Zenith represents the highest point or peak of something, often used to describe the apex of success, achievement, or celestial objects directly overhead. Understanding the concept of zenith can enhance your appreciation of astronomy, career milestones, or personal growth. Explore the rest of the article to discover how zenith applies to various aspects of life and science.
Table of Comparison
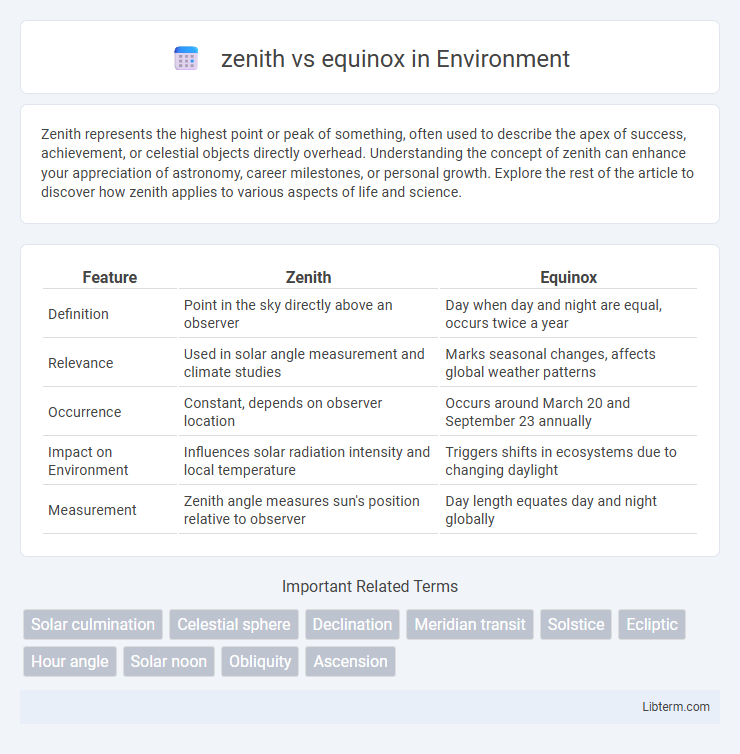
| Feature | Zenith | Equinox |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Point in the sky directly above an observer | Day when day and night are equal, occurs twice a year |
| Relevance | Used in solar angle measurement and climate studies | Marks seasonal changes, affects global weather patterns |
| Occurrence | Constant, depends on observer location | Occurs around March 20 and September 23 annually |
| Impact on Environment | Influences solar radiation intensity and local temperature | Triggers shifts in ecosystems due to changing daylight |
| Measurement | Zenith angle measures sun's position relative to observer | Day length equates day and night globally |
Overview: Zenith vs Equinox
The zenith is the point in the sky directly above an observer, representing the highest position a celestial body can reach. The equinox occurs twice a year when the sun crosses the celestial equator, resulting in nearly equal day and night durations globally. Understanding the zenith's vertical alignment contrasts with the equinox's significance in marking seasonal transitions.
Definition of Zenith
The zenith is the point in the sky directly above an observer, representing the highest position a celestial object can reach relative to that location. It is a key reference in astronomy and navigation, distinct from the equinox, which marks the time when the sun crosses the celestial equator, resulting in equal day and night durations. Understanding the zenith aids in precise celestial measurements and orientation on Earth.
Definition of Equinox
The equinox occurs twice a year, marking the moments when the sun crosses the celestial equator, resulting in nearly equal day and night durations across the globe. Unlike the zenith, which refers to the point directly overhead an observer, the equinox signifies a crucial astronomical event that balances daylight and darkness. This phenomenon is fundamental in understanding Earth's axial tilt and orbital dynamics, influencing seasonal changes worldwide.
Key Differences Between Zenith and Equinox
The zenith is the point in the sky directly above an observer on Earth, representing the highest position of the sun or any celestial object at a given location. The equinox occurs twice a year when the sun crosses the celestial equator, resulting in nearly equal day and night durations worldwide. Unlike the zenith which varies by location and time of day, the equinox is a global astronomical event marking the start of spring or autumn.
Astronomical Significance of Zenith
The zenith is the point in the sky directly above an observer, crucial for measuring the position of celestial bodies and determining local time and latitude. Unlike the equinox, which marks the moment the Sun crosses the celestial equator causing equal day and night, the zenith is a fixed reference for altitude in celestial navigation and astronomical observations. Understanding the zenith's role enhances precise calculations in astronomy, including solar angle measurements and satellite positioning.
Astronomical Significance of Equinox
The equinox marks the precise moment when the Sun crosses the celestial equator, resulting in nearly equal day and night durations across the globe. This astronomical event occurs twice a year, around March 20 and September 23, signaling the beginning of spring and autumn seasons. Unlike the zenith, which refers to the point directly overhead an observer, the equinox provides critical information about Earth's axial tilt and orbital position relative to the Sun.
Effects on Day and Night Duration
The zenith refers to the point directly overhead in the sky, impacting the intensity of sunlight and thus influencing the temperature experienced during the day, while the equinox marks the moment when the sun crosses the celestial equator, resulting in nearly equal day and night durations globally. During an equinox, day and night are approximately 12 hours each worldwide due to the sun's position relative to Earth's axis, whereas the zenith position varies daily depending on latitude and season, affecting local solar altitude and daylight length. The equinox's significance lies in balancing day and night durations, whereas the zenith's impact is more localized, affecting solar intensity and the length of daylight hours depending on geographic location.
Importance in Various Cultures
The zenith, the point directly overhead, holds significant spiritual and navigational importance in many cultures, symbolizing divine connection and marking crucial times for rituals. Equinoxes, occurring twice annually when day and night are equal, are celebrated globally as times of balance, renewal, and agricultural cycles, reflecting profound cosmological meanings. These celestial events shape calendars, festivals, and architectural alignments, highlighting their enduring influence on human societies.
Role in Navigation and Timekeeping
The zenith, representing the point directly overhead, serves as a vital reference for celestial navigation by helping determine latitude through the angle measured between the zenith and celestial bodies. The equinox, marking the two times a year when day and night are equal, establishes a key temporal reference for calibrating calendars and tracking the solar year. Navigators use the equinox as a fixed point to calculate the sun's position, crucial for accurate longitude determination and timekeeping at sea.
Summary: Choosing Between Zenith and Equinox
Choosing between Zenith and Equinox depends on specific astronomical contexts, as Zenith represents the point directly overhead in the sky, while the Equinox marks the moment when day and night are nearly equal globally. Zenith is crucial for precise solar angle measurements and navigation, whereas the Equinox is essential for understanding seasonal changes and solar calendar alignment. Selecting the appropriate concept requires focusing on whether the priority is location-specific solar position or broader temporal-solar balance.
zenith Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com