Tethered aerostats provide a stable platform for surveillance, communication, and weather monitoring by remaining anchored to a fixed point while floating at high altitudes. These balloons use helium to stay aloft, offering long-duration aerial coverage without the complexities of powered flight. Discover how tethered aerostats can enhance your operational capabilities by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
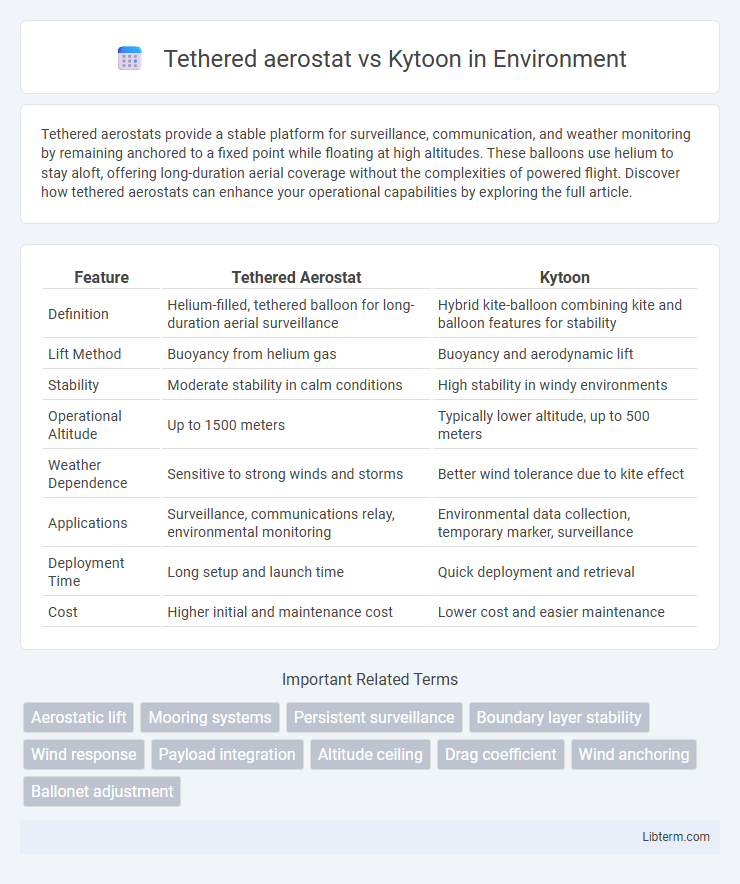
| Feature | Tethered Aerostat | Kytoon |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Helium-filled, tethered balloon for long-duration aerial surveillance | Hybrid kite-balloon combining kite and balloon features for stability |
| Lift Method | Buoyancy from helium gas | Buoyancy and aerodynamic lift |
| Stability | Moderate stability in calm conditions | High stability in windy environments |
| Operational Altitude | Up to 1500 meters | Typically lower altitude, up to 500 meters |
| Weather Dependence | Sensitive to strong winds and storms | Better wind tolerance due to kite effect |
| Applications | Surveillance, communications relay, environmental monitoring | Environmental data collection, temporary marker, surveillance |
| Deployment Time | Long setup and launch time | Quick deployment and retrieval |
| Cost | Higher initial and maintenance cost | Lower cost and easier maintenance |
Introduction to Tethered Aerostats and Kytoons
Tethered aerostats are large, helium-filled balloons anchored to the ground, providing stable aerial platforms for surveillance, communication, and meteorological monitoring. Kytoons combine the buoyancy of balloons with the aerodynamic lift of kites, enabling enhanced stability and control in varying wind conditions. Both systems offer persistent, elevated positioning but differ in design and performance characteristics suited to specific operational requirements.
Basic Design Differences
Tethered aerostats feature a streamlined, elongated envelope filled with helium to provide both lift and aerodynamic stability, designed to remain aloft over long durations. In contrast, kytoons combine the characteristics of kites and balloons, using a kite-like shape to generate lift from wind while also being buoyant due to helium or hydrogen gas. The primary design difference lies in the aerostat's reliance on gas lift with a rigid tether for stability, versus the kytoon's hybrid approach that balances aerodynamic lift and buoyancy for enhanced resistance to adverse weather conditions.
Lift Mechanisms Compared
Tethered aerostats generate lift primarily through buoyant forces using lighter-than-air gases such as helium, enabling them to remain aloft without constant energy input. Kytoons combine buoyant lift from helium with aerodynamic lift produced by wind flow over their kite-like shape, providing enhanced stability and lift in varying wind conditions. While aerostats rely solely on gas for elevation, kytoons exploit both gas and wind dynamics to achieve improved payload capacity and endurance.
Deployment and Setup Requirements
Tethered aerostats require extensive ground support including heavy anchoring systems and mooring equipment for stable deployment, often necessitating large open areas and skilled personnel for safe inflation and tether management. Kytoons, combining features of kites and balloons, are simpler to deploy with lighter anchoring needs and quicker setup times, making them ideal for rapid operations and smaller deployment zones. The structural differences impact operational logistics, where aerostats demand more infrastructure, while kytoons provide flexibility and ease in varied environmental conditions.
Altitude and Stability Performance
Tethered aerostats typically achieve higher altitudes, often ranging from 1,000 to 10,000 feet, due to their larger helium-filled envelopes that provide greater lift capacity compared to Kytoons. Kytoons combine balloon and kite features, offering enhanced stability in varying wind conditions, especially at lower altitudes typically under 2,000 feet, through aerodynamic lifting surfaces that reduce sway and oscillation. While aerostats excel in sustained high-altitude operations, Kytoons maintain superior stability and position accuracy in turbulent environments, making them ideal for applications requiring consistent platform steadiness at moderate elevations.
Payload Capacity and Applications
Tethered aerostats typically offer higher payload capacities ranging from a few hundred to several thousand pounds, enabling them to support heavy radar systems, communication equipment, and surveillance cameras for military and border security applications. Kytoons, combining features of kites and balloons, generally have lower payload capacities but excel in stability and are often used for lighter sensors, weather monitoring instruments, and environmental data collection. The choice between tethered aerostats and kytoons depends on the required payload weight and specific application demands such as altitude stability or operational duration.
Weather Resistance and Durability
Tethered aerostats typically exhibit superior weather resistance due to their robust envelope materials designed to withstand high winds and precipitation, making them suitable for extended outdoor deployments. Kytoons combine the lifting principles of kites and balloons, offering enhanced stability in turbulent weather but often require more frequent maintenance due to fabric wear from constant aerodynamic stress. Durability of aerostats generally surpasses kytoons, attributed to reinforced tethers and advanced composites used in aerostat construction, providing longer service life in harsh environmental conditions.
Operational Costs and Maintenance
Tethered aerostats typically incur higher operational costs due to their larger size, complex mooring systems, and the need for specialized ground crews for inflation and deflation processes. Kytoons, combining characteristics of kites and balloons, require less maintenance as they rely on wind for lift, reducing the need for continuous helium or other lifting gases refills and extensive ground support. Maintenance expenses for tethered aerostats often include regular inspections of tether lines and gas envelopes to prevent leaks, while kytoons have simpler structural components that lower long-term servicing costs.
Safety Considerations and Risks
Tethered aerostats and kytoons differ significantly in safety considerations due to their structural designs and environmental interactions. Aerostats, relying primarily on buoyant gas for lift, face risks such as gas leakage and deflation, which may lead to sudden loss of altitude, while kytoons combine helium with aerodynamic lift, providing greater stability in turbulent winds and reducing the risk of uncontrolled descent. The tether strength and anchoring systems in both must withstand variable wind loads, but kytoons typically offer enhanced safety margins due to their combined lift mechanics and improved drag management.
Choosing Between Tethered Aerostat and Kytoon
Choosing between a tethered aerostat and a kytoon depends on the specific altitude requirements, payload capacity, and environmental conditions of the deployment area. Tethered aerostats offer greater stability and higher payload capacities, making them suitable for long-term surveillance and communication applications, while kytoons provide enhanced stability in turbulent conditions due to their hybrid aerodynamics combining helium lift and kite-like aerodynamic lift. Decision factors include wind speed tolerance, required flight duration, and the nature of the operation, with aerostats favored for stationary, high-altitude tasks and kytoons preferred for areas with variable wind patterns.
Tethered aerostat Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com