Allospecific refers to biological interactions or relationships occurring between different species, often used in genetics and immunology to describe responses to foreign genetic material or antigens. Understanding allospecific mechanisms is crucial for advancements in transplantation, disease resistance, and evolutionary biology. Explore the rest of the article to discover how allospecific processes impact scientific research and medical applications.
Table of Comparison
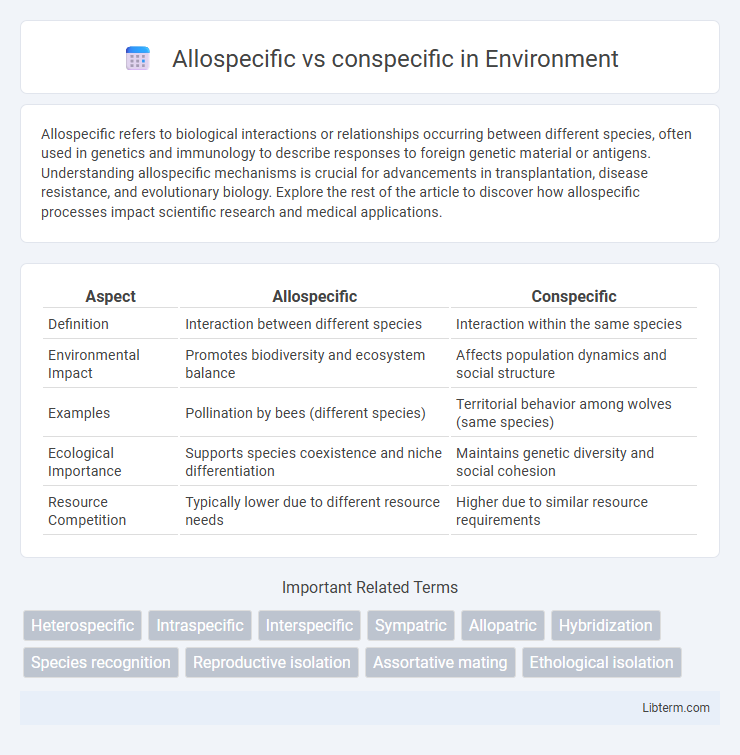
| Aspect | Allospecific | Conspecific |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interaction between different species | Interaction within the same species |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes biodiversity and ecosystem balance | Affects population dynamics and social structure |
| Examples | Pollination by bees (different species) | Territorial behavior among wolves (same species) |
| Ecological Importance | Supports species coexistence and niche differentiation | Maintains genetic diversity and social cohesion |
| Resource Competition | Typically lower due to different resource needs | Higher due to similar resource requirements |
Introduction to Allospecific and Conspecific Concepts
Allospecific refers to interactions or relationships between individuals of different species, highlighting ecological and behavioral distinctions important for biodiversity studies and conservation efforts. Conspecific describes interactions or relationships among individuals within the same species, crucial for understanding social structures, mating systems, and population dynamics. Clear differentiation between allospecific and conspecific concepts aids in analyzing species-specific behaviors and interspecies interactions in ecosystems.
Defining Allospecific Interactions
Allospecific interactions refer to relationships or behaviors occurring between individuals of different species, distinguishing them from conspecific interactions that happen within the same species. These interactions include a wide range of ecological and evolutionary roles such as predation, competition, and mutualism, crucial in shaping biodiversity and ecosystem dynamics. Understanding allospecific interactions provides insights into species coexistence, resource partitioning, and the mechanisms driving natural selection across diverse biological communities.
Understanding Conspecific Interactions
Conspecific interactions refer to the behaviors and communications occurring between individuals of the same species, which are crucial for social structure, mating, and resource competition. These interactions influence population dynamics by facilitating cooperation, territoriality, and reproductive success, contrasting with allospecific interactions that involve different species. Understanding conspecific relationships enhances ecological research on species-specific adaptations and intraspecific communication mechanisms.
Key Differences Between Allospecific and Conspecific
Allospecific refers to organisms belonging to different species, while conspecifics are members of the same species. Key differences include genetic compatibility, with conspecifics capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring, unlike allospecifics which generally cannot. Behavioral interactions also differ, as conspecifics typically exhibit cooperative behaviors important for reproduction and social organization, whereas allospecific interactions may involve competition or predation.
Examples of Allospecific Relationships in Nature
Allospecific relationships occur between individuals of different species, exemplified by mutualisms like the pollination partnership between bees and flowering plants or the cleaning symbiosis where cleaner fish remove parasites from larger fish. Parasitism also illustrates allospecific interaction, such as ticks feeding on mammals or mistletoe extracting nutrients from host trees. These interspecies relationships play crucial roles in ecosystem dynamics, influencing biodiversity and population control.
Examples of Conspecific Relationships in Nature
Conspecific relationships occur between individuals of the same species, enhancing cooperative behaviors such as hunting, mating, and parental care. Examples include wolf packs collaboratively hunting to increase their success rate, zebra herds utilizing group vigilance to detect predators, and elephant family groups exhibiting strong social bonds for mutual protection and nurturing of calves. These interactions promote survival and reproductive success within species, highlighting the importance of conspecific dynamics in natural ecosystems.
Ecological Significance of Allospecific Interactions
Allospecific interactions, involving individuals from different species, play a critical role in maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem stability by facilitating processes like predation, competition, and mutualism. These interspecies relationships influence population control, resource allocation, and habitat structuring, directly impacting ecological community dynamics. Understanding allospecific interactions is essential for conservation biology, as they help predict how changes in species composition affect ecosystem resilience and function.
Ecological Roles of Conspecific Interactions
Conspecific interactions, occurring among individuals of the same species, play crucial ecological roles such as promoting cooperative behaviors like group foraging, territorial defense, and social learning, which enhance survival and reproductive success. These interactions facilitate population regulation through mechanisms like competition for resources, mate selection, and kin cooperation, contributing to genetic diversity and species resilience. Unlike allospecific interactions between different species, conspecific dynamics directly influence intraspecific population structure and ecosystem stability.
Evolutionary Implications of Allospecific vs Conspecific
Allospecific interactions, involving different species, drive evolutionary processes such as coevolution, adaptive radiation, and niche differentiation by promoting genetic diversity and ecological specialization. Conspecific interactions, occurring within the same species, influence natural selection, sexual selection, and social behaviors, shaping traits like cooperation, competition, and reproductive strategies. These dynamics collectively contribute to species adaptation, population structure, and the evolutionary trajectory of biodiversity.
Conclusion: Allospecific and Conspecific in Biological Context
Allospecific interactions occur between individuals of different species, impacting ecological dynamics such as competition and symbiosis, while conspecific relationships involve members of the same species, crucial for mating, social behavior, and population stability. Understanding the distinction between allospecific and conspecific interactions enhances insights into species coexistence, evolutionary processes, and biodiversity conservation. Both interaction types shape ecosystems, but conspecific behaviors primarily influence intraspecies communication and reproduction, whereas allospecific relationships drive interspecies ecological balance.
Allospecific Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com