Pioneer strategy involves being the first to enter a new market or industry, capitalizing on early mover advantages to establish strong brand recognition and customer loyalty. This approach can lead to significant market share and long-term profitability but requires substantial investment in innovation and risk management. Discover how adopting a pioneer strategy could transform your business by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
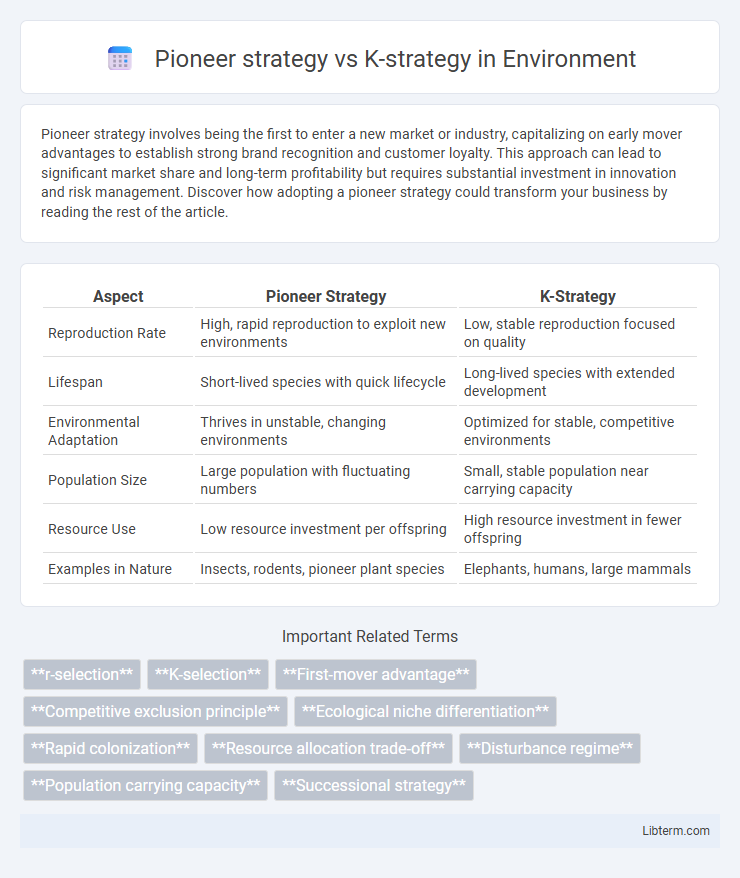
| Aspect | Pioneer Strategy | K-Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Reproduction Rate | High, rapid reproduction to exploit new environments | Low, stable reproduction focused on quality |
| Lifespan | Short-lived species with quick lifecycle | Long-lived species with extended development |
| Environmental Adaptation | Thrives in unstable, changing environments | Optimized for stable, competitive environments |
| Population Size | Large population with fluctuating numbers | Small, stable population near carrying capacity |
| Resource Use | Low resource investment per offspring | High resource investment in fewer offspring |
| Examples in Nature | Insects, rodents, pioneer plant species | Elephants, humans, large mammals |
Introduction to Pioneer and K-Strategy
Pioneer strategy emphasizes rapid market entry and innovation to establish early dominance, often targeting untapped or emerging markets with high growth potential. K-strategy focuses on long-term stability and efficiency, investing in quality and sustainability to maintain a steady population or customer base in competitive, resource-limited environments. Both strategies reflect distinct ecological and business models, where pioneer species or companies exploit change and colonization, while K-selected entities optimize survival through adaptation and resource management.
Defining Pioneer Strategy
Pioneer strategy emphasizes early market entry to gain first-mover advantages, establishing strong brand recognition and customer loyalty before competitors emerge. It relies on innovation and rapid adaptation to changing market conditions, often bearing higher risks and investment costs due to untested demand. In contrast, K-strategy focuses on stability and efficiency by targeting established markets with consistent resources, prioritizing long-term growth and market share retention over aggressive expansion.
What is K-Strategy?
K-strategy refers to a reproductive strategy where species produce fewer offspring but invest significant parental care and resources to ensure higher survival rates. Organisms following K-strategy typically have longer lifespans, stable population sizes near the carrying capacity (K) of their environment, and traits favoring competitive ability in resource-limited habitats. This contrasts with pioneer or r-strategy species, which prioritize rapid reproduction and minimal parental investment.
Key Differences Between Pioneer and K-Strategy
Pioneer strategy emphasizes rapid expansion and high reproductive rates to quickly colonize new environments, often sacrificing long-term survival for short-term growth. K-strategy focuses on stable population sizes with investment in fewer offspring, prioritizing quality, parental care, and competitive ability in resource-limited settings. Key differences lie in reproductive output, growth rate, and survival tactics, with pioneers thriving in unpredictable environments and K-strategists excelling in stable ecosystems.
Ecological Contexts and Applications
Pioneer species typically follow an r-strategy, thriving in disturbed or resource-rich ecological contexts by reproducing quickly and colonizing open or unstable environments. In contrast, K-strategists are adapted to stable ecosystems, investing more in fewer offspring with higher survival rates to maintain population stability near carrying capacity. Understanding these strategies guides habitat restoration, conservation planning, and managing succession stages in ecosystems like forests, grasslands, and wetlands.
Advantages of Pioneer Strategy
Pioneer strategy offers the advantage of establishing strong brand recognition and customer loyalty by entering the market early, often leading to market dominance and higher profit margins. Early movers can set industry standards and build critical partnerships, making it difficult for later entrants to compete. This strategy also enables businesses to leverage first-mover advantage in innovation and resource acquisition, creating significant barriers to entry for competitors.
Benefits of K-Strategy
K-strategy organisms benefit from stable environments by investing in fewer offspring with higher survival rates, leading to enhanced parental care and greater resource allocation per individual. These species typically have longer lifespans, allowing them to maintain population stability and efficiently compete for limited resources. K-strategy fosters ecological balance through sustainable reproduction and optimized population dynamics.
Real-World Examples of Each Strategy
Pioneer strategy companies like Tesla revolutionize markets by introducing innovative products early, capturing significant market share and establishing strong brand loyalty. In contrast, K-strategy firms such as Apple focus on sustainable growth with optimized resource allocation, fine-tuning products to dominate mature markets and maintain long-term customer retention. Real-world examples reveal Tesla's rapid expansion in the electric vehicle market and Apple's consistent revenue growth through iterative innovation and ecosystem control.
Challenges and Limitations
Pioneer strategy faces challenges such as high market uncertainty, elevated research and development costs, and the risk of rapid imitation by competitors, which can limit long-term profitability. K-strategy, characterized by stable population growth and strong competition, encounters limitations in resource allocation, slower adaptation to environmental changes, and vulnerability to sudden market shifts. Both strategies must balance growth and sustainability under differing ecological and economic pressures, influencing their evolutionary success and business performance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Strategy
Choosing the right strategy depends on environmental stability and resource availability; Pioneer (r-strategy) thrives in unpredictable conditions with rapid reproduction, while K-strategy suits stable environments prioritizing quality over quantity. Businesses must evaluate market dynamics to decide between aggressive expansion (Pioneer) or sustainable growth and customer retention (K-strategy). Aligning strategy with organizational goals ensures competitive advantage and long-term success.
Pioneer strategy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com