A specialist possesses deep expertise in a specific field, enabling precise solutions and advanced problem-solving skills tailored to unique challenges. Their focused knowledge enhances the quality and efficiency of outcomes in professional or technical contexts. Explore the rest of the article to discover how a specialist can elevate your projects and career.
Table of Comparison
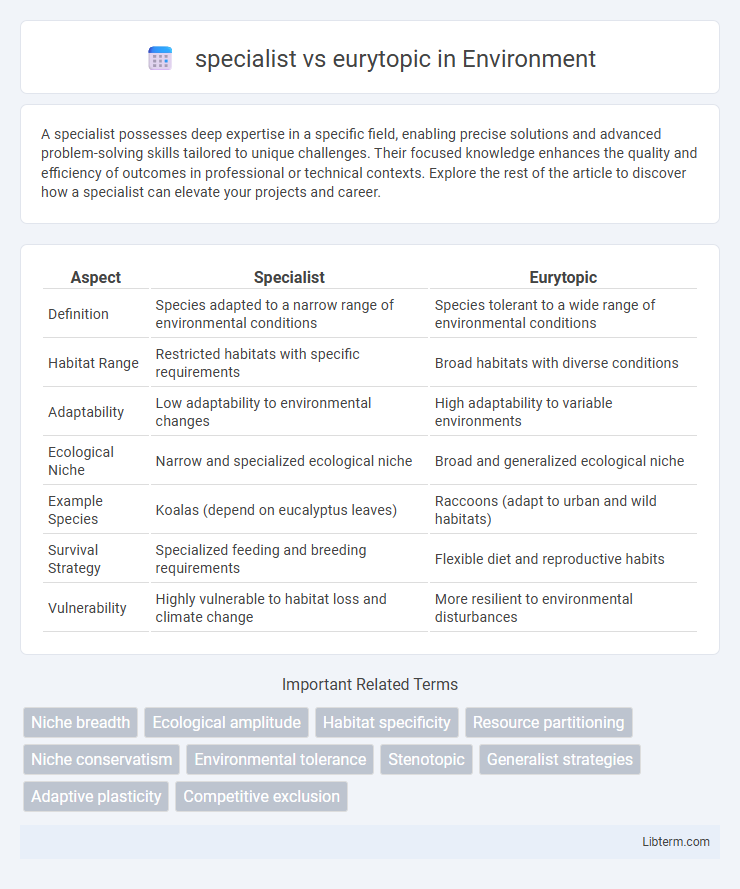
| Aspect | Specialist | Eurytopic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Species adapted to a narrow range of environmental conditions | Species tolerant to a wide range of environmental conditions |
| Habitat Range | Restricted habitats with specific requirements | Broad habitats with diverse conditions |
| Adaptability | Low adaptability to environmental changes | High adaptability to variable environments |
| Ecological Niche | Narrow and specialized ecological niche | Broad and generalized ecological niche |
| Example Species | Koalas (depend on eucalyptus leaves) | Raccoons (adapt to urban and wild habitats) |
| Survival Strategy | Specialized feeding and breeding requirements | Flexible diet and reproductive habits |
| Vulnerability | Highly vulnerable to habitat loss and climate change | More resilient to environmental disturbances |
Introduction to Specialist and Eurytopic Species
Specialist species thrive in narrow ecological niches with specific habitat requirements, exhibiting high adaptation to particular environmental conditions but low tolerance to change. Eurytopic species demonstrate broad ecological tolerance, enabling them to inhabit diverse environments and tolerate a wide range of environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, and soil types. Understanding the distinction between specialist and eurytopic species is critical for biodiversity conservation and habitat management, as specialists are more vulnerable to habitat loss while eurytopic species often indicate ecosystem resilience.
Defining Specialist Species
Specialist species are organisms that thrive in narrow ecological niches, exhibiting specific adaptations to limited environmental conditions or resources. These species rely heavily on particular habitats, food sources, or climatic conditions, making them vulnerable to changes in their ecosystem. Understanding the narrow niche specialization of specialists is essential for conservation efforts targeting habitat preservation and biodiversity maintenance.
Defining Eurytopic Species
Eurytopic species exhibit broad ecological tolerance, thriving across diverse habitats and environmental conditions. Unlike specialists that rely on narrow niches, eurytopic organisms adapt to varying resources, climate, and soil types, demonstrating high plasticity in resource use. This flexibility makes eurytopic species important indicators of habitat generalism and ecological resilience in environmental studies.
Key Differences Between Specialist and Eurytopic Organisms
Specialist organisms thrive in narrow ecological niches with highly specific habitat or dietary requirements, often making them vulnerable to environmental changes. Eurytopic organisms exhibit broad ecological tolerance, enabling them to adapt to diverse habitats and resource variations, which enhances their survival under fluctuating environmental conditions. The key difference lies in their ecological adaptability, with specialists showing limited flexibility and eurytopics demonstrating extensive resilience across multiple ecosystems.
Ecological Niches and Adaptability
Specialists occupy narrow ecological niches, exhibiting high efficiency in resource utilization but limited adaptability to environmental changes, which increases their vulnerability to habitat disturbances. Eurytopics thrive across diverse habitats by exploiting a wide range of resources, demonstrating broad adaptability and resilience to varying environmental conditions. Understanding the balance between specialization and generalism is crucial for predicting species survival and ecosystem stability under shifting ecological pressures.
Survival Strategies in Changing Environments
Specialist species exhibit high survival efficiency in stable environments by exploiting specific niches, relying on narrow habitat and resource requirements. Eurytopic species demonstrate adaptability and resilience by occupying diverse habitats and utilizing a wide range of resources, enhancing survival amid environmental fluctuations. Understanding these contrasting survival strategies aids in predicting species vulnerability and ecosystem responses under climate change and habitat alteration.
Advantages of Being a Specialist
Specialists possess the advantage of optimized efficiency and expertise within a narrow ecological niche, allowing them to exploit resources or environments unavailable to generalists. Their high adaptation to specific conditions enhances survival and reproductive success, often reducing competition with other species. This specialization can result in superior resource utilization and stability in consistent habitats.
Advantages of Being Eurytopic
Eurytopic species exhibit a high degree of ecological plasticity, allowing them to thrive in diverse habitats and varying environmental conditions, which enhances their survival and reproductive success. Their broad tolerance to abiotic factors such as temperature, moisture, and soil types provides resilience against habitat disturbances and climate change. This adaptability facilitates widespread distribution and reduces vulnerability to extinction compared to specialist species with narrow ecological niches.
Impacts of Human Activities on Specialists vs. Eurytopics
Human activities such as habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change disproportionately affect specialist species due to their narrow ecological niches and limited adaptability. Eurytopic species, characterized by broad habitat tolerance and ecological flexibility, generally exhibit greater resilience to environmental disturbances caused by urbanization and agricultural expansion. Consequently, specialists face higher extinction risks, while eurytopics often expand their range and population under anthropogenic pressures.
Conservation Implications and Future Outlook
Specialist species, with narrow habitat requirements, are more vulnerable to environmental changes and habitat loss, making their conservation a priority to prevent extinction. Eurytopic species, possessing broad ecological tolerance, can often adapt to diverse conditions, providing ecosystem resilience amid habitat alterations. Conservation strategies must balance protecting specialist habitats while leveraging the adaptive capacity of eurytopic species to maintain biodiversity and ecosystem function in a changing climate.
specialist Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com