A maelstrom is a powerful, often destructive whirlpool or turbulent situation that can draw in anything nearby with relentless force. Understanding the causes and impacts of a maelstrom helps you navigate both natural phenomena and metaphorical chaos more effectively. Discover the full scope of maelstroms and how they affect environments and lives by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
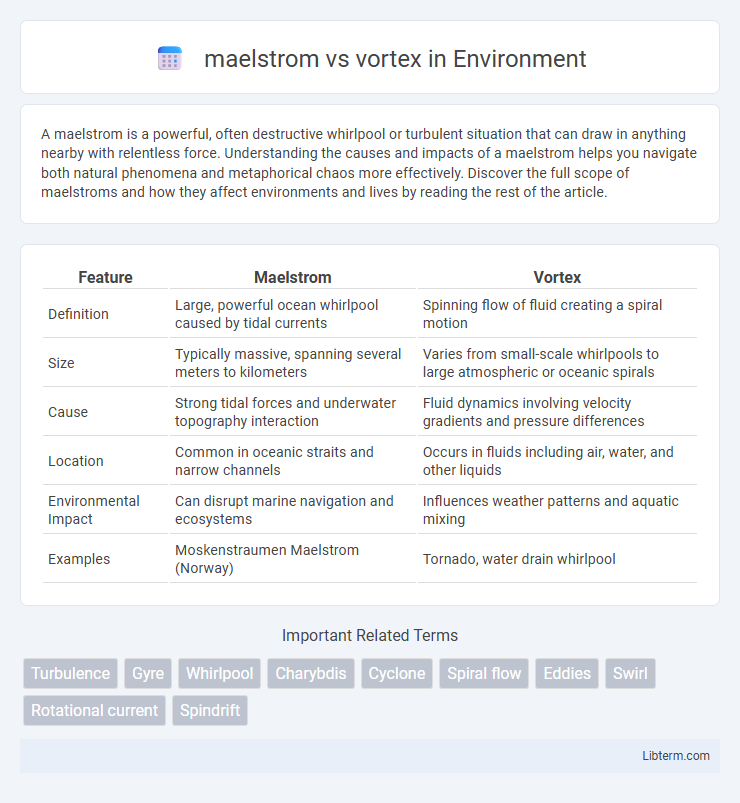
| Feature | Maelstrom | Vortex |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Large, powerful ocean whirlpool caused by tidal currents | Spinning flow of fluid creating a spiral motion |
| Size | Typically massive, spanning several meters to kilometers | Varies from small-scale whirlpools to large atmospheric or oceanic spirals |
| Cause | Strong tidal forces and underwater topography interaction | Fluid dynamics involving velocity gradients and pressure differences |
| Location | Common in oceanic straits and narrow channels | Occurs in fluids including air, water, and other liquids |
| Environmental Impact | Can disrupt marine navigation and ecosystems | Influences weather patterns and aquatic mixing |
| Examples | Moskenstraumen Maelstrom (Norway) | Tornado, water drain whirlpool |
Introduction: Understanding Maelstrom and Vortex
A maelstrom is a powerful, often large-scale whirlpool characterized by intense circular water currents, typically found in oceans or seas, causing dangerous and turbulent conditions. A vortex refers broadly to any rotating fluid mass, including water, air, or plasma, where the flow spins around a central axis, creating a spiral motion that can vary in size and intensity. Understanding the fundamental differences involves recognizing that maelstroms are specific types of vortices with extreme strength and water displacement, often linked to hazardous marine environments.
Definitions: What is a Maelstrom? What is a Vortex?
A maelstrom is a powerful, large-scale whirlpool occurring in oceans or seas, characterized by intense swirling water that can trap and pull objects underwater. A vortex is a general fluid dynamics phenomenon where fluid spins rapidly around a central axis, occurring in various scales from small water drains to large atmospheric cyclones. Both involve rotational motion, but a maelstrom specifically refers to strong maritime whirlpools, while vortex encompasses a broader range of spinning fluid motions.
Origins and Etymology
The term "maelstrom" originates from the Dutch words "malen," meaning "to grind," and "stroom," meaning "stream," referring to a powerful, grinding whirlpool famously depicted off the coast of Norway. In contrast, "vortex" derives from the Latin "vortex" or "vorticis," signifying a whirl or whirlwind, generally used in both literal and metaphorical contexts to describe swirling motions. Both words highlight turbulent water phenomena, yet "maelstrom" specifically evokes a natural maritime whirlpool, while "vortex" encompasses a broader range of rotating fluid dynamics.
Physical Characteristics: Maelstrom vs Vortex
A maelstrom is a powerful, large-scale whirlpool typically found in oceans or seas, characterized by intense, circular water currents capable of swallowing ships. A vortex can occur in various fluids, including air and water, and refers to any rotating flow of fluid around a central axis, often smaller and less intense than a maelstrom. While a maelstrom represents a naturally occurring, massive swirling water body, a vortex is a broader term encompassing phenomena ranging from tornadoes to draining water spirals.
Formation Processes
Maelstroms form primarily from the interaction of opposing tidal currents and underwater topography such as submerged rock formations or narrow straits, creating powerful swirling water movements. Vortices develop through fluid dynamics principles, often appearing in open water due to disturbances like wind shear, rapidly spinning liquids or gases, or draining water creating a downward spiral. Both phenomena depend on velocity gradients and rotational forces but differ as maelstroms are typically tidal and location-specific, while vortices occur in various scales and fluid environments.
Famous Examples in Nature
The Maelstrom off the coast of Norway, particularly near Moskenesoya island, is one of the most famous natural whirlpools, known for its intense tidal currents that can reach speeds of up to 27 km/h. Another renowned vortex is the Naruto whirlpools in Japan's Naruto Strait, created by the large volume of water moving between the Seto Inland Sea and the Pacific Ocean, producing swirling currents up to 20 km/h. These powerful natural phenomena demonstrate how underwater topography and tidal forces combine to generate dramatic and hazardous water movements.
Occurrences in Literature and Mythology
Maelstroms frequently appear in Norse mythology as deadly whirlpools symbolizing chaos and the sea's dangers, notably in the legend of the giantess Maelstrom who controls the waters. Vortex imagery is common in various mythologies and literature to represent portals or forces of transformation, such as in Dante's "Divine Comedy," where vortex-like spirals depict spiritual ascent. Both terms embody powerful natural forces but serve distinct symbolic roles: maelstroms evoke destructive natural phenomena, whereas vortexes often imply mystical or metaphysical energy.
Scientific Differences and Similarities
Maelstroms and vortices both involve rotating water masses driven by fluid dynamics, but a maelstrom is a strong, large-scale whirlpool typically formed at sea where opposing currents or tides collide, while a vortex is a more general term for any rotating fluid motion including smaller-scale water, air, or plasma rotations. Both phenomena exhibit centripetal acceleration and pressure gradients that create spiraling motion, governed by the Navier-Stokes equations in fluid mechanics. The key scientific difference lies in scale and formation context: maelstroms are natural, turbulent whirlpools often with chaotic surface effects, whereas vortices can range from microscopic to atmospheric phenomena with varying stability and persistence.
Impact on Navigation and Human Safety
Maelstroms create powerful, chaotic whirlpools that pose significant hazards to navigation, often pulling vessels into turbulent waters and increasing the risk of capsizing. Vortexes, while also involving spinning currents, tend to be less intense but can still disrupt ship control and endanger small boats or swimmers. Both phenomena demand advanced maritime awareness and safety measures to prevent accidents and ensure human safety in affected water bodies.
Conclusion: Key Differences Summarized
A maelstrom is a large, powerful, and violent whirlpool often found in oceans, whereas a vortex refers to any rotating fluid or air mass, including smaller whirlpools, tornadoes, or cyclones. The key difference lies in scale and context: maelstroms are massive, natural ocean phenomena, while vortices encompass a broader range of rotating motions in different environments. Understanding these distinctions helps clarify their unique physical behaviors and occurrences in nature.
maelstrom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com