academic assessments and collaboration among educators to ensure timely student support.
Measuring Effectiveness: PBIS and RTI Outcomes
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) demonstrates effectiveness through significant reductions in school disciplinary incidents and improvements in student social behavior, measured via discipline referrals and behavior rating scales. Response to Intervention (RTI) effectiveness is assessed by student academic progress using benchmark assessments and progress monitoring tools, with success indicated by increased proficiency in reading and math scores. Both PBIS and RTI rely on data-driven decision making, but PBIS outcomes focus primarily on behavioral improvements while RTI targets academic achievement gains.
Integrating PBIS and RTI for Holistic Student Support
Integrating Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) with Response to Intervention (RTI) creates a comprehensive framework addressing both academic and behavioral needs of students, fostering a supportive school environment. This combined approach leverages data-driven instruction, tiered support systems, and early intervention strategies to enhance student engagement and success. Schools implementing integrated PBIS and RTI benefit from cohesive team collaboration, consistent progress monitoring, and improved outcomes in both behavior management and academic achievement.
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com