Confluence is a powerful collaboration tool designed to help teams create, share, and manage content efficiently in a centralized workspace. It integrates seamlessly with other project management software, enhancing productivity and streamlining communication across your organization. Explore the full article to discover how Confluence can transform your team's workflow and project success.
Table of Comparison
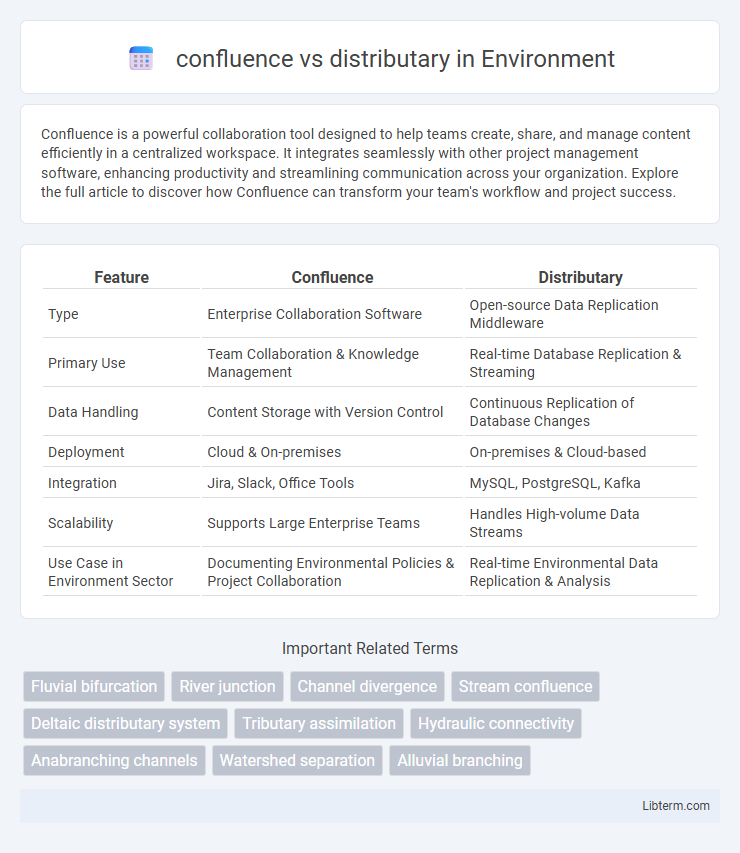
| Feature | Confluence | Distributary |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Enterprise Collaboration Software | Open-source Data Replication Middleware |
| Primary Use | Team Collaboration & Knowledge Management | Real-time Database Replication & Streaming |
| Data Handling | Content Storage with Version Control | Continuous Replication of Database Changes |
| Deployment | Cloud & On-premises | On-premises & Cloud-based |
| Integration | Jira, Slack, Office Tools | MySQL, PostgreSQL, Kafka |
| Scalability | Supports Large Enterprise Teams | Handles High-volume Data Streams |
| Use Case in Environment Sector | Documenting Environmental Policies & Project Collaboration | Real-time Environmental Data Replication & Analysis |
Introduction to Confluence and Distributary
Confluence refers to the point where two or more rivers or streams meet and merge into a single channel, significantly impacting the hydrology, sediment transport, and ecology of the combined water body. Distributary channels are branches that diverge from the main river, often found in delta regions, distributing water and sediment across a broader area and shaping the landscape through deposition. Understanding the dynamics of confluences and distributaries is essential for water resource management, flood prediction, and environmental conservation in fluvial systems.
Defining Confluence: Meaning and Context
Confluence refers to the point where two or more rivers or streams meet and merge into a single watercourse, significantly impacting hydrology and sediment transport in fluvial systems. This natural phenomenon often occurs in varied geographic contexts, influencing local ecosystems and human settlements. Understanding confluence is essential for managing flood risks, water quality, and river navigation in integrated watershed management.
Understanding Distributary: Meaning and Function
Distributary refers to a branch of a river that flows away from the main stream, distributing water and sediments across a delta or floodplain, unlike a confluence where two rivers merge. The primary function of a distributary is to disperse water flow, reducing velocity and depositing sediments that create fertile land and diverse ecosystems. Understanding distributary systems is crucial for managing flood control, agriculture, and habitat conservation in deltaic regions.
Key Differences: Confluence vs Distributary
Confluence refers to the point where two or more rivers or streams merge into a single channel, typically increasing water volume and flow. A distributary is a branch of a river that diverges from the main channel and flows away, often found in river deltas, redistributing water and sediment. Key differences include confluence involving merging waters to form a larger stream, while distributaries involve splitting the flow into separate channels.
Geographical Examples of Confluence
The Ganges and Yamuna rivers converge at the Triveni Sangam in Allahabad, India, symbolizing a major geographical confluence where three rivers meet, including the mythical Saraswati. The confluence of the Blue Nile and White Nile rivers at Khartoum, Sudan, marks a vital hydrological junction contributing to the Nile's flow toward the Mediterranean. The Ohio River forms at the confluence of the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers in Pittsburgh, USA, serving as a critical geographical example of river merging in North America.
Geographical Examples of Distributary
Distributaries are channels that branch off from a main river, commonly found in delta regions such as the Nile Delta in Egypt and the Mississippi River Delta in the United States. These waterways distribute river flow into multiple paths before reaching the sea, contrasting with confluence points where rivers merge. Notable examples include the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta in Bangladesh and the Amazon Delta in Brazil, both featuring extensive distributary networks shaping rich ecosystems.
Environmental Impact of Confluence and Distributary
Confluences often result in increased sediment deposition and nutrient mixing, which can enhance aquatic biodiversity but may also lead to localized pollution accumulation and altered water quality. Distributaries distribute water flow and sediments into multiple channels, promoting wetland creation and floodplain fertility, which supports diverse ecosystems and natural water purification processes. Both features influence regional hydrology and habitat connectivity, making their environmental impacts critical for watershed management and conservation planning.
Importance in River Systems
Confluence points in river systems are crucial for combining water flows, enhancing sediment transport, and supporting aquatic biodiversity by creating diverse habitats. Distributaries play a vital role in delta formation by dispersing river flow into multiple channels, which aids in nutrient distribution and flood control. Both confluences and distributaries significantly influence river morphology, ecosystem dynamics, and water management strategies.
Role in Human Settlements and Development
Confluence zones serve as critical hubs in human settlements by providing fertile land, abundant water resources, and transportation routes that foster urban growth and economic development. Distributary networks play a vital role in delta regions by distributing water and sediments, supporting agriculture, preventing flooding, and sustaining complex ecosystems essential for local livelihoods. Both features shape settlement patterns, influencing infrastructure planning and resource management in densely populated areas.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Confluence and Distributary
Choosing between Confluence and Distributary depends on project requirements and system architecture. Confluence excels in collaborative content management with robust integration options, making it ideal for team-driven documentation workflows. Distributary offers scalable, real-time database replication suited for distributed systems requiring high availability and fault tolerance.
confluence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com