Infill development maximizes urban space by constructing new buildings within underutilized areas of existing neighborhoods, enhancing density without expanding city boundaries. This approach promotes sustainable growth, reduces urban sprawl, and improves access to amenities while preserving green spaces. Discover how infill projects can transform your community and boost local revitalization in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
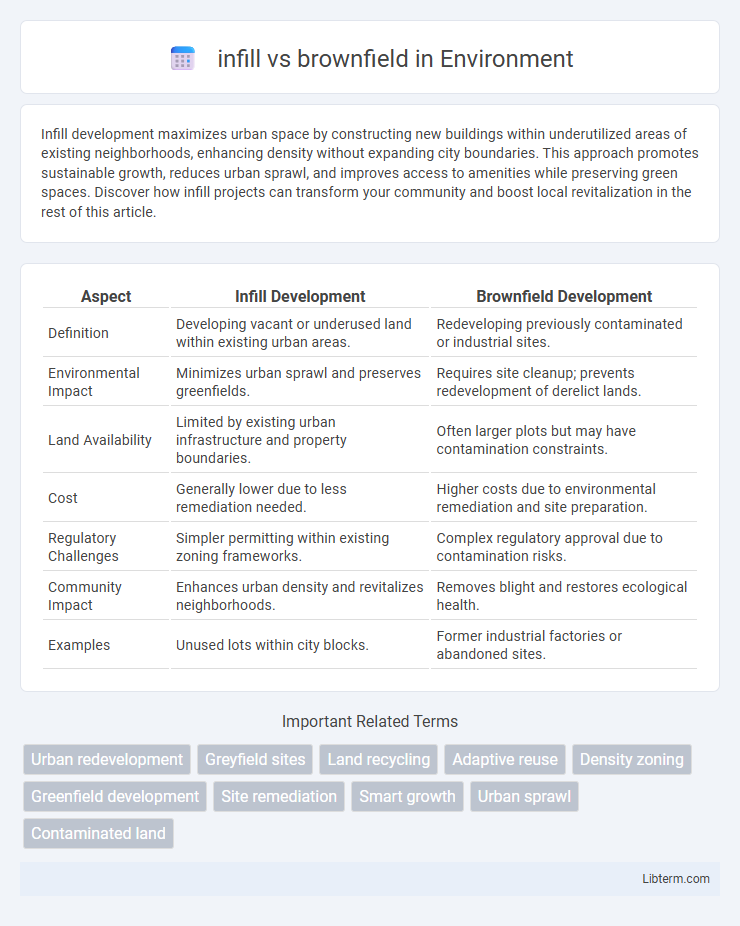
| Aspect | Infill Development | Brownfield Development |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Developing vacant or underused land within existing urban areas. | Redeveloping previously contaminated or industrial sites. |
| Environmental Impact | Minimizes urban sprawl and preserves greenfields. | Requires site cleanup; prevents redevelopment of derelict lands. |
| Land Availability | Limited by existing urban infrastructure and property boundaries. | Often larger plots but may have contamination constraints. |
| Cost | Generally lower due to less remediation needed. | Higher costs due to environmental remediation and site preparation. |
| Regulatory Challenges | Simpler permitting within existing zoning frameworks. | Complex regulatory approval due to contamination risks. |
| Community Impact | Enhances urban density and revitalizes neighborhoods. | Removes blight and restores ecological health. |
| Examples | Unused lots within city blocks. | Former industrial factories or abandoned sites. |
Understanding Infill and Brownfield Development
Infill development involves the use of vacant or underutilized land within existing urban areas, maximizing land efficiency and supporting sustainable growth by reducing urban sprawl. Brownfield development focuses on redeveloping previously contaminated or industrial sites, requiring environmental remediation to prepare the land for new construction and revitalization. Both approaches prioritize sustainable urban regeneration but differ in site conditions and remediation needs.
Key Differences Between Infill and Brownfield Sites
Infill sites are vacant or underused parcels within existing urban areas targeted for new development to maximize land efficiency and reduce urban sprawl. Brownfield sites refer to previously developed land, often contaminated or industrial, requiring remediation before reuse or redevelopment. Key differences include location context, with infill focusing on integrating unused land within active neighborhoods, whereas brownfield sites necessitate environmental cleanup due to prior industrial use.
Benefits of Infill Development
Infill development maximizes the use of existing urban infrastructure, reducing urban sprawl and preserving natural landscapes by focusing growth within established neighborhoods. It promotes sustainable land use, enhances walkability, and supports public transit, leading to reduced traffic congestion and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Economic benefits arise through increased property values, revitalized communities, and cost savings on utilities and public services by utilizing already developed sites.
Advantages of Brownfield Redevelopment
Brownfield redevelopment offers significant advantages such as utilizing previously contaminated or underused urban sites, which helps to mitigate urban sprawl and preserve greenfields. It often benefits from existing infrastructure, reducing costs related to utilities, transportation, and public services. Environmental cleanup associated with brownfield projects improves community health and can increase property values while stimulating local economic growth.
Environmental Impacts: Infill vs Brownfield
Infill development significantly reduces urban sprawl by utilizing vacant or underused land within existing urban areas, minimizing habitat disruption and preserving greenfields. Brownfield redevelopment involves cleaning and repurposing contaminated sites, which can mitigate pollution risks and prevent further environmental degradation. Both approaches promote sustainable urban growth, but brownfield projects often require extensive remediation efforts to address soil and groundwater contamination, impacting project timelines and costs.
Challenges Facing Infill Projects
Infill projects face significant challenges including limited site availability and complicated land ownership often found in urban areas, which can delay development timelines. Infrastructure constraints such as outdated utilities and the need for extensive environmental remediation increase costs and complexity. Balancing community concerns about increased density and preserving neighborhood character also frequently complicates project approvals and stakeholder engagement.
Obstacles in Brownfield Redevelopment
Brownfield redevelopment faces significant obstacles such as soil contamination requiring costly remediation and navigating complex regulatory approvals that delay project timelines. Limited availability of accurate environmental data often complicates risk assessment and increases overall redevelopment costs. Furthermore, financing challenges arise due to perceived risks, discouraging investors from committing to brownfield projects compared to infill developments.
Economic Implications of Each Approach
Infill development often maximizes existing infrastructure, reducing costs related to utilities and transportation while boosting property values and local tax revenues. Brownfield redevelopment involves higher initial expenses due to site remediation and environmental cleanup but can unlock economically distressed areas, attract investment, and stimulate job creation. Both approaches contribute to sustainable urban growth, with infill offering cost efficiency and brownfield redevelopment fostering long-term economic revitalization.
Urban Planning Strategies for Infill and Brownfield
Urban planning strategies for infill focus on maximizing land use within existing urban areas by developing vacant or underutilized parcels, enhancing infrastructure efficiency and reducing urban sprawl. Brownfield redevelopment prioritizes the remediation and transformation of contaminated or abandoned industrial sites into functional urban spaces, promoting environmental sustainability and economic revitalization. Both strategies aim to optimize land resources while improving urban density and community connectivity.
Choosing the Right Path: Infill or Brownfield?
Choosing between infill and brownfield development hinges on site conditions and project goals, with infill targeting underutilized urban land to maximize density and reduce sprawl, while brownfield focuses on rehabilitating contaminated or previously industrial sites to restore environmental health. Infill projects often yield higher returns in walkable neighborhoods with existing infrastructure, whereas brownfield redevelopment requires significant environmental remediation but offers opportunities for large-scale revitalization and community rejuvenation. Evaluating factors such as location, contamination levels, regulatory requirements, and market demand is essential for selecting the right development path that balances economic, environmental, and social benefits.
infill Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com