Transmittance measures how much light or radiation passes through a material, indicating its transparency or opacity. It plays a crucial role in fields like optics, atmospheric science, and material engineering by influencing how substances interact with light. Explore the rest of the article to understand how transmittance affects your applications and technologies.
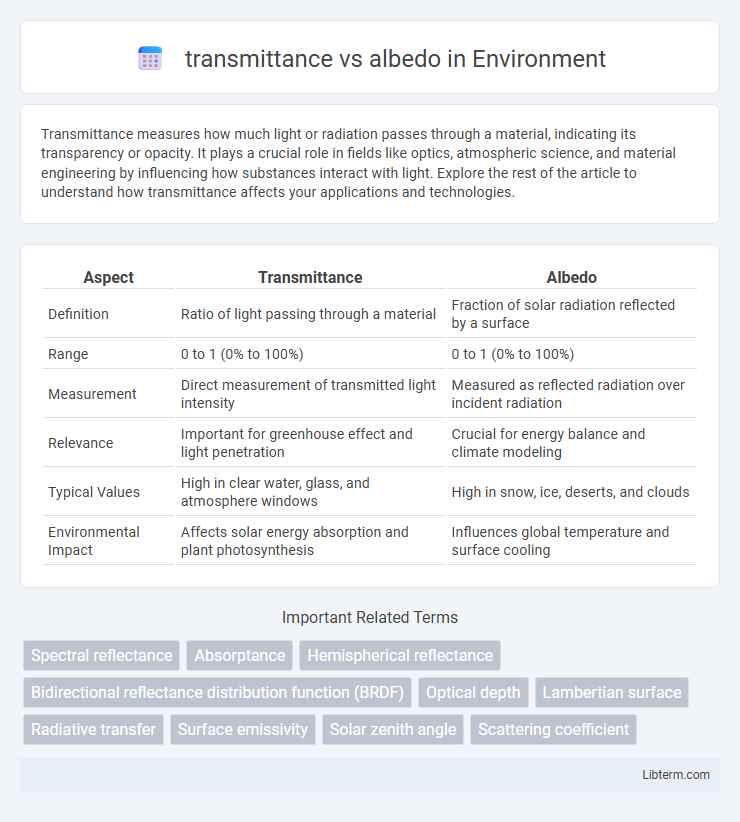
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Transmittance | Albedo |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ratio of light passing through a material | Fraction of solar radiation reflected by a surface |
| Range | 0 to 1 (0% to 100%) | 0 to 1 (0% to 100%) |
| Measurement | Direct measurement of transmitted light intensity | Measured as reflected radiation over incident radiation |
| Relevance | Important for greenhouse effect and light penetration | Crucial for energy balance and climate modeling |
| Typical Values | High in clear water, glass, and atmosphere windows | High in snow, ice, deserts, and clouds |
| Environmental Impact | Affects solar energy absorption and plant photosynthesis | Influences global temperature and surface cooling |
Introduction to Transmittance and Albedo
Transmittance refers to the fraction of incident light that passes through a material, influencing how much radiation penetrates surfaces such as glass or water. Albedo measures the reflectivity of a surface, indicating the proportion of incoming solar radiation reflected back into the atmosphere by surfaces like ice, soil, or vegetation. Both transmittance and albedo are critical parameters in climatology, remote sensing, and energy balance studies, affecting models of light interaction with Earth's surface and atmosphere.
Defining Transmittance: Key Concepts
Transmittance measures the fraction of incident light that passes through a material, quantified as the ratio of transmitted irradiance to the incident irradiance. It is a crucial parameter in optical and atmospheric sciences, influencing how light interacts with surfaces and layers, such as glass or atmospheric gases. Unlike albedo, which represents the reflectivity of a surface, transmittance specifically describes light transmission through a medium, impacting energy transfer and optical clarity.
Understanding Albedo in Environmental Science
Albedo measures the fraction of solar energy reflected by a surface, critical for understanding Earth's energy balance and climate patterns. Transmittance quantifies the amount of light passing through a medium, influencing how radiation interacts with atmospheric layers and vegetation. High albedo surfaces like ice and snow reflect most sunlight, reducing heat absorption, whereas low albedo surfaces absorb more energy, affecting global temperature and environmental processes.
Differences Between Transmittance and Albedo
Transmittance measures the fraction of light that passes through a material, while albedo quantifies the ratio of reflected radiation from a surface to the incident radiation. Transmittance values range from 0 to 1, indicating transparency levels, whereas albedo values indicate reflectivity and typically vary between 0 (no reflection) and 1 (total reflection). Unlike albedo, which directly impacts surface energy balance, transmittance is crucial in applications involving optical properties and light penetration through materials.
Measurement Methods for Transmittance
Measurement methods for transmittance primarily involve spectrophotometry, where a beam of light passes through a sample and the transmitted intensity is recorded to calculate the transmittance ratio. Integrating spheres are often used to measure diffuse transmittance by capturing scattered light that passes through the material. Precise calibration with known reference standards is essential to ensure accurate transmittance values, differentiating them from albedo, which measures reflected rather than transmitted radiation.
Techniques for Calculating Albedo
Techniques for calculating albedo often rely on accurately measuring transmittance alongside reflectance to determine the fraction of solar radiation reflected by surfaces. Instruments like spectroradiometers and pyranometers capture transmitted and reflected light, enabling precise albedo calculations through radiative transfer models. Advanced methods incorporate satellite data and radiative flux measurements to enhance albedo estimation for diverse environmental applications.
Role of Transmittance in Atmospheric Studies
Transmittance measures the fraction of solar radiation passing through the atmosphere without being absorbed or scattered, directly influencing the Earth's energy balance. It plays a critical role in atmospheric studies by determining how much sunlight reaches the surface, affecting surface temperature and climate models. Accurate transmittance data improves predictions of radiative forcing, helping to differentiate between the effects of clouds, aerosols, and greenhouse gases on albedo and overall atmospheric reflectivity.
Impact of Albedo on Climate and Energy Balance
Albedo significantly influences Earth's energy balance by determining the proportion of solar radiation reflected back into space, with higher albedo surfaces like ice and snow reducing heat absorption. Transmittance, the measure of solar energy passing through atmospheric layers, interacts with albedo by affecting how much radiation reaches the surface to be reflected or absorbed. Variations in albedo due to land use changes and melting ice sheets can alter global temperature patterns, impacting climate systems and energy distribution in the atmosphere.
Practical Applications: When to Use Transmittance vs Albedo
Transmittance measures the fraction of light passing through a material, critical in applications like window design, greenhouse efficiency, and optical sensors where light penetration impacts performance. Albedo quantifies surface reflectivity, crucial for climate modeling, solar panel placement, and urban heat management where surface energy balance determines effectiveness. Use transmittance for materials' transparency assessment and albedo for evaluating surface reflectivity and its environmental or energy implications.
Summary: Choosing Between Transmittance and Albedo in Research
Transmittance measures the fraction of light passing through a material, crucial in optics and material science for analyzing transparency and energy flow. Albedo quantifies surface reflectivity, primarily used in climate studies and environmental research to assess energy absorption and reflection. Selecting between transmittance and albedo depends on the research focus: transmittance suits studies on light penetration through mediums, while albedo is ideal for investigations involving surface radiation and energy balance.
transmittance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com