Greenfield projects involve developing new facilities or systems from scratch on undeveloped land, offering a blank slate for innovation and customization. This approach avoids the constraints of existing structures, allowing your team to implement the latest technologies and designs tailored to specific needs. Discover how greenfield development can maximize efficiency and growth by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
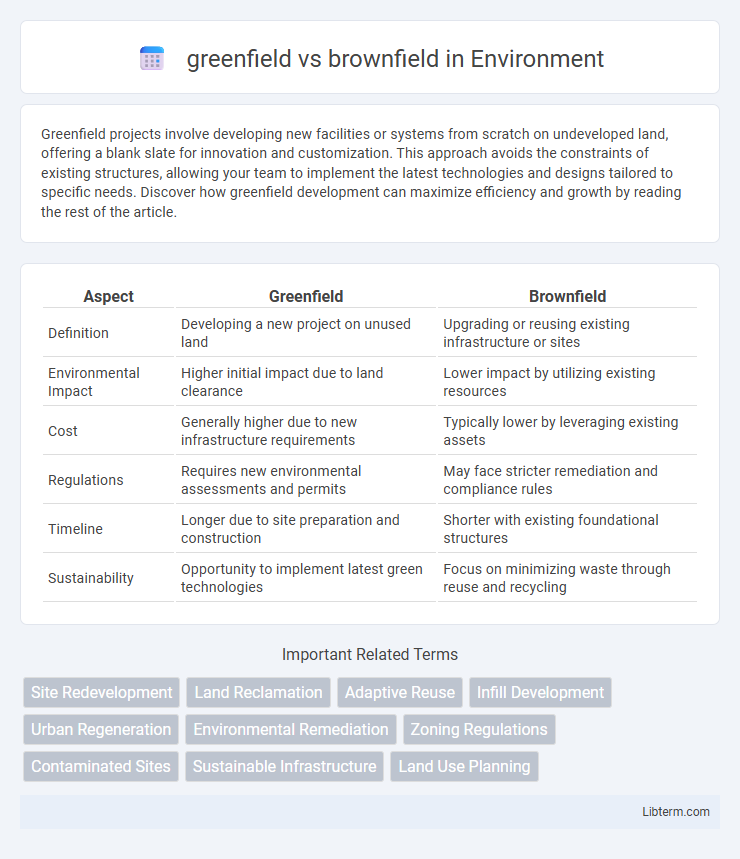
| Aspect | Greenfield | Brownfield |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Developing a new project on unused land | Upgrading or reusing existing infrastructure or sites |
| Environmental Impact | Higher initial impact due to land clearance | Lower impact by utilizing existing resources |
| Cost | Generally higher due to new infrastructure requirements | Typically lower by leveraging existing assets |
| Regulations | Requires new environmental assessments and permits | May face stricter remediation and compliance rules |
| Timeline | Longer due to site preparation and construction | Shorter with existing foundational structures |
| Sustainability | Opportunity to implement latest green technologies | Focus on minimizing waste through reuse and recycling |
Introduction to Greenfield and Brownfield Projects
Greenfield projects involve developing new infrastructure or facilities from scratch on previously undeveloped land, allowing for complete customization and modern design. Brownfield projects focus on renovating, upgrading, or repurposing existing sites that may have environmental contamination or structural challenges, often requiring remediation efforts. Both project types play critical roles in urban development, influencing sustainability, cost, and timelines in construction and industrial expansion.
Defining Greenfield Projects
Greenfield projects refer to initiatives that are developed on previously undeveloped land, allowing complete design freedom without constraints imposed by existing structures. These projects often involve new construction, infrastructure, or technology implementations, enabling organizations to customize solutions from the ground up. In contrast, brownfield projects focus on upgrading or expanding existing facilities, requiring adaptations to pre-existing conditions and legacy systems.
Understanding Brownfield Projects
Brownfield projects involve the redevelopment or upgrading of existing facilities or infrastructure, often requiring the integration of new technologies into legacy systems. These projects demand careful assessment of potential environmental contamination, regulatory compliance, and cost implications related to site remediation. Expertise in adaptive reuse and risk management is critical to successfully transforming brownfield sites into functional, sustainable assets.
Key Differences Between Greenfield and Brownfield
Greenfield projects involve developing new infrastructure or facilities on previously undeveloped land, offering flexibility in design and technology integration, while brownfield projects focus on upgrading or expanding existing sites, often facing regulatory and environmental challenges. Greenfield developments generally incur higher initial costs but benefit from fewer constraints, whereas brownfield projects leverage existing assets, reducing time and investment but requiring remediation efforts. Decision-making hinges on factors like site conditions, budget, compliance requirements, and long-term strategic goals.
Advantages of Greenfield Development
Greenfield development offers the advantage of complete design freedom, enabling developers to create customized infrastructure without constraints from existing structures. It allows for the implementation of the latest technologies, sustainable practices, and optimized layouts, resulting in improved efficiency and scalability. Greenfield projects typically experience fewer regulatory hurdles and reduced costs related to demolition or retrofitting compared to brownfield development.
Benefits of Brownfield Redevelopment
Brownfield redevelopment offers significant environmental benefits by rehabilitating contaminated or underutilized industrial sites, reducing urban sprawl, and preserving green spaces. Economic advantages include cost-effective land reuse, job creation, and increased property values in revitalized communities. It also supports sustainable urban growth by utilizing existing infrastructure, which minimizes construction costs and accelerates project timelines.
Challenges in Greenfield Projects
Greenfield projects face significant challenges including high initial capital investment, extended timelines for regulatory approvals, and complex environmental impact assessments. Managing unforeseen site conditions and ensuring infrastructure connectivity often cause delays and cost overruns. Additionally, attracting skilled labor and aligning stakeholder expectations are critical hurdles in the successful execution of greenfield developments.
Common Issues with Brownfield Sites
Brownfield sites often face soil contamination and environmental hazards that require extensive remediation before development. Structural challenges arise due to aging infrastructure and the need to comply with current building codes, increasing project complexity. Regulatory constraints and lengthy approval processes commonly delay construction timelines and escalate costs in brownfield redevelopment.
Greenfield vs Brownfield: Cost and Investment Analysis
Greenfield projects typically require higher initial capital investment due to land acquisition, infrastructure development, and regulatory approvals, whereas brownfield projects often involve lower upfront costs by utilizing existing facilities and infrastructure. However, brownfield investments may incur additional expenses related to environmental remediation, site decontamination, and retrofitting outdated systems. Careful cost-benefit analysis must weigh greenfield's potential for customized, modern designs against brownfield's faster timelines and reduced land development costs.
Which Approach Is Right for Your Project?
Choosing between greenfield and brownfield approaches depends on project goals, budget, and timeline. Greenfield projects offer full design freedom, ideal for innovative solutions but require higher initial investment and longer development time. Brownfield projects leverage existing infrastructure, accelerating deployment and reducing costs, making them suitable for upgrades or expansions in established environments.
greenfield Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com