Ecohydrology explores the dynamic interactions between water cycles and ecosystems, emphasizing how vegetation influences water movement and availability. This interdisciplinary field integrates hydrology, ecology, and environmental science to promote sustainable water management and ecosystem conservation. Dive into the rest of the article to discover how ecohydrology can enhance Your understanding of natural resource management.
Table of Comparison
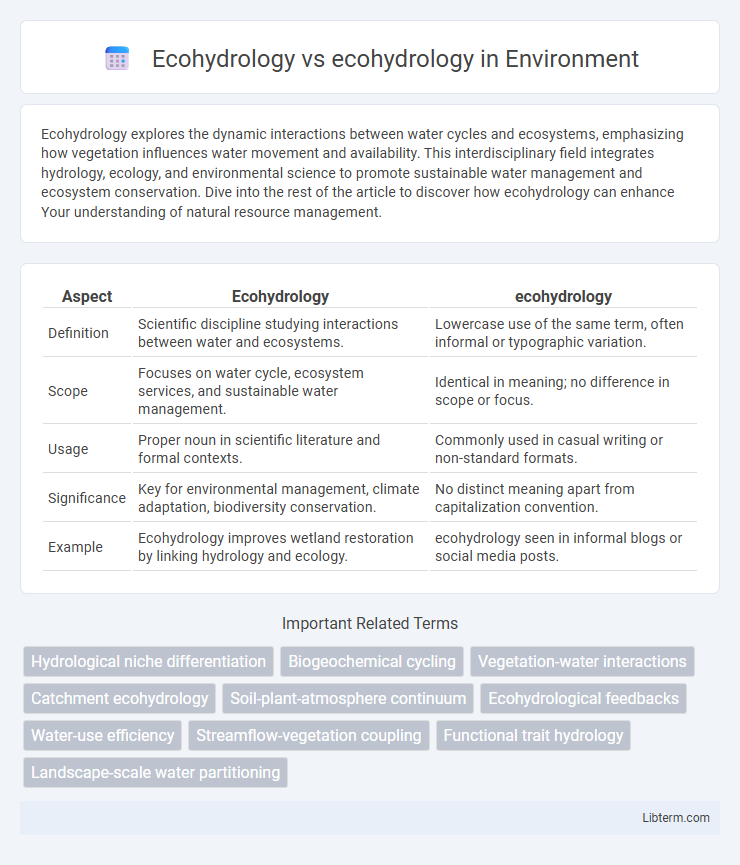
| Aspect | Ecohydrology | ecohydrology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Scientific discipline studying interactions between water and ecosystems. | Lowercase use of the same term, often informal or typographic variation. |
| Scope | Focuses on water cycle, ecosystem services, and sustainable water management. | Identical in meaning; no difference in scope or focus. |
| Usage | Proper noun in scientific literature and formal contexts. | Commonly used in casual writing or non-standard formats. |
| Significance | Key for environmental management, climate adaptation, biodiversity conservation. | No distinct meaning apart from capitalization convention. |
| Example | Ecohydrology improves wetland restoration by linking hydrology and ecology. | ecohydrology seen in informal blogs or social media posts. |
Defining Ecohydrology: Concepts and Scope
Ecohydrology integrates ecological and hydrological processes to analyze interactions between water and ecosystems, emphasizing sustainable water management. The concept explores how vegetation, soil, and water cycles co-regulate ecosystem functions and services, with applications in watershed management, restoration, and climate adaptation. Its scope spans multidisciplinary research including hydrodynamics, biogeochemistry, and landscape ecology to optimize ecosystem resilience and water resource sustainability.
Historical Evolution of Ecohydrology
The historical evolution of Ecohydrology traces back to the 1990s when the term was formally introduced to describe the interdisciplinary study linking hydrological processes and ecological systems. Early research primarily focused on understanding water-energy-biota interactions within river basins, leading to the development of models that emphasized ecosystem sustainability and water cycle feedbacks. This scientific domain has since expanded, integrating advances in remote sensing, watershed management, and climate change impacts to promote resilient ecohydrological systems globally.
Core Principles of Ecohydrology
Ecohydrology, as an interdisciplinary science, emphasizes the interaction between water cycles and ecological processes, integrating hydrology, biology, and environmental science to promote sustainable ecosystem management. Core principles of ecohydrology focus on enhancing water use efficiency in landscapes by restoring natural flow regimes, supporting biodiversity, and maintaining ecosystem services such as water purification and nutrient cycling. The discipline advocates for adaptive management strategies that align hydrological processes with ecological function to improve resilience against climate change and anthropogenic impacts.
Ecohydrology vs Traditional Hydrology
Ecohydrology integrates ecological principles with hydrological sciences to understand and manage water resources while supporting ecosystem health. Traditional hydrology primarily focuses on the physical movement and distribution of water without emphasizing biotic interactions or ecological consequences. Ecohydrology advances water management by incorporating vegetation dynamics, soil processes, and aquatic life to promote sustainable and resilient watershed systems.
Interdisciplinary Nature of Ecohydrology
Ecohydrology integrates principles from hydrology, ecology, and environmental science to analyze interactions between water cycles and ecosystems. This interdisciplinary approach enables researchers to address complex issues such as water resource management, biodiversity conservation, and climate change impacts. By combining quantitative hydrological models with ecological dynamics, ecohydrology fosters a holistic understanding of ecosystem functions and sustainability.
Applications of Ecohydrology in Natural Resource Management
Ecohydrology integrates hydrological and ecological processes to enhance natural resource management by optimizing water use efficiency and improving ecosystem resilience. Applications include watershed management, wetland restoration, and sustainable agriculture, where understanding plant-water interactions helps mitigate drought and flood risks. This approach supports biodiversity conservation and water quality improvement, crucial for maintaining ecosystem services in changing climates.
Advances in Ecohydrology Research
Advances in Ecohydrology research have enhanced understanding of water-ecosystem interactions by integrating hydrological processes with ecological dynamics at multiple scales. Recent studies emphasize modeling vegetation-water feedbacks, improving predictions of ecosystem responses to climate change and land-use alterations. Cutting-edge remote sensing technologies and ecohydrological data assimilation approaches have accelerated quantification of ecohydrological fluxes, optimizing sustainable water resource management.
Challenges in Ecohydrological Studies
Challenges in Ecohydrological studies include accurately quantifying the complex interactions between hydrological processes and ecological systems across diverse spatial and temporal scales. Limited availability of high-resolution data and the difficulty of integrating interdisciplinary models hinder precise predictions of ecosystem responses to environmental changes. Furthermore, addressing climate variability and anthropogenic impacts remains critical for advancing understanding and management within the field of ecohydrology.
Future Directions in Ecohydrology
Future directions in Ecohydrology emphasize integrating advanced remote sensing technologies and machine learning to enhance ecosystem-water interaction models. Innovations in Ecohydrology research focus on addressing climate change impacts by developing adaptive management strategies for water resources in diverse ecosystems. Collaborative efforts in Ecohydrology aim to improve predictive accuracy for hydrological cycles, promoting sustainable environmental policies and resilient ecological networks.
Ecohydrology for Sustainable Ecosystem Management
Ecohydrology integrates hydrological processes and ecological principles to enhance sustainable ecosystem management by optimizing water resources and improving habitat resilience. This interdisciplinary approach supports the restoration of natural water cycles, promotes biodiversity, and mitigates environmental degradation in diverse ecosystems. Effective ecohydrology strategies contribute to climate adaptation, water quality improvement, and the sustainable use of ecological services vital for ecosystem health.
Ecohydrology Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com