LEED certification establishes standards for environmentally responsible building design and construction, promoting energy efficiency, water conservation, and reduced carbon footprint. Achieving LEED status can significantly enhance your property's market value and sustainability reputation. Explore the rest of the article to learn how LEED can transform your building projects.
Table of Comparison
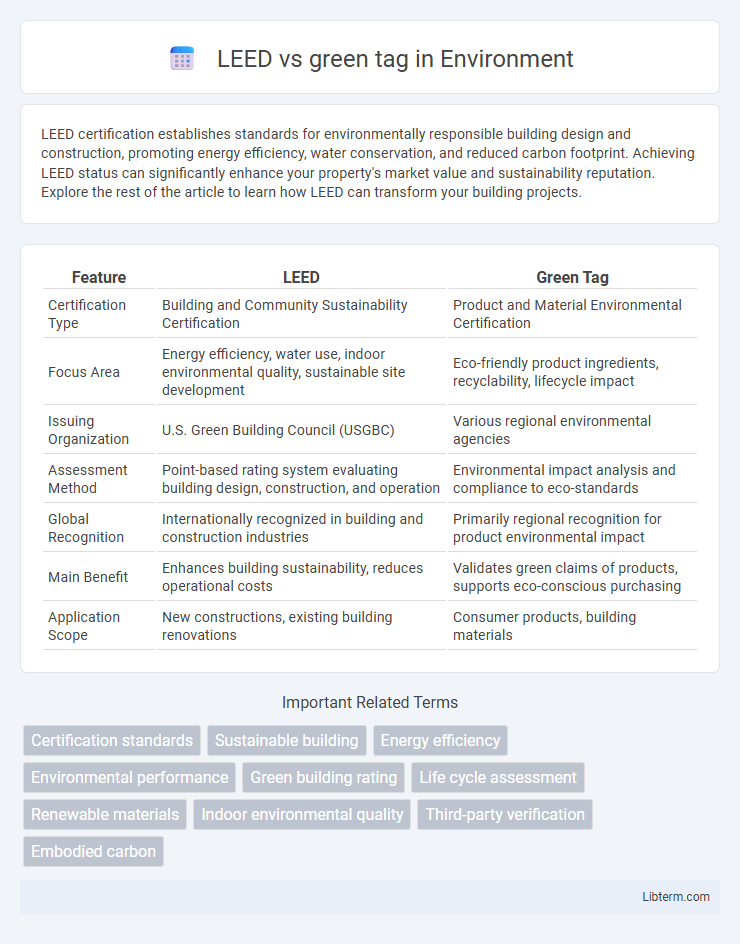
| Feature | LEED | Green Tag |
|---|---|---|
| Certification Type | Building and Community Sustainability Certification | Product and Material Environmental Certification |
| Focus Area | Energy efficiency, water use, indoor environmental quality, sustainable site development | Eco-friendly product ingredients, recyclability, lifecycle impact |
| Issuing Organization | U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) | Various regional environmental agencies |
| Assessment Method | Point-based rating system evaluating building design, construction, and operation | Environmental impact analysis and compliance to eco-standards |
| Global Recognition | Internationally recognized in building and construction industries | Primarily regional recognition for product environmental impact |
| Main Benefit | Enhances building sustainability, reduces operational costs | Validates green claims of products, supports eco-conscious purchasing |
| Application Scope | New constructions, existing building renovations | Consumer products, building materials |
Introduction to LEED and Green Tag
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) is a globally recognized certification system developed by the U.S. Green Building Council that evaluates the environmental performance of buildings through a rigorous points-based framework. Green Tag Certification, primarily used in Australia, assesses sustainable building materials and products to ensure they meet stringent environmental standards for reduced ecological impact. Both systems aim to promote sustainable development, with LEED focusing on whole-building performance and Green Tag emphasizing product-level sustainability verification.
Overview of LEED Certification
LEED certification, developed by the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC), is a globally recognized green building rating system that evaluates the environmental performance of buildings across various categories such as energy efficiency, water usage, indoor environmental quality, and sustainable site development. Projects earn points based on specific sustainability criteria, and certification levels include Certified, Silver, Gold, and Platinum, reflecting increasing degrees of green building performance. LEED certification promotes market transformation towards sustainable design, construction, and operation by providing a comprehensive framework for measuring and verifying building sustainability.
Understanding Green Tag Certification
Green Tag Certification evaluates environmental performance based on comprehensive lifecycle analysis and verified data, emphasizing tangible reductions in carbon footprint and resource use. LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) primarily focuses on building design, construction, and operational strategies to achieve sustainability benchmarks through a points-based system. Understanding Green Tag Certification involves recognizing its role in quantifying real-world impact through precise environmental product declarations, complementing LEED's broader sustainability framework.
Key Differences Between LEED and Green Tag
LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) is a widely recognized green building certification system emphasizing energy efficiency, water conservation, and sustainable site development, while Green Tag focuses primarily on renewable energy verification and carbon offsetting. LEED certification evaluates entire building projects based on a comprehensive points system covering multiple sustainability categories, whereas Green Tag certifies the environmental attributes of renewable energy generation, supporting individual renewable energy certificates (RECs). LEED offers a holistic approach to sustainable building design and construction, whereas Green Tag serves as a tool for validating and trading green energy credits to promote clean energy usage.
Certification Criteria Comparison
LEED certification evaluates buildings based on sustainability, energy efficiency, indoor environmental quality, and water conservation, using a points-based system across categories like Location & Transportation, Materials & Resources, and Innovation. Green Tag certification emphasizes cleaner energy usage and carbon footprint reduction, focusing primarily on renewable energy utilization, emission tracking, and sustainability reporting. While LEED provides a comprehensive assessment of overall building sustainability, Green Tag certification targets energy consumption and carbon impact metrics specifically.
Environmental Impact Assessment
LEED certification evaluates the environmental impact of buildings through a comprehensive Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) that measures energy efficiency, water usage, and material sustainability. Green Tag focuses specifically on quantifying the carbon footprint and ecological benefits of products or projects based on lifecycle analysis and renewable energy credits. Both systems aim to reduce environmental harm, but LEED offers a broader assessment framework encompassing site impact and indoor environmental quality.
Cost and Process of Certification
LEED certification involves a comprehensive evaluation of building design, construction, and operation, typically requiring substantial upfront investment in documentation, third-party verification, and ongoing performance tracking, resulting in higher certification costs. Green Tag certification generally offers a more streamlined process focused on renewable energy and environmental claims, often at a lower cost and faster turnaround due to its emphasis on product or project-specific environmental attributes rather than full building performance. Organizations aiming to balance budget constraints and certification speed may find Green Tag a cost-effective alternative, while LEED provides a more rigorous and widely recognized standard with broader sustainability criteria.
Global Recognition and Market Adoption
LEED certification, developed by the U.S. Green Building Council, is globally recognized with over 100 countries adopting its standards for sustainable building practices. Green Tag certification, originating in Australia, has strong regional market adoption and focuses on environmental product declarations and lifecycle assessment. LEED's broader international market penetration often makes it the preferred choice for multinational projects seeking global sustainability credentials.
Benefits and Challenges of LEED vs Green Tag
LEED certification offers comprehensive recognition for sustainable building design, emphasizing energy efficiency, water savings, and indoor environmental quality, leading to increased property value and marketability. Green Tag certification focuses primarily on verified renewable energy generation, providing clear proof of environmental benefit and supporting carbon offset goals, but may lack the holistic building-level assessment of LEED. Challenges of LEED include higher upfront costs and complex documentation, whereas Green Tag challenges involve limited scope confined to energy attributes and less influence on overall building performance.
Which Certification is Right for Your Project?
Choosing between LEED and Green Tag certification depends on your project's sustainability goals and scope; LEED emphasizes comprehensive building performance and environmental impact, ideal for new constructions and major renovations, while Green Tag focuses on monitoring and reducing operational resource use, suitable for existing buildings seeking incremental improvements. LEED certification requires adherence to strict standards across categories like energy efficiency, water savings, and indoor environmental quality, offering market recognition and potential financial incentives. Green Tag provides flexibility in tracking lifecycle performance and may be more cost-effective for projects prioritizing ongoing environmental management rather than upfront design changes.
LEED Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com