Reforestation plays a crucial role in restoring ecosystems, improving air quality, and combating climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide. This natural process supports biodiversity, protects watersheds, and helps prevent soil erosion. Discover how reforestation impacts your environment and what steps you can take to contribute by reading the rest of the article.
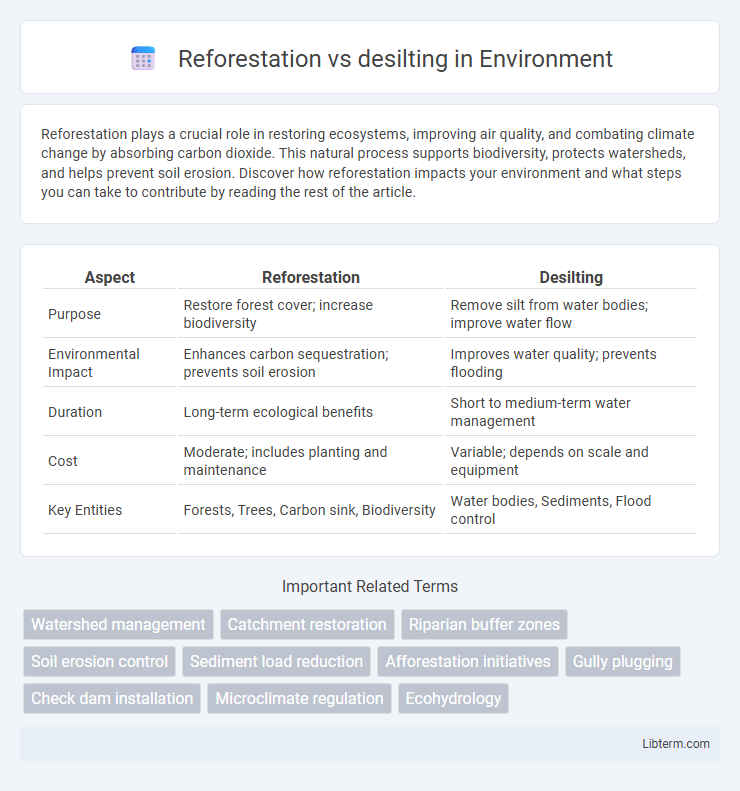
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Reforestation | Desilting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Restore forest cover; increase biodiversity | Remove silt from water bodies; improve water flow |
| Environmental Impact | Enhances carbon sequestration; prevents soil erosion | Improves water quality; prevents flooding |
| Duration | Long-term ecological benefits | Short to medium-term water management |
| Cost | Moderate; includes planting and maintenance | Variable; depends on scale and equipment |
| Key Entities | Forests, Trees, Carbon sink, Biodiversity | Water bodies, Sediments, Flood control |
Introduction to Reforestation and Desilting
Reforestation involves planting trees to restore deforested or degraded land, enhancing biodiversity, improving air quality, and stabilizing soil. Desilting is the process of removing accumulated silt and sediment from water bodies, which improves water flow, prevents flooding, and restores reservoir capacity. Both practices play vital roles in sustainable environmental management by addressing soil erosion and water resource conservation.
Understanding Reforestation: Definition and Methods
Reforestation involves the deliberate planting of trees to restore forests that have been depleted or degraded, promoting biodiversity and enhancing carbon sequestration. Common methods include natural regeneration, where existing tree seeds are allowed to grow, and artificial planting techniques such as direct seeding and sapling transplantation. Effective reforestation contributes to soil stabilization, water cycle regulation, and habitat restoration, distinguishing it from desilting, which primarily focuses on removing sediment deposits from water bodies.
Desilting Explained: Processes and Techniques
Desilting involves the removal of accumulated silt, sediment, and debris from water bodies to restore their capacity and improve water flow. Key processes include mechanical dredging, hydraulic suction, and manual excavation, each tailored to site conditions and environmental impact considerations. These techniques enhance water storage, reduce flood risk, and improve aquatic ecosystems by maintaining clean and functional waterways.
Ecological Benefits of Reforestation
Reforestation enhances biodiversity by restoring habitats for countless species, stabilizing soil to prevent erosion, and improving air and water quality through carbon sequestration and natural filtration processes. It promotes a balanced ecosystem, supports climate regulation by absorbing CO2, and helps maintain hydrological cycles. Unlike desilting, which primarily focuses on sediment removal in water bodies, reforestation offers long-term sustainable ecological benefits that contribute to overall environmental resilience.
Environmental Impact of Desilting
Desilting significantly improves water quality by removing sediment and pollutants from water bodies, thereby enhancing aquatic habitats and reducing flood risks. The process restores reservoir capacity and supports the regeneration of surrounding ecosystems, promoting biodiversity and soil stability. However, improper desilting may lead to habitat disturbance and increased turbidity, necessitating careful management to maximize environmental benefits.
Reforestation vs Desilting: Key Differences
Reforestation involves planting trees to restore forest areas, enhancing biodiversity and improving soil stability, whereas desilting focuses on removing sediment from water bodies to increase water storage capacity and prevent flooding. Reforestation contributes to carbon sequestration and long-term ecosystem health, while desilting primarily addresses immediate water management and flood control. Both methods are vital for environmental sustainability but target different ecological and hydrological challenges.
Cost Analysis and Resource Allocation
Reforestation involves significant initial investment in seedlings, labor, and long-term maintenance but offers enduring ecological benefits and carbon sequestration, making it cost-effective over time. Desilting requires regular expenditure on heavy machinery, manpower, and disposal of sediment, with costs recurring frequently to maintain water flow and prevent flooding. Resource allocation for reforestation prioritizes natural capital restoration, while desilting demands continuous financial and operational inputs for immediate infrastructure functionality.
Long-term Outcomes and Sustainability
Reforestation enhances long-term ecosystem resilience by restoring native vegetation, improving soil stability, and increasing biodiversity, which supports sustainable water cycles and carbon sequestration. Desilting primarily addresses short-term water storage capacity and flood prevention but may require frequent repetition, limiting its sustainability impact. Combining reforestation with desilting creates a balanced approach that promotes durable watershed health and reduces sediment runoff over time.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Approaches
Reforestation faces challenges such as long regeneration periods, soil quality dependency, and vulnerability to climate change and pests, while desilting is limited by high operational costs, disruption of aquatic ecosystems, and the temporary nature of sediment removal. Both approaches require significant resource investment and careful planning to balance ecological benefits with practical constraints. The effectiveness of reforestation and desilting varies widely based on local environmental conditions and long-term maintenance capabilities.
Integrated Solutions for Land and Water Management
Reforestation enhances soil stability and promotes water retention by restoring vegetation cover, while desilting improves water flow and storage capacity by removing accumulated sediments from water bodies. Integrated solutions combine reforestation with desilting to maximize land productivity, reduce erosion, and improve watershed health. This holistic approach supports sustainable agriculture, mitigates flooding risks, and enhances groundwater recharge, leading to comprehensive land and water resource management.
Reforestation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com