Heterospecific refers to organisms belonging to different species that interact or coexist within the same environment. These interactions can include competition, predation, or mutualism, significantly impacting ecological dynamics and biodiversity. Explore the article to understand how heterospecific relationships influence ecosystems and affect your observations of the natural world.
Table of Comparison
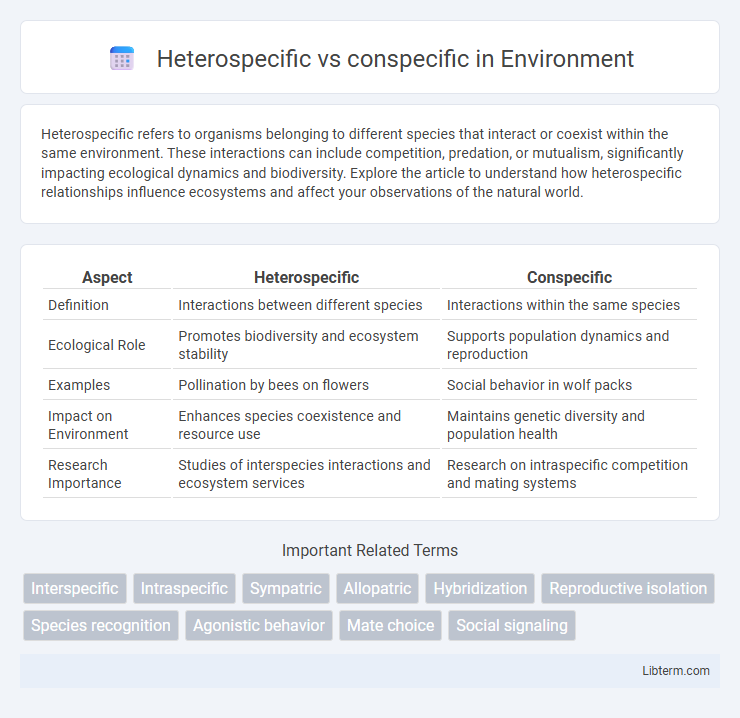
| Aspect | Heterospecific | Conspecific |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interactions between different species | Interactions within the same species |
| Ecological Role | Promotes biodiversity and ecosystem stability | Supports population dynamics and reproduction |
| Examples | Pollination by bees on flowers | Social behavior in wolf packs |
| Impact on Environment | Enhances species coexistence and resource use | Maintains genetic diversity and population health |
| Research Importance | Studies of interspecies interactions and ecosystem services | Research on intraspecific competition and mating systems |
Understanding Heterospecific and Conspecific Interactions
Heterospecific interactions occur between individuals of different species, influencing ecological dynamics such as competition, predation, and mutualism, while conspecific interactions involve individuals of the same species, affecting social behaviors like mating, cooperation, and territoriality. Understanding these interactions is crucial for studying community structure, resource allocation, and evolutionary processes. Research in behavioral ecology and population biology highlights how heterospecific and conspecific interactions determine species coexistence and ecosystem stability.
Defining Heterospecific Relationships
Heterospecific relationships occur between individuals of different species, often involving interactions such as competition, predation, or mutualism that influence ecological dynamics. These relationships contrast with conspecific interactions, which happen among members of the same species and typically involve behaviors related to reproduction, social bonding, or territoriality. Understanding heterospecific relationships is crucial for studying biodiversity, ecosystem function, and species coexistence strategies.
Exploring Conspecific Associations
Conspecific associations refer to interactions occurring between individuals of the same species, playing a critical role in social behavior, mating systems, and cooperative activities. These associations often influence survival and reproductive success by facilitating resource sharing, protection, and communication. In contrast, heterospecific interactions involve individuals of different species, typically relating to competition, predation, or mutualistic relationships.
Ecological Significance of Species Interactions
Heterospecific interactions involve different species, playing a critical role in ecosystem dynamics by influencing resource distribution, competition, and mutualism. Conspecific interactions occur within the same species, affecting population regulation, mating systems, and social structures. Both interaction types drive biodiversity, community stability, and adaptive evolutionary processes essential for ecosystem resilience.
Behavioral Differences: Heterospecific vs Conspecific
Behavioral differences between heterospecific and conspecific interactions significantly influence social dynamics and survival strategies in animals. Conspecific behavior typically involves cooperation, mating, and territorial defense among members of the same species, enhancing reproductive success and resource sharing. In contrast, heterospecific interactions often center around competition, predation, or mutualism, with distinct communication signals and adaptive behaviors tailored to interspecies relationships.
Communication in Intra- and Interspecific Contexts
Communication in heterospecific contexts involves the transmission of signals between individuals of different species, facilitating interactions such as predator-prey dynamics, mutualisms, or competition, while conspecific communication occurs within the same species, crucial for mating, social organization, and territory defense. Acoustic, chemical, visual, and tactile signals are adapted to maximize effective information transfer in both contexts, with heterospecific communication often relying on signal recognition or mimicry to influence behavior across species boundaries. Understanding these communication mechanisms sheds light on ecological relationships and evolutionary pressures shaping signal evolution in intra- and interspecific interactions.
Heterospecific Interactions in Wildlife Communities
Heterospecific interactions in wildlife communities involve relationships between individuals of different species, which can include competition, predation, mutualism, and commensalism. These interactions influence community structure, resource distribution, and species diversity, shaping ecological dynamics and evolutionary processes. Understanding heterospecific interactions provides insights into habitat preferences, niche differentiation, and the adaptive strategies of coexisting species.
Evolutionary Implications of Conspecific vs Heterospecific Links
Conspecific links, involving interactions within the same species, often promote genetic cohesion and facilitate adaptive evolution by reinforcing beneficial traits through reproductive isolation and cooperative behaviors. Heterospecific links, occurring between different species, drive coevolutionary dynamics such as mutualism, competition, and predator-prey relationships, significantly influencing ecological niches and biodiversity. Understanding the balance between conspecific and heterospecific interactions is crucial for exploring evolutionary mechanisms, species diversification, and ecosystem stability.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Case studies on heterospecific and conspecific interactions reveal varied ecological impacts, such as pollination efficiency in plant species where heterospecific pollen deposition often reduces seed set compared to conspecific pollen. In marine biology, conspecific shoaling enhances survival rates of fish species by improving coordinated defense mechanisms, while heterospecific associations may facilitate resource sharing but sometimes increase predation risk. Behavioral experiments in primates demonstrate that conspecific social bonding strengthens group cohesion and reproductive success, contrasting with heterospecific encounters that can lead to competitive exclusion or mutualistic benefits depending on environmental context.
Importance of Distinguishing Heterospecific and Conspecific Dynamics
Distinguishing heterospecific and conspecific dynamics is crucial for understanding ecological interactions, as conspecific interactions influence intraspecific competition and cooperative behaviors, while heterospecific interactions affect interspecific competition, predation, and mutualism. Accurate identification of these dynamics allows for better modeling of population growth rates, resource allocation, and community structure. This differentiation informs conservation strategies by highlighting species-specific relationships that impact biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Heterospecific Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com