Industrial zones are designated areas specifically planned to accommodate manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution activities, optimizing logistics and infrastructure for business efficiency. These zones often offer tax incentives and streamlined regulations to attract companies and boost local economic development. Explore the rest of the article to understand how an industrial zone can impact Your business growth and community dynamics.
Table of Comparison
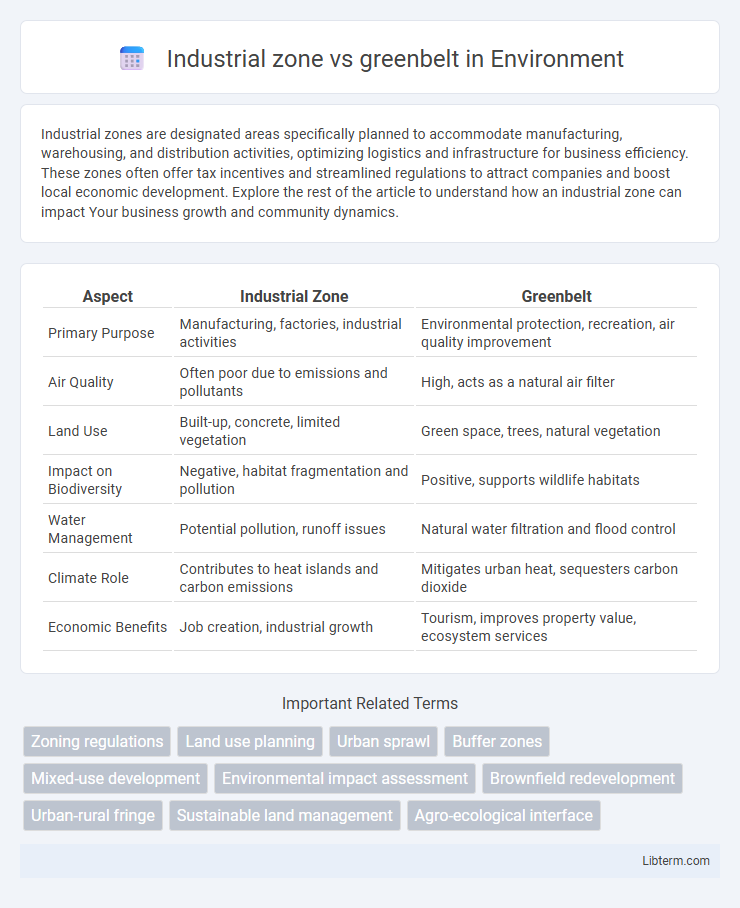
| Aspect | Industrial Zone | Greenbelt |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Manufacturing, factories, industrial activities | Environmental protection, recreation, air quality improvement |
| Air Quality | Often poor due to emissions and pollutants | High, acts as a natural air filter |
| Land Use | Built-up, concrete, limited vegetation | Green space, trees, natural vegetation |
| Impact on Biodiversity | Negative, habitat fragmentation and pollution | Positive, supports wildlife habitats |
| Water Management | Potential pollution, runoff issues | Natural water filtration and flood control |
| Climate Role | Contributes to heat islands and carbon emissions | Mitigates urban heat, sequesters carbon dioxide |
| Economic Benefits | Job creation, industrial growth | Tourism, improves property value, ecosystem services |
Introduction: Defining Industrial Zones and Greenbelts
Industrial zones are designated areas planned for manufacturing, warehousing, and commercial activities that support economic growth and job creation. Greenbelts are protected regions of open land surrounding urban areas, intended to limit sprawl, preserve natural habitats, and provide recreational spaces. The strategic distinction between industrial zones and greenbelts lies in balancing urban development with environmental sustainability.
Historical Background of Land Use Planning
The historical background of land use planning reveals a clear distinction between industrial zones and greenbelts, developed to balance economic growth and environmental preservation. Industrial zones emerged during the Industrial Revolution to concentrate manufacturing activities, minimize conflicts with residential areas, and facilitate infrastructure development. Greenbelts originated in the early 20th century as a response to urban sprawl, designed to protect natural landscapes, maintain air quality, and provide recreational spaces around cities.
Core Functions of Industrial Zones
Industrial zones are designated areas specifically planned to concentrate manufacturing, warehousing, and distribution activities, optimizing logistics and infrastructure to enhance production efficiency. Core functions include providing specialized facilities, reducing environmental impact through regulated operations, and fostering economic growth by attracting investment and employment opportunities. Greenbelts, in contrast, serve as buffer zones preserving natural landscapes, limiting urban sprawl, and protecting air and water quality around these industrial areas.
Key Characteristics of Greenbelt Areas
Greenbelt areas are characterized by extensive natural vegetation, strict land-use regulations, and a focus on environmental conservation to limit urban sprawl. These zones often serve as buffers between industrial zones and residential areas, preserving air quality and biodiversity while providing recreational spaces. Greenbelts typically restrict industrial development and promote sustainable land management practices to maintain ecological balance.
Economic Impacts: Industrial Zones vs Greenbelts
Industrial zones stimulate economic growth by attracting manufacturing firms, creating jobs, and increasing tax revenues through higher commercial activity. Greenbelts, while limiting urban sprawl and preserving environmental quality, often restrict land availability for development, potentially constraining local economic expansion and increasing property prices. The trade-off between these land uses impacts long-term economic sustainability, balancing industrial productivity with environmental preservation.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Industrial zones often contribute to increased pollution, habitat destruction, and higher carbon emissions, challenging environmental sustainability efforts. Greenbelts act as critical buffers that preserve biodiversity, improve air quality, and mitigate urban heat island effects, promoting ecological balance. Sustainable urban planning prioritizes integrating industrial development with greenbelt preservation to minimize environmental impact and enhance long-term resilience.
Urban Planning and Zoning Regulations
Industrial zones are designated areas within urban planning frameworks that permit manufacturing, warehousing, and heavy commercial activities, governed by zoning regulations to control environmental impact and land use compatibility. Greenbelts serve as buffer zones around cities, preserving open space and limiting urban sprawl by restricting industrial development and maintaining ecological balance. Zoning regulations differentiate these areas to optimize sustainable urban growth, mitigate pollution, and enhance residents' quality of life while promoting economic activities.
Social and Community Impacts
Industrial zones often lead to increased employment opportunities but may also contribute to air and noise pollution, negatively affecting community health and well-being. Greenbelts provide essential recreational spaces and improve mental health by preserving natural environments, fostering a sense of community and social cohesion. Balancing industrial development with greenbelt preservation is crucial to ensuring sustainable, livable neighborhoods that support both economic growth and quality of life.
Conflicts and Challenges in Land Use Decisions
Industrial zones often conflict with greenbelt preservation due to competing demands for land, environmental sustainability, and urban expansion. Challenges in land use decisions include balancing economic development with ecological protection, managing pollution and habitat disruption, and addressing community concerns about health and quality of life. Effective planning requires integrating environmental impact assessments, stakeholder engagement, and enforcement of zoning regulations to mitigate these conflicts.
Future Trends in Industrial and Greenbelt Development
Emerging trends in industrial zone development emphasize smart manufacturing technologies and sustainable infrastructure integration to minimize environmental impact. Greenbelt planning increasingly incorporates urban agriculture and biodiversity corridors to enhance ecosystem services while balancing urban growth. Future developments prioritize a hybrid approach where industrial expansion coexists with greenbelt preservation through advanced spatial planning and green technology adoption.
Industrial zone Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com