Environmental engineering focuses on developing sustainable solutions to protect natural resources and reduce pollution. This discipline combines principles from science and technology to address challenges such as waste management, water treatment, and air quality improvement. Explore the article to understand how your actions and innovations can contribute to a healthier environment.
Table of Comparison
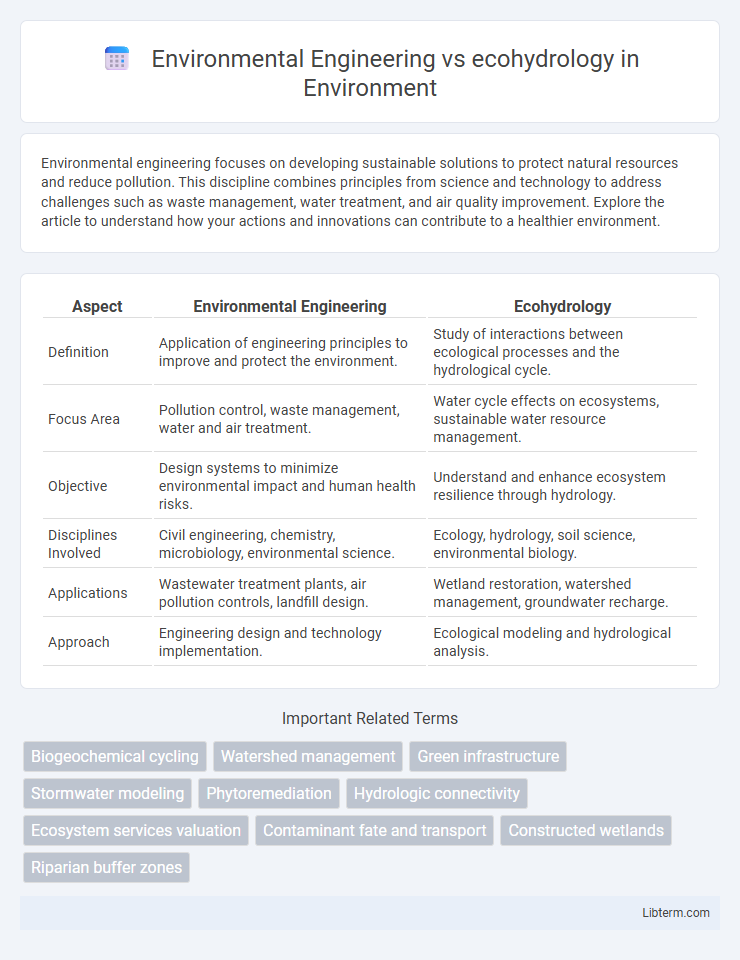
| Aspect | Environmental Engineering | Ecohydrology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Application of engineering principles to improve and protect the environment. | Study of interactions between ecological processes and the hydrological cycle. |
| Focus Area | Pollution control, waste management, water and air treatment. | Water cycle effects on ecosystems, sustainable water resource management. |
| Objective | Design systems to minimize environmental impact and human health risks. | Understand and enhance ecosystem resilience through hydrology. |
| Disciplines Involved | Civil engineering, chemistry, microbiology, environmental science. | Ecology, hydrology, soil science, environmental biology. |
| Applications | Wastewater treatment plants, air pollution controls, landfill design. | Wetland restoration, watershed management, groundwater recharge. |
| Approach | Engineering design and technology implementation. | Ecological modeling and hydrological analysis. |
Introduction to Environmental Engineering and Ecohydrology
Environmental Engineering combines principles of biology, chemistry, and engineering to develop sustainable solutions for pollution control, waste management, and water treatment, addressing human impacts on the environment. Ecohydrology examines the interactions between water and ecosystems, emphasizing the role of hydrological processes in the distribution and functioning of biological communities. Both fields integrate interdisciplinary approaches to promote sustainable resource management, with Environmental Engineering focusing on technological interventions and Ecohydrology on ecological feedback mechanisms within hydrological cycles.
Core Principles: Environmental Engineering vs Ecohydrology
Environmental Engineering centers on applying principles of chemistry, biology, and physics to design systems that prevent pollution, manage waste, and improve water and air quality. Ecohydrology integrates ecological processes with hydrological cycles to restore and sustain water bodies and their surrounding ecosystems, emphasizing natural interactions between vegetation, soil, and water dynamics. While Environmental Engineering adopts engineered solutions for environmental protection, Ecohydrology focuses on understanding and enhancing ecosystem services through the hydrological context.
Key Objectives and Approaches
Environmental engineering focuses on designing sustainable systems to reduce pollution, manage waste, and protect water resources through technological innovations and infrastructure development. Ecohydrology studies the interactions between water and ecosystems to understand and optimize natural processes for maintaining biodiversity and water quality. Both fields prioritize sustainability, but environmental engineering emphasizes engineered solutions while ecohydrology relies on ecological principles and hydrological modeling.
Educational Pathways and Career Opportunities
Environmental engineering education typically involves coursework in chemistry, biology, physics, and mathematics, with programs offered at bachelor's, master's, and doctoral levels focusing on designing sustainable solutions for pollution control and resource management. Ecohydrology integrates hydrology, ecology, and environmental science to study water ecosystems, often requiring interdisciplinary training through specialized graduate programs emphasizing watershed management and ecological restoration. Career opportunities in environmental engineering include roles as environmental consultants, water resources engineers, and sustainability managers, while ecohydrology graduates often pursue research scientist positions, ecosystem managers, and environmental policy advisors.
Methodologies and Tools Used
Environmental engineering employs methodologies such as pollutant source tracking, risk assessment, and sustainable design using tools like geographic information systems (GIS), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and water quality modeling software. Ecohydrology integrates hydrological modeling, remote sensing, and biogeochemical analysis to study interactions between ecological processes and the water cycle, leveraging tools such as GIS, satellite imagery, and ecohydrological simulation models like SWAT or DHSVM. Both disciplines utilize advanced data analytics and field instrumentation, but environmental engineering emphasizes engineered solutions while ecohydrology focuses on natural system feedbacks and ecosystem sustainability.
Role in Climate Change Mitigation
Environmental engineering applies advanced technologies and sustainable design to reduce pollution, manage waste, and improve energy efficiency, directly mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and supporting climate resilience. Ecohydrology studies interactions between hydrological processes and ecosystems to restore natural water cycles, enhance carbon sequestration, and reduce flood risks. Both fields contribute to climate change mitigation by integrating ecosystem-based approaches with engineered solutions to promote sustainable environmental management.
Applications in Water Resource Management
Environmental engineering applies principles of chemistry, biology, and engineering to design systems for water treatment, pollution control, and sustainable water supply management. Ecohydrology integrates ecological processes with hydrological cycles, enhancing watershed management, flood control, and habitat restoration by emphasizing the interactions between water and ecosystems. Both disciplines contribute to improving water quality, ensuring sustainable water availability, and mitigating environmental impacts, but environmental engineering focuses on technological solutions while ecohydrology prioritizes ecological balance.
Sustainability and Ecosystem Impacts
Environmental Engineering integrates sustainable design principles to minimize environmental degradation by controlling pollution and managing natural resources efficiently. Ecohydrology studies the interactions between water and ecosystems to enhance ecosystem services, focusing on maintaining biodiversity and resilience. Both fields emphasize sustainability by promoting ecosystem health and diverse approaches to water and resource management.
Collaborative Potential and Interdisciplinary Research
Environmental engineering and ecohydrology intersect through their shared focus on sustainable water management and ecosystem restoration, offering significant collaborative potential in addressing complex environmental challenges. Interdisciplinary research combining environmental engineering's technological innovations with ecohydrology's ecological understanding facilitates integrated solutions for pollution control, habitat conservation, and climate resilience. Such collaboration enhances the development of adaptive infrastructures and predictive models that promote both human well-being and ecological health.
Future Trends in Environmental Engineering and Ecohydrology
Future trends in Environmental Engineering emphasize the integration of advanced technologies such as AI-driven water treatment, sustainable waste management, and renewable energy systems to enhance ecosystem resilience. Ecohydrology increasingly focuses on understanding hydrological processes' role in ecosystem functions, promoting nature-based solutions to restore water cycles and improve biodiversity under climate change pressures. Both fields converge on precision monitoring and adaptive management to mitigate environmental impacts and support sustainable resource use.
Environmental Engineering Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com