Intraspecific interactions refer to relationships and behaviors occurring within the same species, impacting population dynamics, resource competition, and social structures. These interactions drive evolutionary adaptations and influence survival and reproduction rates. Explore the rest of this article to understand how intraspecific factors shape ecosystems and affect Your environment.
Table of Comparison
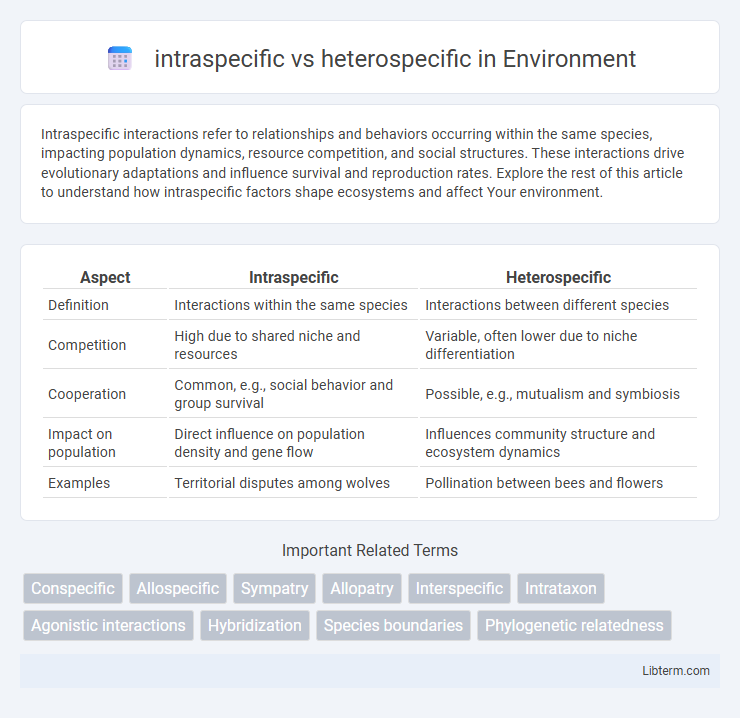
| Aspect | Intraspecific | Heterospecific |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Interactions within the same species | Interactions between different species |
| Competition | High due to shared niche and resources | Variable, often lower due to niche differentiation |
| Cooperation | Common, e.g., social behavior and group survival | Possible, e.g., mutualism and symbiosis |
| Impact on population | Direct influence on population density and gene flow | Influences community structure and ecosystem dynamics |
| Examples | Territorial disputes among wolves | Pollination between bees and flowers |
Introduction to Intraspecific and Heterospecific Interactions
Intraspecific interactions occur between individuals of the same species, influencing population dynamics, resource competition, and social behaviors essential for survival and reproduction. Heterospecific interactions happen between different species, shaping ecosystems through predation, mutualism, and competition that affect community structure and biodiversity. Understanding these interactions provides critical insights into ecological balance and evolutionary processes.
Defining Intraspecific Relationships
Intraspecific relationships occur between members of the same species, involving interactions such as competition, cooperation, and reproduction that directly influence population dynamics and survival. These relationships include behaviors like territoriality, social hierarchies, and mating systems, which are critical for species adaptation and gene flow. Understanding intraspecific interactions provides insight into ecological balance and evolutionary processes within species populations.
Understanding Heterospecific Interactions
Heterospecific interactions involve relationships between individuals of different species, often influencing community structure and ecosystem dynamics. These interactions include competition, predation, mutualism, and commensalism, each playing a critical role in shaping biodiversity and species coexistence. Understanding heterospecific interactions enhances ecological management by revealing how species influence each other's survival, reproduction, and resource use within shared habitats.
Key Differences Between Intraspecific and Heterospecific Dynamics
Intraspecific dynamics involve interactions among individuals of the same species, often leading to competition for resources like food, mates, and territory, which shapes population structure and evolutionary outcomes. Heterospecific dynamics occur between different species, including predator-prey relationships, mutualism, and competition, influencing community composition and ecosystem functioning. Understanding these differences is crucial for ecological modeling, biodiversity conservation, and managing species interactions in natural habitats.
Ecological Importance of Intraspecific Competition
Intraspecific competition, occurring among individuals of the same species, regulates population size by limiting resources such as food, space, and mates, thereby maintaining ecosystem balance. This type of competition drives natural selection and promotes genetic diversity, enhancing species adaptability and resilience in changing environments. Unlike heterospecific competition, which happens between different species, intraspecific competition directly influences species evolution and community dynamics through intense resource allocation conflicts.
Ecological Roles of Heterospecific Associations
Heterospecific associations play crucial ecological roles by enhancing biodiversity, facilitating resource partitioning, and providing mutualistic benefits such as protection against predators and improved foraging efficiency. These interactions often lead to niche differentiation, reducing competition and promoting coexistence among species within ecosystems. Unlike intraspecific interactions, which occur within the same species, heterospecific associations enable complex community dynamics and contribute significantly to ecosystem stability and resilience.
Intraspecific Cooperation and Social Structures
Intraspecific cooperation involves interactions and collaborative behaviors among individuals of the same species, often leading to complex social structures such as hierarchies, division of labor, and collective decision-making. These cooperative behaviors enhance survival and reproductive success through practices like group hunting, shared parenting, and coordinated defense against predators. Social structures in intraspecific cooperation are critical for resource allocation, communication, and maintaining group cohesion, which ultimately supports evolutionary advantages within populations.
Heterospecific Relationships: Mutualism, Competition, and Predation
Heterospecific relationships occur between individuals of different species and include mutualism, competition, and predation. Mutualism benefits both species involved, such as the symbiotic relationship between pollinators and flowering plants, enhancing survival and reproduction. Competition arises when species vie for the same resources, leading to niche differentiation, while predation involves one species consuming another, regulating population dynamics and maintaining ecological balance.
Evolutionary Implications of Species Interactions
Intraspecific interactions, occurring within the same species, drive natural selection by influencing traits like competition, cooperation, and mate choice, which shape evolutionary trajectories. Heterospecific interactions, involving different species, promote coevolutionary dynamics such as predator-prey relationships, mutualism, and parasitism, resulting in reciprocal adaptations. These species interactions collectively enhance biodiversity and ecosystem stability by fostering niche differentiation and adaptive radiation.
Case Studies Illustrating Intraspecific vs Heterospecific Interactions
Case studies on intraspecific vs heterospecific interactions reveal critical differences in behavior and ecological impact. For instance, intraspecific competition among African elephants (Loxodonta africana) for limited water resources leads to social hierarchy adjustments, while heterospecific interactions between lions (Panthera leo) and hyenas (Crocuta crocuta) showcase complex territorial disputes influencing predator-prey dynamics. Research on coral reef fish highlights how intraspecific cooperation improves resource defense, contrasted with heterospecific facilitation enhancing habitat complexity and biodiversity.
intraspecific Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com