An ecological pyramid visually represents the distribution of energy, biomass, or organisms across different trophic levels in an ecosystem. Each level shows the amount of energy or matter available, highlighting the efficiency of energy transfer from producers to top consumers. Discover how understanding ecological pyramids can enhance your insight into ecosystem dynamics in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
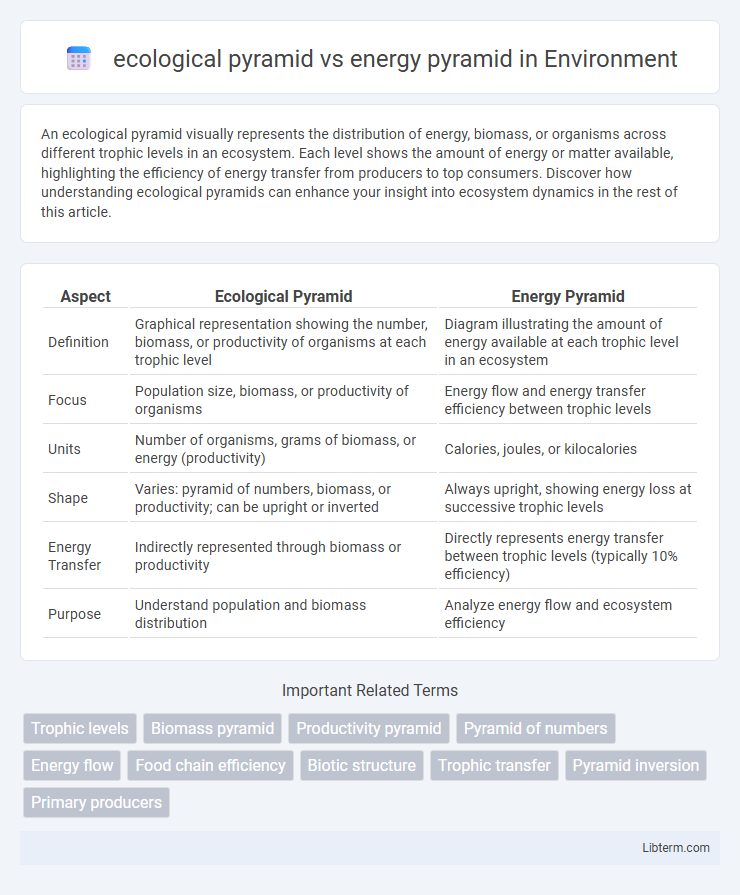
| Aspect | Ecological Pyramid | Energy Pyramid |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Graphical representation showing the number, biomass, or productivity of organisms at each trophic level | Diagram illustrating the amount of energy available at each trophic level in an ecosystem |
| Focus | Population size, biomass, or productivity of organisms | Energy flow and energy transfer efficiency between trophic levels |
| Units | Number of organisms, grams of biomass, or energy (productivity) | Calories, joules, or kilocalories |
| Shape | Varies: pyramid of numbers, biomass, or productivity; can be upright or inverted | Always upright, showing energy loss at successive trophic levels |
| Energy Transfer | Indirectly represented through biomass or productivity | Directly represents energy transfer between trophic levels (typically 10% efficiency) |
| Purpose | Understand population and biomass distribution | Analyze energy flow and ecosystem efficiency |
Introduction to Ecological and Energy Pyramids
Ecological pyramids represent the distribution of living organisms across different trophic levels, illustrating biomass, number of individuals, or energy flow in an ecosystem. Energy pyramids specifically depict the flow of energy from primary producers through various consumers, showing energy loss at each trophic level. Both pyramids are essential tools for understanding ecosystem structure, energy transfer efficiency, and the relationships between organisms within food chains.
Definition of Ecological Pyramid
Ecological pyramids represent the graphical depiction of the trophic levels in an ecosystem, illustrating the number, biomass, or energy of organisms at each level. These pyramids can be categorized into three types: pyramid of numbers, pyramid of biomass, and pyramid of energy, each highlighting different ecological parameters. The energy pyramid specifically shows the flow of energy through each trophic level, emphasizing energy loss due to metabolic processes.
Definition of Energy Pyramid
The energy pyramid represents the flow of energy through trophic levels in an ecosystem, illustrating the amount of energy available at each stage from producers to top consumers. Unlike the ecological pyramid, which can depict numbers or biomass, the energy pyramid strictly quantifies energy transfer efficiency, showing significant energy loss as heat at each trophic level. This concept highlights the critical limitation of energy availability in sustaining higher trophic levels within ecosystems.
Key Components of Ecological Pyramids
Ecological pyramids depict the biomass, numbers, or energy at various trophic levels within an ecosystem, emphasizing producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers as their key components. Energy pyramids specifically illustrate energy flow and loss through each trophic level, with producers capturing solar energy and subsequent consumers relying on the energy stored in organic matter. Understanding the differences in focus--biomass or number distribution in ecological pyramids versus energy transfer efficiency in energy pyramids--is crucial for analyzing ecosystem dynamics and energy conservation.
Major Features of Energy Pyramids
Energy pyramids represent the flow of energy through trophic levels in an ecosystem, illustrating the decrease in usable energy from producers to top consumers. The major features include a clear depiction of energy loss, typically around 90% per trophic level, showcasing energy transfer efficiency. Unlike ecological pyramids that may represent biomass or population, energy pyramids emphasize energy availability and transfer, highlighting the fundamental principle of energy diminution in food chains.
Comparison of Structure: Ecological vs Energy Pyramid
The ecological pyramid represents the number or biomass of organisms at each trophic level, often depicted as a pyramid of numbers, biomass, or productivity, showing population or mass distribution across levels. The energy pyramid, however, specifically illustrates the flow of energy through these levels, emphasizing the diminishing energy available as it moves from producers to apex consumers. Structurally, ecological pyramids can vary in shape depending on ecosystem dynamics, while energy pyramids consistently display a decreasing pattern due to energy loss in metabolic processes.
Flow of Energy and Biomass in Pyramids
Ecological pyramids visually represent the distribution of biomass, numbers, or energy across trophic levels, while energy pyramids specifically illustrate the flow of energy through an ecosystem, showing energy loss at each level due to metabolic processes. Biomass pyramids depict the total mass of living organisms at each trophic level, often decreasing as energy transfer efficiency declines, reflecting the energy pyramid's gradient from producers to apex consumers. Understanding these pyramids highlights how energy diminishes by approximately 90% between trophic levels, influencing biomass accumulation and ecosystem structure.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Model
Ecological pyramids effectively illustrate biomass, population, or energy distribution across trophic levels, offering clear visualization of ecosystem structure with advantages in simplicity and clarity. However, they often fail to capture complex interactions such as energy flow efficiency or temporal changes, limiting their dynamic representation. Energy pyramids, while more detailed in depicting actual energy transfer and loss between levels, can be challenging to quantify accurately and may overlook the ecological nuances represented in biomass or population data.
Ecological Significance and Real-World Examples
Ecological pyramids illustrate the distribution of biomass, numbers, or energy across trophic levels, highlighting ecosystem structure and productivity, while energy pyramids specifically depict the flow of energy, emphasizing the loss of energy at each trophic transfer due to metabolic processes. In real-world ecosystems, a forest food web shows an ecological pyramid with towering numbers of herbaceous plants supporting fewer herbivores and even fewer carnivores, while the corresponding energy pyramid reflects a steep decline in available energy from primary producers to apex predators. Coral reef ecosystems demonstrate the ecological pyramid's diversity of species and biomass at various levels and the energy pyramid underscores the rapid energy dissipation from photosynthetic algae to large predatory fish, essential for understanding energy efficiency and ecosystem stability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Pyramid for Ecosystem Analysis
Ecological pyramids illustrate the quantitative distribution of organisms at different trophic levels, while energy pyramids focus on the flow and loss of energy through an ecosystem. Selecting the appropriate pyramid depends on the analysis goal: biomass or population dynamics favor ecological pyramids, whereas energy transfer efficiency requires energy pyramids. Accurate ecosystem assessments integrate both models to capture structural and functional aspects effectively.
ecological pyramid Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com