The organic label guarantees that products meet strict standards for natural farming, free from synthetic pesticides and GMOs, ensuring healthier choices for your lifestyle. It also reflects environmentally sustainable practices that support biodiversity and soil health. Discover how the organic label benefits you and the planet by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
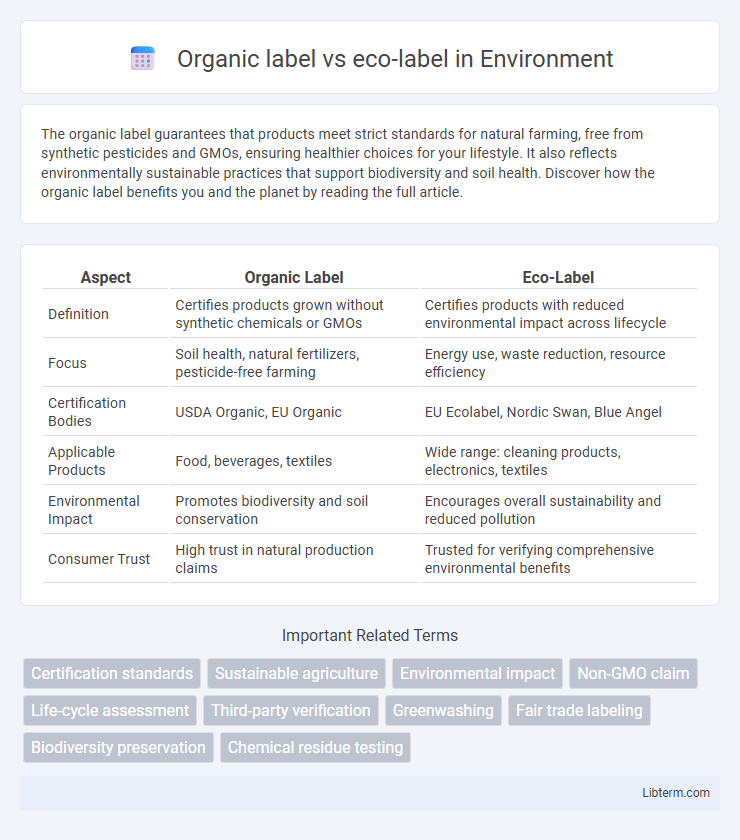
| Aspect | Organic Label | Eco-Label |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Certifies products grown without synthetic chemicals or GMOs | Certifies products with reduced environmental impact across lifecycle |
| Focus | Soil health, natural fertilizers, pesticide-free farming | Energy use, waste reduction, resource efficiency |
| Certification Bodies | USDA Organic, EU Organic | EU Ecolabel, Nordic Swan, Blue Angel |
| Applicable Products | Food, beverages, textiles | Wide range: cleaning products, electronics, textiles |
| Environmental Impact | Promotes biodiversity and soil conservation | Encourages overall sustainability and reduced pollution |
| Consumer Trust | High trust in natural production claims | Trusted for verifying comprehensive environmental benefits |
Understanding Organic Labels: What Do They Mean?
Organic labels certify that products meet strict standards for natural farming methods, avoiding synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs). These labels guarantee that the food is grown with environmentally sustainable practices promoting soil health and biodiversity. Understanding organic labels helps consumers identify truly natural products and support sustainable agriculture.
Defining Eco-Labels: Scope and Standards
Eco-labels encompass a broad range of environmental certifications that assess products based on multiple criteria such as sustainability, resource efficiency, and reduced environmental impact. Unlike organic labels, which specifically certify agricultural products free from synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms, eco-labels apply to various industries including textiles, electronics, and cleaning products with standards set by independent organizations. These standards typically require compliance with criteria related to lifecycle assessments, waste reduction, and ethical sourcing, ensuring comprehensive environmental responsibility beyond just organic production.
Key Differences Between Organic Labels and Eco-Labels
Organic labels certify that products meet specific agricultural standards emphasizing natural inputs and prohibiting synthetic chemicals, ensuring food safety and sustainability. Eco-labels encompass a broader range of environmental criteria, including resource efficiency, reduced pollution, and biodiversity conservation, applicable to diverse product categories beyond agriculture. The primary distinction lies in organic labels' strict focus on agricultural practices, while eco-labels address overall environmental impact across industries.
Certification Processes: Organic vs Eco-Label
Organic certification involves rigorous agricultural practices verified by authorities such as USDA Organic or EU Organic, focusing on soil health, pesticide use, and non-GMO standards. Eco-label certification, like the EU Ecolabel or Blue Angel, assesses broader environmental impacts including resource efficiency, pollution reduction, and product lifecycle sustainability. Both certifications require extensive documentation and periodic audits, but organic emphasizes agricultural inputs while eco-labels target overall environmental performance.
Trust and Transparency in Labeling Systems
Organic labels are regulated certifications that guarantee products meet strict agricultural and production standards, offering consumers high trust through government oversight and standardized criteria. Eco-labels encompass a broader range of environmental claims and may vary in rigor and certification processes, which can affect transparency and consumer confidence. Both labeling systems aim to inform buyers, but organic labels typically provide clearer assurance due to their well-defined regulatory frameworks and inspection protocols.
Environmental Impact: Organic vs Eco-Labeled Products
Organic labels guarantee products are made without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, significantly reducing soil and water pollution while promoting biodiversity. Eco-labels encompass broader environmental criteria, including carbon footprint, energy use, and waste management, providing consumers insight into overall sustainability performance. Choosing organic often prioritizes soil health and ecosystem balance, whereas eco-labeled products emphasize comprehensive environmental impact reduction.
Consumer Perceptions: Which Label Carries More Weight?
Consumers often perceive organic labels as more trustworthy due to strict regulatory standards and certification processes, associating them with higher quality and health benefits. Eco-labels, while valued for environmental impact, can suffer from less recognition and varying criteria, leading to confusion or skepticism among shoppers. Market research indicates organic labels generally carry more weight in purchase decisions, especially in food and personal care products.
Industry Regulations: Global and Local Perspectives
Organic labels are governed by strict global standards like USDA Organic and EU Organic, ensuring products meet rigorous criteria for chemical-free farming and processing. Eco-labels vary widely, with organizations such as the Global Ecolabelling Network setting guidelines that reflect local environmental priorities and regulatory frameworks. Industry regulations require transparent certification processes and frequent audits to maintain consumer trust and compliance across both global organic and regional eco-label systems.
Choosing for Health: Organic or Eco-Labeled?
Choosing between organic and eco-labels for health involves understanding their distinct certifications and standards. Organic labels guarantee products are grown without synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, or GMOs, prioritizing consumer health and environmental sustainability. Eco-labels emphasize broader environmental impact, including resource use and carbon footprint, but may not always ensure the absence of synthetic chemicals relevant to personal health.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Food and Product Labels
Future trends in organic and eco-labels emphasize enhanced transparency through blockchain technology and artificial intelligence, ensuring traceability and authenticity in food and product certifications. Consumer demand for sustainability drives the integration of multi-criteria eco-labels that combine organic standards with carbon footprint and biodiversity impact metrics. Digital labels and QR codes are becoming standard, enabling real-time access to product origin, farming practices, and environmental assessments.
Organic label Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com