Efficient irrigation techniques are essential for maximizing crop yield while conserving water resources. Understanding different irrigation methods such as drip, sprinkler, and surface irrigation can help you choose the best system for your agricultural needs. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to optimize your irrigation strategy for sustainable farming.
Table of Comparison
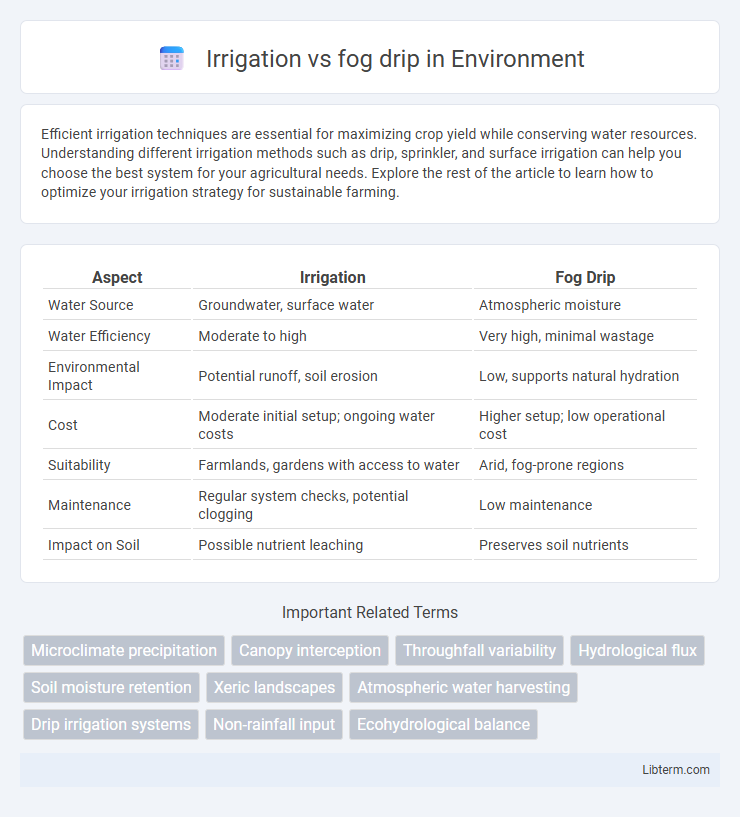
| Aspect | Irrigation | Fog Drip |
|---|---|---|
| Water Source | Groundwater, surface water | Atmospheric moisture |
| Water Efficiency | Moderate to high | Very high, minimal wastage |
| Environmental Impact | Potential runoff, soil erosion | Low, supports natural hydration |
| Cost | Moderate initial setup; ongoing water costs | Higher setup; low operational cost |
| Suitability | Farmlands, gardens with access to water | Arid, fog-prone regions |
| Maintenance | Regular system checks, potential clogging | Low maintenance |
| Impact on Soil | Possible nutrient leaching | Preserves soil nutrients |
Introduction to Irrigation and Fog Drip
Irrigation systems deliver controlled water directly to crops, optimizing soil moisture for improved plant growth and yield. Fog drip harnesses natural fog moisture, capturing water droplets on surfaces like leaves or nets, which then drip to the soil, providing a sustainable, low-energy hydration method in arid environments. Both techniques address water scarcity with distinct resource efficiency and application suited to varying agricultural conditions.
Defining Irrigation Methods
Irrigation methods encompass a variety of techniques designed to supply water to plants, including surface, drip, sprinkler, and subsurface irrigation. Fog drip irrigation specifically involves the collection of water from fog or mist using specialized nets or surfaces, which then delivers moisture directly to crops or soil. Compared to traditional irrigation, fog drip leverages natural atmospheric moisture, reducing water usage and improving efficiency in arid or fog-prone environments.
What is Fog Drip?
Fog drip is a natural irrigation process where moisture from fog condenses on leaves and then drips to the ground, supplying water to plants in arid or foggy environments. Unlike traditional irrigation systems that rely on direct water application through sprinklers or drip lines, fog drip harnesses atmospheric moisture, reducing water usage and supporting ecosystems in regions with scarce rainfall. This method is particularly effective in coastal and mountainous areas where fog is frequent, enhancing soil hydration without additional energy inputs.
Mechanisms of Water Delivery
Irrigation systems deliver water through controlled applications such as drip emitters, sprinklers, or surface flooding, allowing precise targeting of plant roots or soil surfaces. Fog drip relies on natural condensation of fog on leaves or specialized meshes, where water droplets coalesce and drip to the soil below, supplementing moisture in arid environments. The key difference lies in irrigation's active water supply from external sources versus fog drip's passive harvesting of ambient atmospheric moisture.
Efficiency: Irrigation vs Fog Drip
Irrigation systems typically deliver water directly to plants through controlled methods like drip or sprinkler systems, optimizing water use efficiency with measurable application rates. Fog drip harnesses natural fog moisture, condensing water onto leaves and soil without mechanical input, making it highly efficient in arid, fog-prone environments but variable in output. Efficiency comparisons reveal irrigation provides consistent water supply, while fog drip excels in sustainability and energy savings in suitable climates.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Irrigation systems often consume significant water resources, leading to potential runoff, soil erosion, and nutrient leaching, which can negatively affect local ecosystems. Fog drip harnesses natural atmospheric moisture, minimizing water extraction and reducing environmental disruption by promoting soil moisture retention without excessive runoff. Compared to traditional irrigation, fog drip offers a sustainable alternative that conserves water and supports biodiversity by maintaining native vegetation and reducing chemical inputs.
Suitability for Different Climates
Irrigation systems are highly adaptable for arid and semi-arid climates where consistent water delivery is essential for crop growth, while fog drip is most effective in coastal or mountainous regions with high humidity and frequent fog, utilizing natural moisture capture. Fog drip minimizes water consumption by harnessing atmospheric moisture, making it suitable for drought-prone areas with limited freshwater resources but less practical in dry, fog-scarce environments. Choosing the appropriate method depends on climatic factors such as precipitation patterns, humidity levels, and water availability, optimizing water use efficiency and crop productivity.
Cost and Resource Considerations
Irrigation systems typically require higher upfront investment and ongoing water usage compared to fog drip, which leverages natural fog condensation to provide moisture with minimal energy input. Fog drip minimizes water consumption and reduces operational costs, making it a resource-efficient option in fog-prone regions. Cost savings from fog drip are especially notable in areas with limited water availability or high water prices, enhancing sustainable agriculture and landscaping practices.
Applications in Agriculture and Ecosystems
Irrigation systems deliver controlled water directly to crops, enhancing growth in diverse agricultural settings, especially where rainfall is insufficient or irregular. Fog drip, a natural form of water capture from fog condensation on vegetation, supports ecosystems by supplementing moisture in arid and fog-prone environments, benefiting plants and wildlife without external water inputs. In agriculture, fog drip can reduce irrigation needs by providing supplemental water, promoting sustainable water management practices in semi-arid regions.
Future Trends in Water Management
Future trends in water management emphasize precision irrigation techniques and fog drip systems to maximize water efficiency in arid regions. Sensor-driven irrigation optimizes water delivery based on real-time soil moisture data, reducing waste and enhancing crop yields. Fog drip technology harnesses atmospheric moisture, offering a sustainable alternative for water-scarce environments by capturing fog water to supplement irrigation needs.
Irrigation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com