Apprenticeships offer hands-on training that bridges the gap between education and career, enabling you to gain valuable industry experience while earning. This practical approach boosts your skills and enhances employability in competitive job markets. Explore the full article to discover how an apprenticeship can transform your professional journey.
Table of Comparison
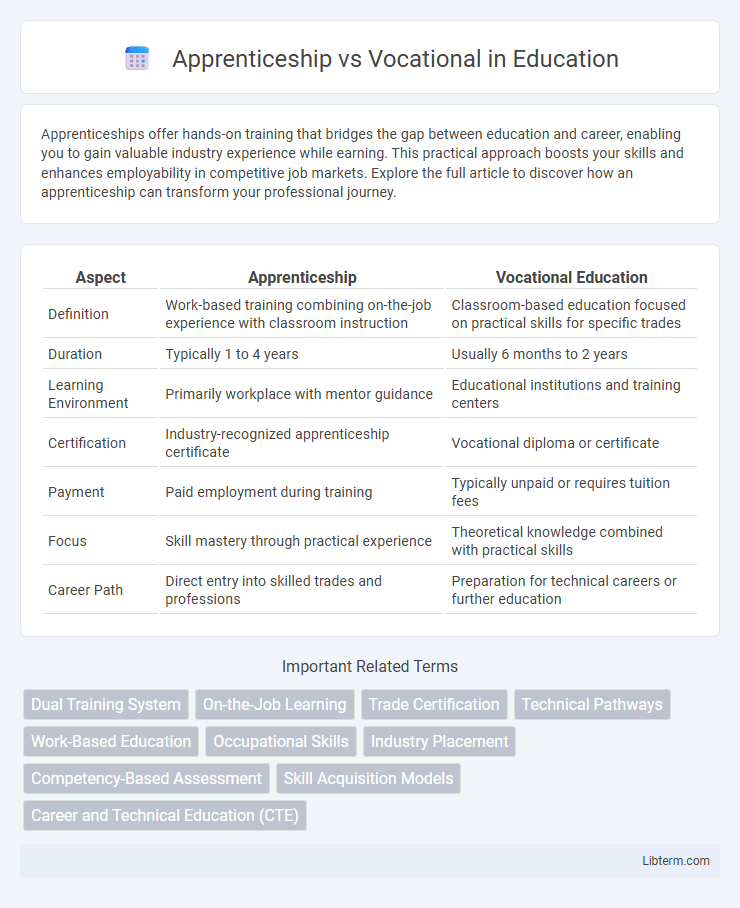
| Aspect | Apprenticeship | Vocational Education |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Work-based training combining on-the-job experience with classroom instruction | Classroom-based education focused on practical skills for specific trades |
| Duration | Typically 1 to 4 years | Usually 6 months to 2 years |
| Learning Environment | Primarily workplace with mentor guidance | Educational institutions and training centers |
| Certification | Industry-recognized apprenticeship certificate | Vocational diploma or certificate |
| Payment | Paid employment during training | Typically unpaid or requires tuition fees |
| Focus | Skill mastery through practical experience | Theoretical knowledge combined with practical skills |
| Career Path | Direct entry into skilled trades and professions | Preparation for technical careers or further education |
Understanding Apprenticeship Programs
Apprenticeship programs offer hands-on learning by combining paid work experience with classroom instruction, enabling apprentices to acquire industry-specific skills and certifications. These programs often involve a structured partnership between employers, educational institutions, and regulatory bodies to ensure comprehensive training aligned with labor market needs. Unlike traditional vocational training, apprenticeships emphasize real-world application and direct mentorship within a professional environment.
Defining Vocational Education
Vocational education provides specialized training focused on practical skills and knowledge required for specific trades or occupations, contrasting with apprenticeships that combine on-the-job training with classroom instruction. This form of education emphasizes career readiness and industry-specific competencies to prepare students for immediate employment in technical fields such as healthcare, engineering, or information technology. Vocational programs are designed to align with labor market demands, offering certifications and diplomas that validate professional expertise and enhance employability.
Key Differences Between Apprenticeship and Vocational Training
Apprenticeship combines paid, on-the-job training with classroom instruction, emphasizing hands-on experience in a real work environment. Vocational training primarily occurs in educational institutions, focusing on developing specific technical skills without guaranteed employment during the learning period. Apprenticeships often result in industry-recognized certifications and direct job placements, while vocational programs may require additional steps for employment entry.
Structure and Curriculum Comparison
Apprenticeship programs typically combine on-the-job training with classroom instruction, emphasizing hands-on experience under the supervision of skilled professionals. Vocational education usually takes place in a classroom setting, focusing on theoretical knowledge and technical skills relevant to specific trades or industries. The apprenticeship curriculum is structured around practical skill mastery over a longer period, while vocational courses often have a fixed timeframe with defined modules aimed at quick entry into the workforce.
Duration and Commitment Required
Apprenticeships typically require a longer commitment, ranging from one to six years, combining on-the-job training with classroom instruction, while vocational programs generally last from a few months to two years, focusing primarily on classroom-based skill development. Apprenticeships demand consistent work hours alongside training, often involving full-time employment with an employer, whereas vocational courses offer more flexible schedules suited for part-time learning. The extended duration and hands-on experience of apprenticeships result in deeper industry immersion compared to the shorter, skills-focused training of vocational programs.
Certifications and Qualifications Gained
Apprenticeships offer certifications that combine on-the-job training with industry-recognized qualifications, often resulting in nationally accredited diplomas or certificates of competence. Vocational education primarily provides formal qualifications through classroom instruction, such as diplomas or certificates aligned with specific trades or technical fields. Both pathways emphasize practical skill development, but apprenticeships typically lead to certifications directly linked to employer standards and immediate workforce integration.
Career Paths and Job Opportunities
Apprenticeships provide hands-on training in specific trades such as electrical work, plumbing, and manufacturing, often leading directly to skilled labor positions with higher earning potential and job security. Vocational programs cover a broader range of career paths including healthcare, information technology, and automotive technology, offering certifications that qualify graduates for various technical roles and entry-level jobs. Both pathways enhance employability, but apprenticeships tend to emphasize on-the-job experience while vocational training focuses on classroom-based technical education.
Hands-On Experience vs Theoretical Learning
Apprenticeship programs provide extensive hands-on experience by immersing learners in real-world work environments, allowing them to apply practical skills directly on the job. Vocational education emphasizes theoretical learning through structured classroom instruction and technical coursework, building foundational knowledge across various trades. Combining apprenticeship with vocational training often results in a balanced skill set, optimizing both practical competence and theoretical understanding.
Cost and Financial Considerations
Apprenticeships often offer a cost-effective pathway as trainees typically earn a wage while gaining hands-on experience, reducing the financial burden compared to vocational training which usually requires upfront tuition fees. Vocational programs may involve costs for materials, registration, and certification, potentially totaling several thousand dollars depending on the trade. Financial aid, scholarships, and employer sponsorships are more commonly available for apprenticeships, making them an attractive option for individuals aiming to minimize education-related debt.
Choosing the Right Path: Apprenticeship or Vocational?
Choosing between apprenticeship and vocational training depends on career goals and learning preferences. Apprenticeships offer hands-on experience by combining paid work with on-the-job training, ideal for those seeking practical skills in trades like electrical work or plumbing. Vocational programs provide structured, classroom-based education focusing on specific industries, making them suitable for careers in healthcare, technology, or culinary arts.
Apprenticeship Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com