Mesophytes are plants adapted to environments with moderate water availability, thriving neither in extremely dry nor excessively wet conditions. They possess specialized structures that balance water retention and transpiration, ensuring optimal growth and survival in temperate habitats. Explore the rest of the article to understand how mesophytes contribute to ecosystem stability and what makes your garden plants resilient.
Table of Comparison
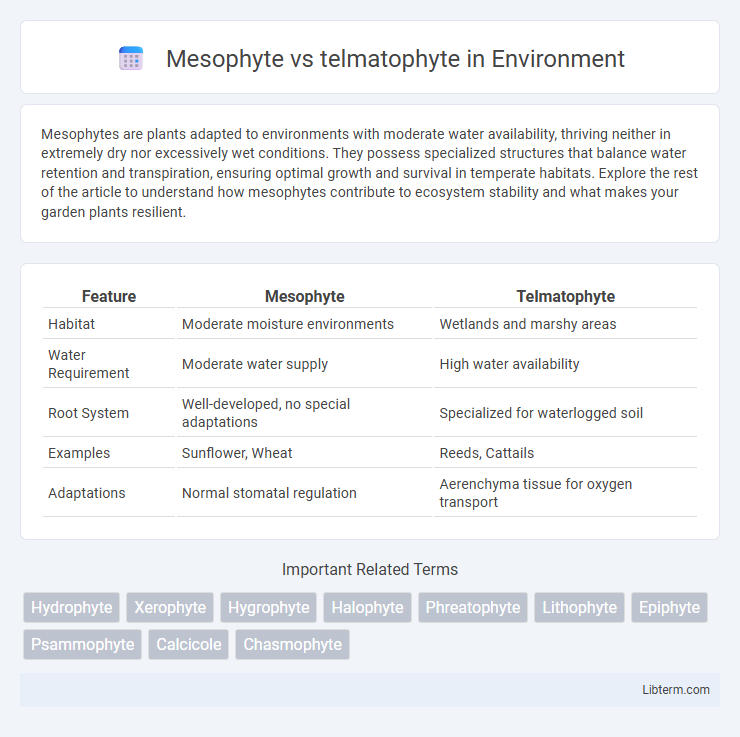
| Feature | Mesophyte | Telmatophyte |
|---|---|---|
| Habitat | Moderate moisture environments | Wetlands and marshy areas |
| Water Requirement | Moderate water supply | High water availability |
| Root System | Well-developed, no special adaptations | Specialized for waterlogged soil |
| Examples | Sunflower, Wheat | Reeds, Cattails |
| Adaptations | Normal stomatal regulation | Aerenchyma tissue for oxygen transport |
Introduction to Mesophytes and Telmatophytes
Mesophytes are plants adapted to environments with moderate water availability, possessing well-developed root systems and stomata to regulate water loss efficiently. Telmatophytes, also known as hydrophytes or swamp plants, thrive in permanently saturated or flooded habitats, exhibiting specialized adaptations like aerenchyma tissue for oxygen transport in waterlogged soils. Understanding the distinct physiological and morphological traits of mesophytes and telmatophytes is essential for studying plant ecology and habitat-specific adaptations.
Defining Mesophytes: Characteristics and Habitat
Mesophytes are plants adapted to environments with moderate water availability, displaying well-developed root systems and balanced leaf structures for optimal water absorption and transpiration. They typically inhabit temperate regions with neither excessive drought nor waterlogging, contributing to diverse terrestrial ecosystems such as grasslands and deciduous forests. Unlike telmatophytes, which thrive in water-saturated soils or wetlands, mesophytes require well-drained soils to maintain stable physiological processes.
Understanding Telmatophytes: Features and Ecology
Telmatophytes are plants adapted to grow in water-saturated, marshy environments, exhibiting specialized features like aerenchyma tissue for oxygen transport and strong anchorage in soft substrates. Their ecological role includes stabilizing wetland soils and providing habitat for aquatic organisms, distinguishing them from mesophytes, which thrive in moderate, well-drained conditions. Understanding telmatophyte adaptations reveals their critical function in maintaining wetland ecosystem health and hydrological balance.
Key Differences Between Mesophytes and Telmatophytes
Mesophytes thrive in moderate environments with balanced water availability, while telmatophytes are adapted to waterlogged or marshy habitats. Mesophytes possess well-developed root systems and stomata for efficient water regulation, whereas telmatophytes often feature specialized structures such as aerenchyma to survive in oxygen-poor soils. Key differences include habitat preference, root adaptations, and mechanisms for water and oxygen management.
Adaptations of Mesophytes for Moderate Environments
Mesophytes exhibit adaptations such as well-developed root systems for efficient water absorption and broad leaves with numerous stomata to optimize gas exchange in moderate environments. Their moderate cuticle thickness balances water retention and transpiration, supporting survival without extreme drought or waterlogging. Unlike telmatophytes, which thrive in wet, swampy conditions, mesophytes are suited to balanced moisture levels, making them common in temperate forests and grasslands.
Adaptations of Telmatophytes for Wetland Environments
Telmatophytes exhibit specialized adaptations for thriving in wetland environments, including aerenchyma tissue for enhanced oxygen transport in waterlogged soils and shallow root systems that prevent anoxia damage. They also develop adventitious roots and lenticels, facilitating gas exchange in saturated conditions. These traits contrast with mesophytes, which lack such features and are better suited to moderate moisture levels.
Examples of Common Mesophyte Plant Species
Common mesophyte plant species include dandelions (Taraxacum officinale), sunflowers (Helianthus annuus), and oak trees (Quercus spp.), all adapted to environments with moderate water availability. These plants possess well-developed root systems and broad leaves optimized for efficient water uptake and photosynthesis under mesic conditions. Unlike telmatophytes, which thrive in waterlogged or marshy habitats, mesophytes occupy terrestrial ecosystems with balanced moisture levels, supporting diverse agricultural and forestry crops.
Examples of Typical Telmatophyte Plant Species
Typical telmatophyte plant species include cattails (Typha latifolia), sedges (Carex spp.), and bulrushes (Schoenoplectus spp.), which thrive in waterlogged or marshy environments. These hydrophilic plants display adaptations such as aerenchyma tissues for oxygen transport in submerged roots. Compared to mesophytes that prefer moderate moisture levels, telmatophytes are specialized for saturated soils with low oxygen availability.
Ecological Importance of Mesophytes vs Telmatophytes
Mesophytes play a crucial ecological role by thriving in environments with moderate water availability, supporting diverse terrestrial ecosystems through efficient nutrient cycling and providing habitat stability. Telmatophytes, adapted to water-saturated soils and wetlands, contribute significantly to water purification, carbon sequestration, and maintaining hydrological balance. The contrasting water dependency of mesophytes and telmatophytes underpins their respective contributions to biodiversity, ecosystem resilience, and soil conservation in varying habitats.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Mesophyte and Telmatophyte Plants
Selecting between mesophyte and telmatophyte plants depends on environmental conditions and water availability. Mesophytes thrive in moderate moisture environments with well-aerated soils, while telmatophytes are adapted to waterlogged or marshy habitats requiring high tolerance to submerged roots. Understanding soil moisture levels and habitat type ensures optimal plant survival and growth.
Mesophyte Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com