Algicidal substances effectively control and eliminate unwanted algae growth in aquatic environments, maintaining water clarity and quality. These agents target harmful algal blooms that can disrupt ecosystems and harm aquatic life. Discover how algicidal treatments can protect your water resources by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
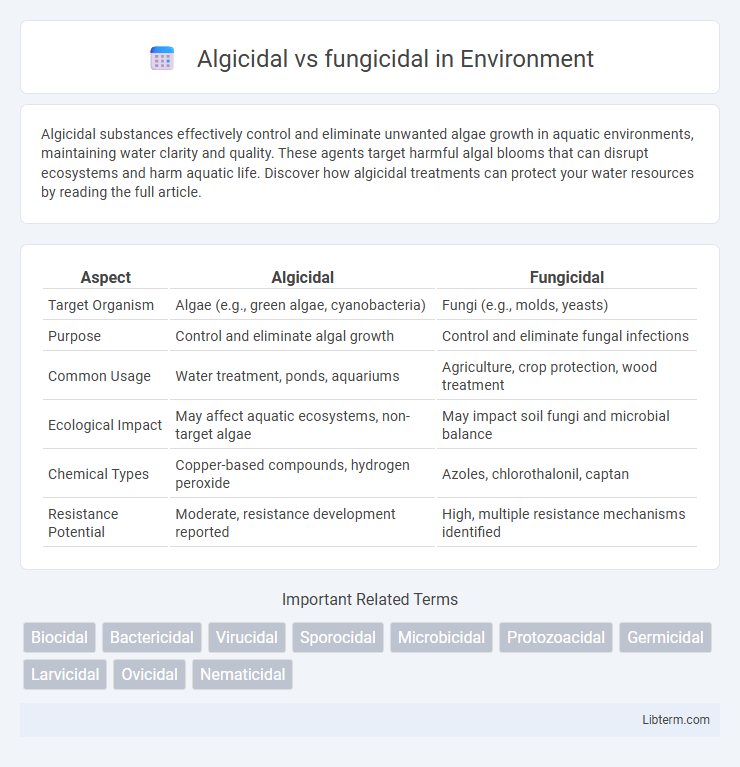
| Aspect | Algicidal | Fungicidal |
|---|---|---|
| Target Organism | Algae (e.g., green algae, cyanobacteria) | Fungi (e.g., molds, yeasts) |
| Purpose | Control and eliminate algal growth | Control and eliminate fungal infections |
| Common Usage | Water treatment, ponds, aquariums | Agriculture, crop protection, wood treatment |
| Ecological Impact | May affect aquatic ecosystems, non-target algae | May impact soil fungi and microbial balance |
| Chemical Types | Copper-based compounds, hydrogen peroxide | Azoles, chlorothalonil, captan |
| Resistance Potential | Moderate, resistance development reported | High, multiple resistance mechanisms identified |
Introduction to Algicidal and Fungicidal Agents
Algicidal agents target algae by inhibiting their growth or directly causing cell death, playing a crucial role in controlling harmful algal blooms in aquatic environments. Fungicidal agents destroy or inhibit fungi, preventing fungal infections in agriculture, horticulture, and medicine by disrupting fungal cell wall synthesis or metabolism. Both algicides and fungicides are essential for maintaining ecosystem balance and protecting crops, water quality, and public health.
Understanding Algicidal Compounds
Algicidal compounds specifically target and eliminate algae by disrupting their cellular processes or inhibiting photosynthesis, making them vital for controlling algal blooms in aquatic environments. These substances include copper-based chemicals, quaternary ammonium compounds, and certain natural extracts that exhibit selective toxicity toward algal species without severely affecting non-target organisms. Understanding the mode of action and environmental impact of algicidal agents is crucial for optimizing their use in water treatment and ecosystem management while minimizing potential ecological risks.
Overview of Fungicidal Agents
Fungicidal agents are specialized chemicals used to inhibit or eliminate fungal growth on plants, surfaces, and materials, playing a critical role in agriculture and healthcare. These compounds disrupt fungal cell membranes or interfere with vital processes such as ergosterol synthesis, thus preventing spore germination and mycelial expansion. Unlike algicidal agents, which target algae, fungicides focus specifically on combating pathogenic fungi to protect crops, prevent spoilage, and reduce disease transmission.
Key Differences Between Algicidal and Fungicidal Products
Algicidal products are formulated to target and eliminate algae by disrupting their cellular structure or inhibiting photosynthesis, while fungicidal products specifically combat fungal pathogens by interfering with fungal cell membranes or metabolic processes. Algicides are often used in aquatic environments or on surfaces prone to algae growth, whereas fungicides are applied in agriculture and horticulture to prevent or treat fungal infections in plants. The mode of action, target organisms, and application environments are the primary distinctions defining algicidal versus fungicidal products.
Mechanisms of Action: Algicidal vs. Fungicidal
Algicidal agents disrupt the photosynthetic processes or damage the cell membranes of algae, leading to cell lysis and inhibited growth. Fungicidal compounds typically target fungal cell wall synthesis, ergosterol production, or nucleic acid synthesis, effectively killing or preventing fungal proliferation. Understanding the distinct biochemical pathways targeted by algicides and fungicides is crucial for developing specialized treatments in aquatic and agricultural environments.
Common Applications and Uses
Algicidal products are commonly used in water treatment, swimming pools, and aquariums to control and prevent algae growth, ensuring clear water and maintaining aquatic health. Fungicidal agents find widespread application in agriculture for protecting crops from fungal diseases, as well as in wood preservation, building materials, and healthcare to prevent mold and fungal infections. Both algicides and fungicides play crucial roles in environmental management and disease prevention across various industries.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Algicidal agents target algae and can reduce harmful algal blooms but may disrupt aquatic ecosystems by harming non-target algae species critical for oxygen production. Fungicidal compounds eliminate fungal pathogens but often contain persistent chemicals that risk soil and water contamination, affecting beneficial microorganisms. Choosing biodegradable and species-specific formulations minimizes environmental impact and enhances safety for non-target organisms and human health.
Choosing the Right Treatment: Algicide or Fungicide?
Selecting between algicide and fungicide depends on the type of infestation damaging your plants or surfaces. Algicides target algae growth caused by excess moisture and sunlight, effectively eliminating slimy, green buildup in aquatic or damp environments. Fungicides combat fungal diseases such as powdery mildew or rust by disrupting fungal cell growth, essential for protecting crops and ornamental plants from decay and infection.
Regulatory Aspects and Guidelines
Regulatory aspects for algicidal and fungicidal products are governed by agencies such as the EPA in the United States and the EU's Biocidal Products Regulation (BPR), with distinct registration processes reflecting their specific target organisms. Guidelines emphasize safety, environmental impact, and efficacy testing, requiring detailed toxicological and ecological risk assessments tailored to algae or fungal pathogens. Compliance demands adherence to labeling requirements, usage restrictions, and post-market surveillance to ensure products meet approved standards for human health and environmental protection.
Future Trends in Algae and Fungi Control
Emerging algicidal technologies leverage bio-based compounds and nanomaterials to enhance targeted algae suppression while minimizing environmental impact. Fungicidal innovations emphasize resistance management through molecular docking and gene editing to combat evolving fungal pathogens in agriculture. Integration of AI-driven monitoring systems facilitates precise application timing, promoting sustainable algae and fungi control in future ecosystem management.
Algicidal Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com