Reducing your carbon footprint involves adopting sustainable habits such as using renewable energy, minimizing waste, and choosing eco-friendly transportation. Small lifestyle changes can significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions and help combat climate change. Explore the rest of this article to discover practical tips for shrinking your carbon footprint effectively.
Table of Comparison
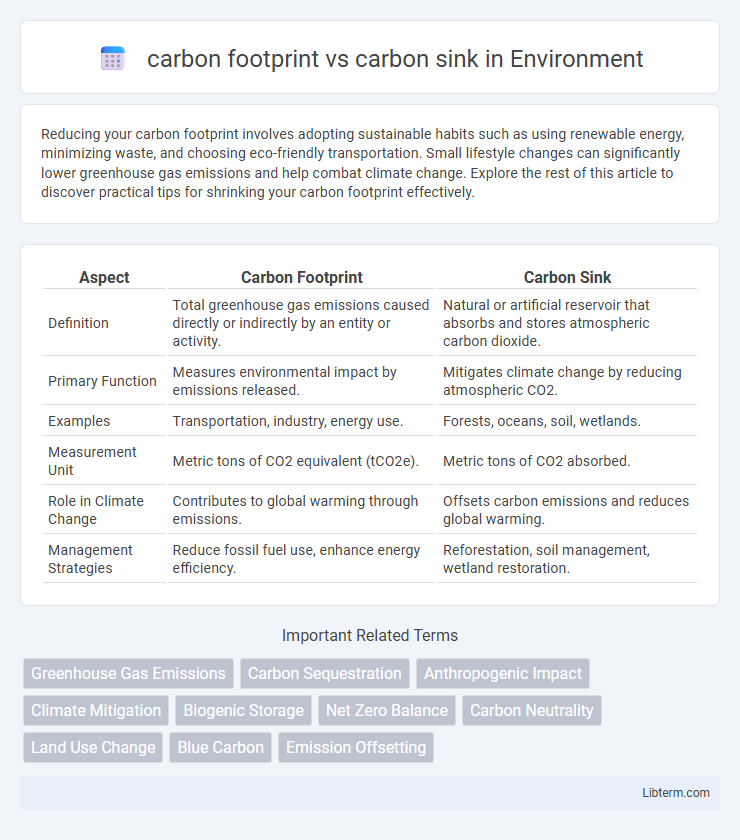
| Aspect | Carbon Footprint | Carbon Sink |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Total greenhouse gas emissions caused directly or indirectly by an entity or activity. | Natural or artificial reservoir that absorbs and stores atmospheric carbon dioxide. |
| Primary Function | Measures environmental impact by emissions released. | Mitigates climate change by reducing atmospheric CO2. |
| Examples | Transportation, industry, energy use. | Forests, oceans, soil, wetlands. |
| Measurement Unit | Metric tons of CO2 equivalent (tCO2e). | Metric tons of CO2 absorbed. |
| Role in Climate Change | Contributes to global warming through emissions. | Offsets carbon emissions and reduces global warming. |
| Management Strategies | Reduce fossil fuel use, enhance energy efficiency. | Reforestation, soil management, wetland restoration. |
Understanding Carbon Footprint: Definition and Impact
A carbon footprint measures the total greenhouse gas emissions caused directly or indirectly by an individual, organization, or product, expressed in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO2e). It quantifies the environmental impact of activities such as transportation, energy consumption, and manufacturing processes that release carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. Carbon sinks, such as forests, oceans, and soil, naturally absorb and store CO2, helping to offset carbon footprints by reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and mitigating climate change.
What Is a Carbon Sink? Functions and Types
A carbon sink is a natural or artificial reservoir that absorbs and stores carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, playing a crucial role in mitigating climate change. Key functions of carbon sinks include reducing atmospheric CO2 levels, supporting ecosystem health, and regulating the global carbon cycle. Major types of carbon sinks encompass forests, oceans, soil, and wetlands, each varying in carbon storage capacity and impact on environmental sustainability.
Key Differences Between Carbon Footprint and Carbon Sink
A carbon footprint measures the total greenhouse gas emissions caused directly or indirectly by an individual, organization, or product, quantified in CO2 equivalents. In contrast, a carbon sink refers to natural or artificial reservoirs, such as forests and oceans, that absorb and store atmospheric carbon dioxide, reducing overall carbon levels. The key difference lies in carbon footprint representing emissions output, while carbon sink denotes carbon absorption and storage capacity.
Sources Contributing to Carbon Footprint
Industrial activities such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and agriculture are primary sources contributing to the global carbon footprint, emitting significant quantities of carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere. Transportation sectors, including road vehicles, aviation, and shipping, also release large volumes of greenhouse gases, intensifying climate change. Urbanization and land-use changes reduce natural carbon sinks like forests and wetlands, further exacerbating the imbalance between carbon emissions and absorption.
Natural and Artificial Carbon Sinks Explained
Natural carbon sinks such as forests, oceans, and soil absorb and store large amounts of CO2, playing a crucial role in regulating the global carbon cycle and mitigating climate change. Artificial carbon sinks include technologies like carbon capture and storage (CCS) and bioenergy with carbon capture and storage (BECCS), designed to actively remove CO2 from the atmosphere and securely store it underground or in engineered materials. Understanding the efficiency and scalability of both natural and artificial carbon sinks is essential for developing effective strategies to reduce the overall carbon footprint.
The Importance of Reducing Carbon Footprint
Reducing carbon footprint is crucial for mitigating climate change and preserving biodiversity by decreasing greenhouse gas emissions from human activities. Carbon sinks, such as forests, oceans, and soil, naturally absorb and store significant amounts of CO2, helping to balance atmospheric carbon levels. Enhancing carbon sink capacities alongside minimizing carbon footprints accelerates global efforts to achieve net-zero emissions and safeguard ecosystems.
Enhancing Carbon Sink Capacity: Methods and Benefits
Enhancing carbon sink capacity involves increasing the ability of forests, soils, and oceans to absorb and store atmospheric carbon dioxide, effectively mitigating climate change impacts. Methods such as reforestation, afforestation, soil carbon sequestration, and blue carbon initiatives boost carbon storage while promoting biodiversity and ecosystem health. These approaches reduce the overall carbon footprint by offsetting emissions, improving air quality, and supporting sustainable land management practices.
Human Activities: Increasing Footprint vs. Supporting Sinks
Human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, deforestation, and industrial processes significantly increase the carbon footprint by releasing large amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere. Conversely, supporting carbon sinks like forests, wetlands, and soil carbon sequestration plays a crucial role in absorbing and storing carbon, helping to offset emissions. Expanding reforestation projects and sustainable land use practices enhances the capacity of these sinks to mitigate the impact of rising anthropogenic carbon footprints.
Global Strategies: Balancing Footprint and Sink
Global strategies for balancing carbon footprint and carbon sink emphasize enhancing natural ecosystems like forests, wetlands, and oceans to absorb CO2 while reducing emissions from industrial, agricultural, and transportation sources. Innovative approaches include reforestation, afforestation, regenerative agriculture, and carbon capture and storage technologies deployed to maximize carbon sequestration. Governments and organizations implement policies targeting net-zero emissions by integrating carbon pricing, renewable energy expansion, and sustainable land management practices to align carbon output with the planet's absorption capacity.
Future Outlook: Sustainable Solutions for Carbon Management
Future outlook for carbon management emphasizes expanding carbon sinks through reforestation, soil carbon sequestration, and blue carbon ecosystems to balance increasing carbon footprints from industrialization. Innovations in carbon capture and storage (CCS) and enhanced weathering techniques offer scalable solutions to reduce atmospheric CO2 concentrations effectively. Sustainable practices integrating renewable energy deployment and circular economy models are essential to achieving net-zero emissions and mitigating climate change impacts.
carbon footprint Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com